Chapter 7:Cell Structure and Function
advertisement

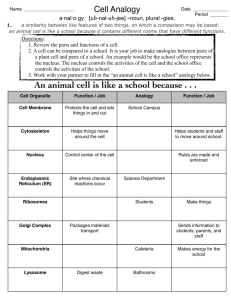
Chapter 7:Cell Structure and Function Sec7.1: Cell theory and cell types Do Now • In about 4-5 sentences, discuss the relationship between structure and function; use the examples of petals and/or sepals to support your discussion. • Read the article provided in your notes packet and answer the questions that follow. A. The discovery of cells 1. Invention of the microscope (around 1590) was important to the discovery of cells 2. 1665 ~ Robert Hooke publishes the first drawings of cells 3.1674 ~ Anton van Leeuenhoek found organisms in pond water 4.1838 ~ Matthias Schleiden concluded that all plants are made of cells 5. 1839 ~ Theodore Schwann concluded that all animals are made of cells. 6.1855 ~ Rudolf Virchow concludes that all cells come from pre-existing cells B. Cell Theory 1. Discoveries in the 1600’s through the 1800’s led to the development of Cell Theory. 2. Three components of cell theory: a. All living things are composed of cells b. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things c. All cells come from preexisting cells Inquiry Activity • “All new cells arise from existing ones”. In your pairs, discuss and answer the following questions: 1. What characteristics of life are enumerated through this statement? 2. Why is it important for new cells to arise from existing ones? C. Two Major groups of cells = Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. 1.Prokaryotic Cells 2.Eukaryotic Cells a. Simple, single celled organisms whose DNA is NOT a. Complex cells whose DNA is stored in a nucleus. stored in a nucleus b. Do not have a nucleus and lack organelles that are surrounded by membranes c. Tiny ~ much smaller than eukaryotic cells d. Internal Structure is very simple e. Example = bacteria b. Have a nucleus and several other organelles that are surrounded by membranes. c. Larger than prokaryotic cells d. Complex internal structure e. Can be single celled or part of a multicellular organism f. Examples: i. Plants and animals (multicellular) ii. Protists = single celled eukaryotes •Ex. = Amoeba, paramecium, euglena D. Viruses 1.Particles made of nucleic acids and proteins that reproduce by infecting living cells a. Are viruses living??? Closure Activity • Write down, in complete sentences, three things you learnt today. Animal Cell Vs. Plant Cell Inquiry Activity • Compare and contrast an animal cell and a plant cell using a Venn Diagram. Plasma Membrane • Plasma Membrane is also known as cell membrane. • Plasma membrane are made of a phospholipid bilayer that is embedded with proteins. • Plasma membrane acts as a selective barrier that allows only certain material to enter or leave the cells. Analogy: Nucleus • The function of the nucleus is to house all of the cell’s genetic material. • The nucleus is made of a nuclear envelope (an outer membrane) that protects the nucleus. • The nucleolus is the inner fluid that makes up the nucleus. Analogy: Cytoplasm • Is the region between the plasma membrane and the nucleus. • It ensures smooth transportation of material inside the cell. It also helps in providing structure for the cell. • Analogy: Cell Wall • Cell wall is the outermost membrane of plant cells, algae and fungi. • Cell walls are made of a tough carbohydrate fiber known as cellulose- The cellulose result in strong and rigid cells. • Cell walls are also made of pores that allow for essentials to pass through. • All in all the cell wall protects and supports the cell. Analogy: Looking at the picture above, what can you deduce about the functions of cell wall? Explain in about 2-3 sentences. Ribosomes • Ribosomes are small particles of RNA and proteins. • Their job is to manufacture proteins. Analogy: Rough ER • Rough ER are packed with ribosomes and are found close to the nucleus. • Their job is to make fats (lipids) and proteins and to store the proteins. • Analogy: Smooth ER • Smooth ER are found close to nucleus are not covered with ribosomes. • Their job is to make lipids, store proteins and detoxify the cells. Analogy: Inquiry Activity • The job of the liver is to detoxify chemicals. Based on this function which organelle is found in abundance in the cells of the liver? Justify. Golgi Bodies • The golgi bodies are made of many membranes stacked up together. They look very similar to the ER. • Their job is to package and modify the proteins from the ER, to deliver them to the various different destinations inside and outside the cell. Analogy: Vacuole • Vacuoles are large saclike structures that are found in plant cells. • Their job is to store, water and food. Analogy: Lysosome • Lysosomes are small circular organelles that are packed with enzymes. • Their job is to breakdown food and decompose dead matter. Analogy: Chloroplast • Chloroplast are found in plant cells and are organelles that are stacked with chlorophyll. • The job of the chloroplast is to trap sunlight and water to manufacture food for the plant in a process called photosynthesis. • The compartmentalization of the chloroplast allows for efficient synthesis of carbohydrates. Analogy: Mitochondria • Mitochondria is known as the powerhouse of the cell • It is found in all eukaryotic cells • The function of the mitochondria is to produce energy. • The compartmentalization of mitochondria allows for efficient production of energy. Analogy: Closure activity • http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/tdc02.sci.life.cell.organel les/organelles-in-the-cytoplasm/