CAREWARE TRAINING Adult Learners
advertisement

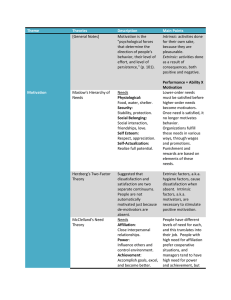
CAREWARE TRAINING Adult Learners Approach Getting It Done Framework Concepts vs. Recipes Content Characteristics of Adult Learners Motivators and Barriers to Learning Learning Process: Motivation Reinforcement Retention Transference Adults As Learners Autonomous and Self-Directed: Get input and focus on facilitation. Guide to knowledge rather than supplying facts. Life Experience & Knowledge: Connect new with old Goal-Oriented: Outcomes are presented and steps to achieve them are clearly defined Relevancy-Oriented: Be clear about importance Practical: Not necessarily interested in knowledge for its own sake Respect: Treat as equals and acknowledge experience Motivators Social Relationships: meet new people External Expectations: compliance and fulfilling expectations Social Welfare: improve ability to serve and participate in the community Personal Advancement: achieve higher status Escape/Stimulation: relieve boredom, break routine Cognitive Interest: learn something new Which motivators apply to your situation? Barriers Multiple responsibilities Lack of time Low interest No confidence Scheduling problems Which of these barriers apply? Enhance motivators and decrease barriers Tips Learning is continuous People learn at their own speed Positive reinforcement Proper timing Stimulate as many senses as possible Motivation Set a tone for the lesson: Friendly, open atmosphere Set appropriate level of concern: Adjust tension to meet the importance of the objective Set an appropriate level of difficulty: High enough to challenge without frustrating participants through information overload Predict and reward participation and success: Have expectations Reinforcement Positive reinforcement is generally used when teaching new skills Negative reinforcement help to eliminate certain behaviors Use frequently and regularly early in the process to promote retention of knowledge Later on use reinforcement only to maintain consistent and positive behavior Retention Instructor is not finished until the learner has been assisted with retention In order to retain, must see a meaning or purpose for the information Must be able to understand, interpret, and apply information Retention improves if initial learning goes well After students demonstrate ability to perform, encourage them to practice to retain the information Transference Ability to use the information in a new setting Association: participants can associate the information with something they already know Similarity: information is similar to what participants already know, revisits a logical framework/pattern Degree of original learning: high original learning leads to high transference Critical attribute element: information learned contains elements that are critical to the job Content Characteristics of Adult Learners Motivators and Barriers to Learning Learning Process Motivation Reinforcement Retention Transference Application When do you see yourself needing to train others? How do you envision the training environment? What do you need to be successful?