States (Phases) of Matter Vocabulary
advertisement

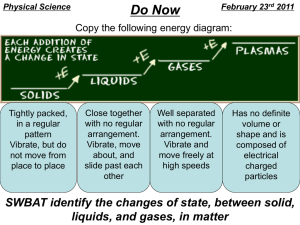
States (Phases) of Matter Vocabulary Boiling/Boiling Point- The application of heat to change something from a liquid to a gas. The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid boils at a fixed pressure. The boiling point is the same as the temperature of condensation. Occurs inside the liquid and at the surface. Bose-Einstein Condensate- The fifth state of matter, only a few billionths of a degree above -2730C or Absolute Zero. This super-cooled state has the atoms lose their individual properties and form into one big blob. It has less energy than a solid, and is called a “super-atom”. Condensation- The change of a gas or vapor to a liquid, either by cooling or by increasing pressure. When water vapor cools in the atmosphere, for example, it condenses into tiny drops of water, which form clouds. Deposition- The opposite of sublimation, where a gas changes directly into a solid; gaseous vapor turning into frost. Ex. Frost forming on the windshield, the night after it does not rain or snow---warm air (with water vapor) hits the much colder windshield. Energy- the ability to do work; when changing from one state of matter to another, energy in the form of heat must be added or taken away. Evaporation- A form of vaporization. The ability to convert or change the substance into a vapor from a liquid state. Occurs at the surface of a liquid, at a temperature below the boiling point. Freezing/Freezing Point- To pass from the liquid to the solid state by loss of heat. The freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid of specified composition solidifies under a specified pressure. Gas- The state of matter that has no fixed size or shape. It has the ability to diffuse readily throughout a container and distribute evenly throughout. Heat- the energy transferred from one substance to another. This is due to a temperature difference, and as a result it is transferred from where there is more heat energy to where there is less. Kinetic Theory- The theory that molecules will move constantly and randomly and will often collide with each other. They also collide with the walls of any container they may be in. Adding heat will increase molecular movement and collisions; removing heat will decrease molecular movement and collisions Liquid- A state of matter that shows a readiness to flowing, it has no fixed shape, taking on the shape of its container, but it does have a fixed volume. EXAMPLES- Mercury, liquid H2O, ammonia, vinegar Melting/Melting Point- To pass from the solid state to the liquid state by the gain of heat. The melting point is the same as the freezing point of a substance. Ex. Ice changing into liquid. Molecules- the smallest identifiable part of a substance; the combination of two or more atoms (these may be the same or different atoms; O2 or H2O are both molecules) Phase Change- a change from one state of matter (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition. It is caused by adding or taking away heat energy. A physical change. Plasma- The 4th state of matter, most similar to a gas, (but consisting of positively charged ions with most or all of their detached electrons moving freely about). Produced by high temperatures, and existing mostly in space (such as the Sun and stars), but also in fluorescent light bulbs and neon signs. Solid- A state of matter that keeps a definite size and shape. The molecules move around, but only slightly (shivering, in the case of water). EXAMPLES- Wood, skin, pencil, ice. Sublimation- The process of changing from a solid to a gas without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. Carbon dioxide, at a pressure of one atmosphere, sublimates at about -78 degrees Celsius. Nitrogen sublimates from solid form as well, with vapor coming off. Surface Tension- The attraction of water molecules for each other (cohesion) at the surface of a liquid. This “skin” that is produced can resist external forces and allow things to sit/stand on water that may even be denser than water itself. Temperature- a measure related to the motion of atoms, ions or molecules of a substance. Vaporization- the process of becoming a vapor; conversion of a substance from the liquid or solid phase into the gaseous (vapor) phase. Boiling and evaporation are both examples of the phase change of vaporization. Viscosity- The resistance of a substance (a liquid or a gas) to flow. The viscosity increases as density increases. EXAMPLE: Maple syrup has greater viscosity than water, because it flows more slowly.