Mass

Lesson 3
Classifying Matter
Anything in black letters = write it in your notes (‘knowts’)
Matter -
Anything that has mass and takes up space.
Have any examples of matter?
Is anything NOT matter?
Which of these things is not considered matter?
Cell Phone Gravity Rainbow
Fire
Air
Happiness
Sound
Light Bulb
Empty Pop Bottle
With your lab partner, write down how you could prove to someone that air has mass.
Matter Anything that has
mass
Mass -
Measure of the amount of matter in an object
Matter
Mass
We need a better definition for mass…
Mass Measure of an object’s inertia.
Inertia Resistance to change in motion.
Which of the above has more inertia?
Volume amount of space occupied by an object
Common units of volume: mL or L (liquids) cm 3 or m 3 (solids)
1 cm 3 = 1 mL
Density = mass volume
UNITS mass grams volume mL or cm 3 density g/mL or g/cm 3
The density of an object normally decreases as its temperature increases.
Hot air rises!!
The density of water is approx. 1 g/mL
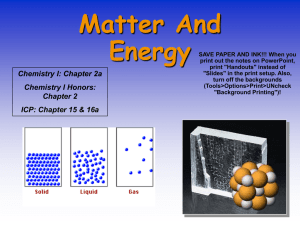
States of Matter
Solid
Particles are packed closely together; definite shape and volume
Liquid
Particles are close but are free to flow past one another; shape depends on container
Gas
Particles are far apart and move freely; shape and volume depend on container; can be compressed
Physical Change
A change in appearance but NOT in the chemical identity of a substance.
The melting point of gallium metal is 30 ˚C. The figure shows how the heat from a person’s hand can melt a sample of gallium.
Phase Changes
melt freeze sublimate evaporate condense deposit
The difference between a vapor & a gas
A vapor is a gas that evaporates from a liquid.
The difference between evaporation & boiling
Evaporation occurs only at the surface, boiling occurs throughout the liquid.
The white cloud is NOT steam. It is actually hot water vapor condensing to form a mist of water droplets
Element, Compound, or Mixture?
Mixture physical blend of 2 or more things
Homogeneous – same composition throughout, uniformly mixed; solutions
Heterogeneous – variable composition, nonuniformly mixed; contains more than
1 phase.
Olive oil
Homogeneous
Vinegar
Homogeneous
Oil & Vinegar
Heterogeneous
(2 phases)
Separating Mixtures
Filtration – separates a solid from a liquid.
Liquid that passes through the filter paper
Distillation – separates a mixture into parts based on the boiling points of each part.
Element – fundamental building block of matter; made of atoms. Each element has a chemical symbol.
1 st - Capital letter
2 nd - Lowercase
Compound – 2 or more atoms chemically bonded in a fixed proportion. Has a chemical formula.
Compounds can be broken down into simpler substances, but elements cannot.
Chemical
Formula
H
2
O
Subscript
2 H atoms and 1 oxygen atom
The properties of compounds are different from the elements that form them.
+
Sodium (Na)
Metal so reactive it reacts with water
Chlorine (Cl
2
)
Toxic gas used in
WWI for chemical warfare
Salt (NaCl)
Relatively harmless
2 poisonous substances react to form a completely benign compound that is necessary for us to live.
Periodic Table 7 Periods (Rows)
18 Columns (Groups or Families
)
Elements in each column have similar chemical properties
Law of Conservation of Mass
In any chemical reaction, reactant mass = product mass