K/H Spring Final Exam review
advertisement

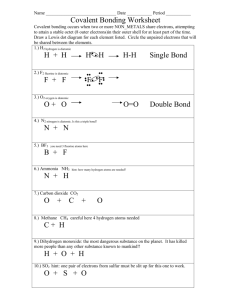
Name ________________________________ K/H Spring Final Exam review Unit 6 1. The energy levels in an atom correspond to what on the periodic table? 2. The number of valence electrons in an atom corresponds to what on the periodic table? 3. Which group on the periodic table has an octet in the outermost energy level of its atoms? 4. What are the 4 sublevels that exist in atoms? 5. Which energy level has the least amount of energy associated with it? 6. What is a valence electron? 7. How many dots would Bromine have in its Lewis dot diagram? 8. What is the maximum number of dots in a Lewis dot diagram? What do the dots represent? 9. How many empty orbitals will there be in the 4th energy level of nickel? 10. Element: strontium a. Lewis dot diagram b. Electron configuration (and label energy level, sublevel, orbital, # valence electrons) c. Noble gas electron configuration d. Orbital filling diagram Unit 7 1. As you go from Te to S on the periodic table the ionization energy generally ___________. 2. As you go across period 4 from Y to Sb, the atomic radius _________________. 3. Which would have the largest ionization energy? (circle) a. Na Mg K b. P S Cl 4. Which has the greatest desire to gain electrons? (circle) a. Cs Na b. As Al S Cl 5. Which is the most metallic (circle) a. K Ca Ga b. Mg Ca Sr 6. Which has the largest atomic radius? (circle) a. Na Mg K b. P S Cl 7. Write the name of the element is described by the following statements: a. largest atomic radius in period 2 _____________ b. largest ionization energy in period 4 ____________ c. most active metal of the alkali earth metals ____________ d. metalloid in period 3 _____________ e. Smallest atomic radius in group VA _______________ 1 f. highest electronegativity in period 4 _____________ g. Most nonmetallic element of the halogens __________________ h. Which element would form a cation, Cu or Cl? 8. How are the elements arranged in the modern periodic table ______________________? 9. List 3 properties of metals: a. b. c. 10. List 3 properties of nonmetals: a. b. c. 11. Elements in a group have similar properties. Why? _____________________________ 12. Members of a group have the same # of ___________________________ electrons. 13. Name the Noble Gases: 14. Is a cation larger or smaller than the neutral atom? ____________Explain _______________________ 15. Is an anion larger or small than the neutral atom? ___________ Explain ________________________ 16. Define electronegativity. _______________________________________________ 17. Define ionization energy. _______________________________________________ Unit 8 1. What is an ionic bond? 2. What is the most electronegative element? ____ The least electronegative? ______ 3. What is the charge on an ionic compound? ________________ 4. Metals (gain,lose) electrons which makes them have a (negative,positive) charge. These ions are called ______________. 5. Nonmetals (gain,lose) electrons which makes them have a (negative,positive) charge. These ions are called ________________. 6. What does the Roman Numeral in the name Copper (II) Oxide represent? 7. Every ionic compound contains a _________________ and a _________________. 8. What happens to Magnesium when it becomes an ion? 9. What does the group number for an element indicate?___________________________ 10. Write the symbols for all 16 type I metals. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 11. Write the symbol, oxidation #, and criss-cross to get the correct chemical formula for the following compounds: a. sodium phosphide _________________________ b. ammonium nitride _________________________ c. copper (II) chloride _________________________ d. zinc nitride ________________________________ e. cobalt (III) sulfate ___________________________ f. aluminum hydroxide _______________________ 2 12. Write thename for the following compounds: a. K(OH) _________________________ b. CuCl2 __________________________ c. Ni3(PO4)2 _______________________ d. FeCl2 __________________________ e. (NH4 )(NO2) _____________________ f. CaO ___________________________ 13. Write the namefor the following polyatomics: a. (NO2) -1________________________ b. (NH4) +1 _______________________ c. (PO4) -3 ________________________ d. (C2H3O2) -1 _____________________ 14. Write the formula, including charge, for the following polyatomics. Draw parentheses around the symbols and subscripts. Write the charge outside of the parentheses. a. carbonate _______________________________ b. hydroxide _______________________________ c. nitrate ________________________________ d. sulfate __________________________________ 16. Draw the Lewis dot diagram for the ionic compound, K2S. 17. Calculate the number of atoms in 2.15 moles of gold. 18. Calculate the number of molecules in 0.151 moles of N2O. 19. Calculate the number of moles of the substance that contains the following number of particles. a. 8.92 x 1023 atoms of barium b. 5.50 x 1025 molecules of CO2 20. Determine the percent composition of each element in the following compounds. a. C3H8O b. Ca3(PO4)2 21. Which of the following ionic compounds has a 2:1 ratio? a. NaCl b. Na2S c. MgBr2 d. MgO Unit 9 Match the following statement with the correct bond type. Some statements may have more than one answer. Ionic Bond (I) __ 1 __ 2 __ 3 __ 4 __ 5 __ 6 __ 7 __ 8 __ 9 __ 10 Polar Covalent Bond (PC) Nonpolar Covalent Bond (NPC) This type of bond occurs between a metal and a nonmetal. This type of bond involves valence electrons. A Roman numeral is used when naming some compounds formed with this type of bond. This type of bond results from the unequal sharing of electrons. This type of bond results from the equal sharing of electrons. This type of bond results from the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another. This type of bond forms between the atoms in diatomic molecules. This type of bond forms between most nonmetal atoms in molecules that are not diatomic. This type of bond is the result when there is a large difference in electronegativity of atoms. Prefixes are used when naming molecules with this type of bond. 3 Write the name of the compound. 11. SO3 ___________________ 12. CO3 ___________________ 13. SF6 _____________________ 14. NO2 _____________________ 15. ClO3 _____________________ 16. H2O ____________________ 17. Write all of the number/prefix combos used in naming covalent molecules. Write the formulas for the following covalent molecules. 18. carbon monoxide ________________________ 19. dinitrogen trioxide _________________________ 20. phosphorous heptachloride_________________ Chemical formula: CS2 21. Determine the number of valence electrons. 22. Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram. 23. Determine the shape of the molecule. 24. Write the name of the molecule. 25. What is the total number of electrons shared between the atom? Given NH3 26. Determine the number of valence electrons 27. Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram. 30. Determine the shape of the molecule. 31. Write the name of the molecule. 32. What is the total number of electrons shared between the atom? Use the following structural formulas to fill in the chart. Compound # of Carbon atoms # of Hydrogen atoms Molecular formula Empirical formula Ethene Propene Butene 33. A sample contains 94.07% sulfur and 5.93% hydrogen. What is its empirical formula? 4 34. A compound contains 65.2% Scandium and 34.8% oxygen. What is the molecular formula if the molar mass of the compound is 276 g/mol? 35. The picture shows a covalently bonded compound. The small particle is hydrogen and the larger is carbon. What is the empirical and molecular formula of the compound? Unit 10 1. Calculate ΔH for each of the following reactions. Show all work. Circle endothermic or exothermic and write the energy value on the correct side of the equation. a. NO + O3 NO2 + O2 endo or exo b. 4 NH3 (g) + 7 O2 (g) 4 NO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) ΔH endo or exo Match the definition in column A with the vocabulary word in column B. Answer COLUMN A COLUMN B 3. Reactants are more stable; ΔH is positive; absorbs heat a. catalyst 4. Minimum amount of energy required to form the activated complex. b. exothermic 5. A substance that slows down reaction rates c. inhibitor 6. Substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up; provides an alternate pathway for the reaction; lowers the activation energy of the reaction d. activation energy (Ea) 7. Products are more stable; ΔH is negative; releases heat e. endothermic 5 O3 (g) 142.2 NO (g) 90.4 HCl (g) -92.31 CaCO3(s) -1207.0 CaO(s) -635.1 CO2 (g) -393.5 NH3(g) -46.3 O2(g) 0 NO2(g) 33.9 H2O(l) -285.8 8. Using the diagram to the left, answer the following questions. a. Label Reactants (R), Products (P), activated complex (AC) b. Calculate Ea c. Calculate ∆Hrxn d. What is the PE of the reactants? e. What is the PE of the products? f. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? g. Using a dashed line, sketch the alternate pathway that a catalyst would provide. 9. Using the diagram above, identify what each letter represents: a. b. c. e. f. g) Is the forward reaction endothermic or exothermic? h) In the forward reaction, are the reactants or the products more stable? i) Write the symbols for the reactants. j) Write the symbols for the products. k) On which side of the equation should the energy term be written? 10. What do the letters (g), (s), (l), and (aq) mean in a chemical equation? 6 Unit 11 1. Given the equation: CaCl2(aq) + Na3PO4(aq) Ca3(PO4)2(s) + NaCl(aq) a. Balance the equation and label the type of equation _______________ b. Is NaCl a reactant or product? ________________________________ c. Will there be a precipitate formed?if so, name it: ________________ d. What do you call the numbers that you put in front of the formulas to balance the equation?______________________ e. If 20.0 g of reactants are used, how many grams of products are formed? f. Name the products and the reactants. 2. Balance & list the type of the following reactions and the sum of the coefficients: Type of Reaction a. ___AlCl3 ___ Al + ___Cl2 ________________________ b. ___C2H5OH + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O ________________________ c. ___Cl2 + ___KI ___KCl + ___I2 ________________________ d. ___K + ___O2 ___K2O ________________________ Sum _____ _____ _____ _____ 3. For an endothermic reaction which side of the arrow is energy on, reactant or product? 4. Label the following compounds as soluble (aq) or not soluble (s) a. CaSO4 b. Mg3(PO4)2 c. NH4Br d. Al(NO3)3 e. BaCO3 f. Fe2S3 5. Balance the following equations by inserting the proper coefficients. Draw Before and After particle diagrams to show the particles involved in the reaction. Provide a key. a. ____ CuCl ____Cu + ____Cl2 b. ____Al + ____HCl ____AlCl3 + ____H2 c. ____ BaCl2 + ____H2SO4 ____BaSO4 + ____HCl 6. Define the law of conservation of matter? 7. Which type of reaction may form a precipitate? 8. Using the activity series, select which metal is most active from the following pairs. a. H or Co ________ b. Au or Li _______ c. Cl or F ______ d. Sn or Pb ________ e. Fe or Zn ______ f. I or S ______ 9. Would the following single replacement reactions take place? a. F2 + CaCl2 b. K + FeCl2 c. Ni + NaBr d. Br2 +NaI Unit 12 Define the following terms: 1. Stoichiometry 2. Limiting reactant 3. Excess reactant 4. Actual yield 5. Theoretical yield 6. Percent Yield 7 Solve the following problems using stoichiometry. YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK. THIS INCLUDES UNITS AND CHEMICAL FORMULAS. H2O NaOH Na2O + 7. How many grams of NaOH are produced from 120 grams of Na2O? 8. How many moles of Na2O are required to produce 160 grams of NaOH? 9. How many grams of H2O are required to produce 2.25 x 1024 atoms of NaOH? 10. If 3.69 L of carbon dioxide formed at STP, how many grams of iron also formed? Given/ Unknown Equation – balance CO + Fe2O3 Fe + CO2 The diagram below shows Magnesium reacting with Hydrochloric acid forming magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. Write the equation for this particle diagram. Balance the equation and then answer the following questions. + + 6.5 grams of magnesium react with 8.9 grams of hydrochloric acid. 10. What is the limiting reactant? 11. How many grams of hydrogen gas are produced? 12. Bob performs this experiment in his chemistry class and obtains 0.18 grams of hydrogen gas. Calculate Bob’s percent yield. Unit 13 1. Determine if the following statements best describe acid, base, both acid and base or a neutral substance. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. turns phenolphthalein indicator pink pH of 10.2 has more H+ than OHis a proton donor 0.10 M KOH 0.10 M HClO pH of 7 gives up OH- ions in water. turns litmus paper red turns litmus paper blue 3. What volume of 12 M HCl is needed to neutralize during the titration of 75 ml of 0.5 M NaOH? 8 4. What is the molarity of HNO3 if 154 mL is neutralized by 125 ml of 1.2 M Mg(OH)2? 5. How many liters of 0.400 M HBr solution can be made from 5.68 L of 8.00 M HBrstock solution? 6. What is the molarity of a solution that contains 7.2 moles of HCl in 3.4 L of solution? 8. Fill in the missing information in the table below. [H+] pH ACID or BASE 1.66 x 10-10 M 3.89 x 10-13 M 1.38 x 10-2 M 4.37 x 10-5 M 3.47 x 10-8 M 8.71 x 10-4 M 9. Define: a. pH b. neutralization c. Bronsted-Lowry acid and base d. Arrhenius acid and base e. molarity f. binary g. ternary 10. Define strong acid and base. 12. Write the names for the following formulas: a. H2S b. H(C2H3O2) c. H2ClO2 d. HCl e. KOH f. Fe(OH)2 13. Write the formulas for the following: a. nitrous acid b. nitric acid c. cobalt (II) hydroxide d. hydrofluoric acid e. magnesium hydroxide 14. What is the range for acids on the pH scale?_ ___ What is the range for bases on the pH scale?___ 15. Label the Bronsted-Lowry Acid, Bronsted-Lowry Base, Conjugate Acid, Conjugate Base below: HCl 16. + H2O → H3O+1 + Cl-1 The particle diagram to the left shows an acid. Is it strong or weak? Explain your answer. 9