Chpt13
advertisement

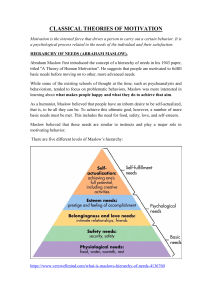
Mgt - 485 CHAPTER 13 MOTIVATION ACROSS CULTURES Irwin/McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 Motivation across cultures How big a role does “employee motivation” play in the performance of the firm? Is it appropriate to hold “management accountable for the performance of the firm? Mgt-485 13-2 The Nature of Motivation The Basic Motivation Process Unsatisfied need Drive toward goal to satisfy need Motivation is a psychological process through which unsatisfied wants or needs lead to drives that that are aimed at goals or incentives Attainment of goal (need satisfaction) Mgt-485 13-3 Universalist Assumption The motivation process (not content) is universal People are motivated by the goals they value The specific content and goals are influenced by culture Mgt-485 13-4 Assumption of Content and Process Content Theories Explain work motivation in terms of what arouses, energizes, or initiates employee behavior Process Theories Explain how employee behavior is initiated, redirected, and halted Mgt-485 13-5 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self - Actualization Desire to reach one’s full potential Esteem Need for power and status Social Need to interact and feel wanted by others Safety Desire for security and stability Physiological Need for food, clothing, and shelter Mgt-485 13-6 Maslow’s assumptions Lower-level needs must be satisfied before higher-level needs become motivators Once a need is satisfied, it no longer serves as a motivator There are more ways (options) to satisfy higherlevel needs than lower-level needs Mgt-485 13-7 Contrasting Views of Satisfaction-Dissatisfaction Traditional View Satisfaction Dissatisfaction Herzberg’s View Motivators Satisfaction No Satisfaction Hygiene Factors No Dissatisfaction Dissatisfaction Mgt-485 13-8 Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory Hygiene Factors Salary Technical Supervision Company Policies and Administration Interpersonal Relations Working Conditions Motivators Achievement Recognition Responsibility Advancement The Work Itself Mgt-485 13-9 International Findings on Herzberg’s Theory Motivators are more important to job satisfaction than hygiene factors Job content is more important than job context Managers from different cultures differ regarding perceived importance of job outcomes and level of satisfaction Mgt-485 13-10 Maslow Vs. Herzberg Maslow’s need hierarchy Herzberg’s two-factor theory Self-actualization Motivators Achievement Recognition Responsibility Advancement The work itself Esteem Social Safety Physiological Hygiene Factors Salary Technical supervision Company policies Interpersonal relations Working conditions Mgt-485 13-11 Equity Theory Relationships (Perceived) Ratio Comparison Outcome A Outcome B = Input(s) A Meaning to Employe = Equity Input(s) B Mgt-485 13-12 Simplified Expectancy Theory Individual Effort A Individual Performance B Organizational Rewards A = Effort-performance linkage B = Performance-reward linkage = Attractiveness C C Individual Goals Mgt-485 13-13 Achievement Motivation Characteristics of Higher Achievers 1. Like situations where they take personal responsibility for finding solutions to problems 2. Moderate risk-takers rather than high risk-takers 3. Want concrete feedback on their performance 4. Tend to be loners Ways to Develop High Achievers 1. 2. 3. 4. Obtain feedback on performance Emulate people who have been successful achievers Develop an internal desire for success and challenge Daydream in positive terms by picturing oneself as successful Mgt-485 13-14 Job Design Job design consists of a job’s content, the methods used on the job, and how the job relates to others in the organization Impact of Culture • • • • United States Low Uncertainty Avoidance Weak Power Distance High Masculinity High Individualism Japan • Strong Uncertainty Avoidance • High Power Distance • High Masculinity • Low Individualism Mgt-485 13-15 Work Centrality Value of Work – Misconceptions of Japanese workers Work long hours because cost of living is high Workers accomplish far less in a business day Workers not given lifetime employment Job Satisfaction – Misconceptions of Japanese workers Workers less satisfied than that of U.S. and EU Workers are less committed to organizations Mgt-485 13-16