REVIEW FOR EXAM 2 DECEMBER 7, 2015 Your second exam is
advertisement

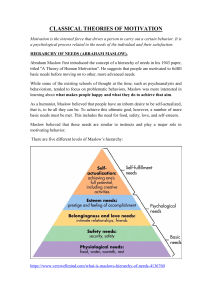
REVIEW FOR EXAM 2 DECEMBER 7, 2015 Your second exam is on Chapters 5, 6, 8 & 9. There are multiple choice questions, true & false questions and short identification or short essay. Chapter 11 What are examples of programmed decisions and non programmed decisions? What are the steps in the rational decision making process? What other types of decision making is there? How do these processes work? What are major biases that affect decision making? Explain each. What are advantages and disadvantages of group decision making? What is group think? What actions can be taken to counteract it? Chapter 5 What are the 3 functions of performance> Which element is most important for being successful? Describe Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Describe cultural differences. How can organizations satisfy employee needs that are included in Maslow’s hierarchy? Herzberg’s theory of motivation discusses hygiene factors and motivators. Give examples of hygiene factors and examples of motivators. Which hygiene factor is often considered a motivator? McClelland discusses another need theory of motivation. Explain the aspects of this theory. Compare and contrast expectancy theory with reinforcement theory. What are the differences between procedural, interactional, and distributive justice? List actions you could take to increase each justice perceptions. Chapter 6 What is scientific management? What are the differences between job rotation, job enrichment, and job enlargement. What are the 5 major components of the job characteristics model. How would you increase the empowerment levels of employees? Give an example of a SMART goal. A company is interested in increasing customer loyalty. Using the MBO approach, what would be the department and individual level goals supporting this organization-wide goal? While performance appraisals provide an opportunity to give feedback to employees about their job performance, there are inherent biases associated with the process. Name 3. Companies offer a variety of financial incentives. Identify 3 different types and discuss the pro’s & con’s of each. Key terms Motivation Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs >> 5 Needs >> Lower Order versus Higher Order Needs McClelland's Three Needs >> Achievement, Affiliation, Power Herzberg's Two Factor Theory >> Hygiene Factors versus Motivators Law of Effect Reinforcement Theory Positive Reinforcement, Negative Reinforcement, Punishment, Extinction Equity Theory “Benevolents” versus “Entitleds” Justice >> Procedural, Interactional, Distributive Expectancy Theory >> M = E x I x V CHAPTER 6 -- MOST IMPORTANT TOPICS Scientific Management and Job Specialization Job Redesign >> Job Rotation, Job Enlargement, Job Enrichment Job Characteristics Model >> with V-I-S-A-F Growth Needs Strength Empowerment >> Structural versus Felt SMART Goals MBO -- 5 Key Steps Performance Appraisal Absolute versus Relative Rankings in Performance Appraisal Five Key Performance Incentives (Out of nine on the last Slide of the Power Points) Piece-rate Incentives, Merit Pay, Sales Commissions, Team Bonuses, Profit Sharing Chapter 8 Communication Major Barriers to Effective Communication Encode-Decode Problem (The major problem from my point-of-view) Semantics and Jargon Differences in Meaning (including Gender Differences) Noise Filtering Selective Perception Information Overload Emotional Interference (text calls it "Emotional Disconnects") Workplace "Gossip" >> Grapevine Verbal versus Nonverbal Communication Verbal >> Oral and Written Nonverbal >> Paralanguage, Body Language, Object Language (nit), Space Channel Richness Model (Slides and Fig 8.10) Upward, Downward, and Lateral Communication CHAPTER 9 -- MOST IMPORTANT TOPICS Group Formal versus Informal Groups Stages of Group Development >> Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, Adjourning Cohesion Groupthink Social Loafing Process Loss ( 3 Different Types of Team Tasks >> Production, Idea Generation, Problem Solving Team Roles >> Task versus Social + Boundary Spanning Some Types of Teams >> Task Force. Cross-Functional Teams, Virtual Teams, >> Traditional Manager-Led Teams versus Self-Managed Teams