aldehydes , Acids, Amines
advertisement

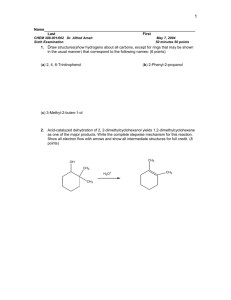
Aldehdydes , ketones,
carboxylic acids & amines
Dr/ Nabila Al-Jaber
Professor of Chemistry,
King Saud University
Aldehydes & ketones
CnH2nO
Aldehyd
R
C
H
R
Ar
C
O
H
aromatic ald
O
alphatic ald.
Ketone
R
C
O
R
alphatic ket.
(+)C=O(-)
Ar
C
O
R
Aromatic ket.
polar react with acid and base
Nomenclature:
A] Aldehyde
1] Ald. up to 4 c by common name of the acids to
which they related.
2] More than 4 by replacing e(from alkane) by –al.
3] C of ald. Always No. 1 (not appear in the name)
H
C
H
O
comm. : formaldehyde
IUPAC: Methanal
CH3CH2CH2CHO
CH3
C
H
O
CH3-CH2-C-H
O
Comm.: Acetaldehyde
IUPAC: Ethanal.
(IUPAC: Butanal /
Comm. Prpionaldehyde
IUPAC: Propanal
Comm. Butyraldehyde)
Nomenclature:
4] Substituted ald. By alphabet. If (OH > C=C or CC )
ClCH2CH2CH2CH2CHO
5-Chloropentanal
CH3CHOHCHClCH2CHO
3-Chloro-4-hydroxy pentanal
CH3CH2CH=CHCHO
2-Pentenal
5] Aromatic aldehyd derivatives of
simplest aromatic (bezald.)
O
H
O
H
O
H
O
H
OH
Bezaldehyde
o-hydroxy benzald.
NO2
P-nitrobezald.
OCH3
p-Methoxy benzald.
(Anisaldehyd.)
B] Ketones
1) Simple by alkyl substituent and word ketone
O
CH3-C-CH3
O
CH3-C-CH2CH3
Comm. Acetone
IUPAC: Dimethyl ketone
Methyl ethyl ketone
O
Methyl phenyl ketone
(Acetophenone)
O
CH3-C-CH=CH2
Methyl vinyl ketone
O
Diphenyl ketone
(Benzophenone
2] complicated ketones by IUPAC by replacing (e) by(-one)
(in longest cont. chain with C=O) ket. Take lower no.
CH3CH2COCH3
CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
Butanone
2-Hexanone
CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3
3-
hexanone
CH3CH2CHClCOCH2CH3
4-chloro-3-hexanone
CH3CH2CH=CHCOCH3
3-hexene-2-one
O
NH2
Br
4-Amino-5-Bromo-2-pentanone
O
NH2
CH3CH2CH=CHCOCH3
3-hexene-2-one
Br
4-Amino-5-Bromo-2-pentanone
3] If position of C=O not clear no. is needed for no.
O
CH3-C-CH2-CH3
O
CH3-C-CH2-CH2-CH3
2-pentanone
2-Butanone
O
O
Cyclopentanone
O
CH3
2-methyl cyclohexanone
CH3
3-methylcyclohexanone
Physical Properties.
Solubility
-Simple (1-6) ald. & keto. Soli. in H2O
- If R (inc) soli. (dec.)
- more than 6 C insole.
Boiling point
C=O polar, So Ald. & ket Polar (intermolecular attraction)
Dipole- dipol attractions
O
--------
C
C -------- O
B.P
ald &ket. > alkane (same m.wt)
Preparation of Aldehydes & ketones
1] Oxidation of 1& 2 alcohol :
RCH2OH
O
R-C-H + H2O
CrO3 / pyridine
or, Cu /heat(week oxidi).
R
R-C-OH
H
O
R-C-R
KMnO4
neutral
2] Ozonolysis of alkenes:
CH3
C=CH2
CH3
1) O3
2)Zn, H2O
CH3
C=O
CH3
CH2O
Preparation of Aldehydes & ketones
3] Hydrolysis of alkynes:
HC≡CH+ H2SO4
H2O
aldhyde
H2SO4, H+
H2SO4, H+
H2O
(CH3)2-C=O
(acetone)
O
4] Friedel Craft acylation:
O
O
+ Cl-C-R
i)
O
O
+ Cl-C-CH3
ii)
CH3
iii)
R
AlCl3
CH3
AlCl3
CH3
O
+ Cl-C-C2H5
AlCl3
O
C2H5
+ para
Reactions of Aldehydes and ketones
1] Addition of metal hydrides( formation of
alcohol)
H2 / Pt
H
CH3-CH=CH-CH2-C=O
CH3CH32-CH2-CH2-CH2OH
1)NaBH4 CH -CH=CH-CH -CH OH
3
2
2
2)H2O
O
1) LiAl H4, ether
R-C-R'
2)H3O+
R-CHOH-R'
(2 alco.)
Reactions of Aldehydes and ketones
1] Addition of metal hydrides( formation of
alcohol)
O
1) LiAl H4, ether 2)H3O+
R-C-H
or 1) Na BH4 2) H2O
O
CH3-C-H
1) Na BH4
2) H2O
O
1) Na BH4
CH3-C-CH3
2) H2O
R-CH2OH
CH3-CH2OH
CH3-CHOHCH3
0
(1 alco.)
(10alco.)
(20 alco.)
2] Reactions with Grignard reagent:
1)dry ether
2) H3O
1)dry ether
CH3-CHO + CH3-MgCl
2) H3O
R-CHO + R'-MgX
R-CO-R' +R''-MgX
1)dry ether
2)H2O
CH3CO-CH3 +CH3-MgX
R-CHOH-R'
CH3CHOHCH3
R''
R-C-R'
OH
1)dry ether
2)H2O
OH
CH3-C-CH3
CH3
2] Reactions with Grignard reagent:
OH
C2H5
O
1)dry ether
+ CH3CH2-MgX 2)H O ,H+
2
CH2OH
MgBr
+ CH2O
o
(3 alc.)
1)dry ether
2)H2O ,H+
3]Addition of alkynide ions: {R-C≡C(-)}
R-CO-R'+ R''-C
H3O+ R-COH-C
C-Na
R'
+
CH3CH2CHO + CH3C CNa
H3O
H
C-R''
+NaOH
OH
CH3C-C C-CH3
H
+NaOH
4]Addition of hydrogen cyanide
(cyanohydrins formations):
Ald or Ket. + HCN
NC-C-OH (cyanohydrin)
O
CN
COH
H
H
+ HCN
O
HCN
OH
CN
Li Al H4
H3O
mandelo nitrile
OH
CH2NH2
cyanohydrins formations
OH
H
t
P
/
O
OH
HCN
H
CH3
H
CH3
CN
H2
CH3
CH2NH2
H
3O
OH
H
CH3
COOH
cyanohydrins formations
CHO
HCN
OH
C-CN
H
1)Li Al H4
2)H2O
H3O+
heat
OH
CCH2NH2
H
OH
C-COOH
H
5] Addition of alcohols
Ald.. + alcoh.
Ket. + alcoh.
— H+--— H+---
hemiacital
hemiketal
a) Hemiacitals formation
O
H
+
CH
-OH
CH3-CH
3
CH3CHO + CH3CH2OH
OH
CH3-C-OCH3
(1-methoxy ethanoal)
H
hemiacetal
H+
OH
CH3-CH
OCH2CH3
5] Addition of alcohols
b) Hemiketals formation
H+
CH3COCH3 + CH3OH
CH3COH-OCH3
CH3
c) Acetal formation:
OH
+ CH3CH2OH
CH3-CH
OCH2CH3
HCl
(hemiacetal)
OCH2CH3
CH3-CH
OCH2CH3
hydrolysis
2CH3CH2OH + CH3CHO
(acetal)
d) Ketal formation:
OC2H5
CH3-C-CH3
OC2H5
OH
CH3-C-CH3 + CH3-CH2OH HCl
OC2H5
(ketal)
hydrolysis
CH3COCH3 + 2 CH3-CH2OH
O
+2 CH3CH2OH
HCl
(hemiketal)
OC2H5
OC2H5
ketal
OH
OC2H5
(C2H5)OH
hydrolysis
(H2O)
6] Addition of ammonia and it's derivatives
O
NR
+ R-NH2
+H2O
(Imine)
O
NOH
+NH2OH
+H2O
(Oxime)
N-NH2
O
+ NH2-NH2
(hydrazine)
O
+H2N-OH
+
H2O
(hydrazone)
NOH
cyclohexanone oxime
Reduction of oxime
NOH
R
H
1) Li Al H4 ,ether
2)H3O
R-CH2-NH2
( 1 amine)
N-OH
R
R
1)Li Al H4
2) H3O+
R-CH-NH2
R
( 2 amine)
7] Iodoform reaction
O
R + 3I2 + 4 NaOH
CH3
CHI3 + 3NaI +RCOONa + 3H2O
O
CH3
C2H5 + 3I2 + 4 NaOH
CHI3 + 3NaI +C2H5COONa + 3H2O
8]Aldol condensation:
Aldehydes
O
2
CH3
+ dil OH
H
O
CH3-CH-CH2-CH
OH
(3-hydroy butanal)
(aldol)
O
2
H
CH3
+ dil OH
O
CH3-CH-CH2-CH
OH
(3-hydroy butanal)
(aldol)
8]Aldol condensation:
Ketones
2 CH3-CO-CH3
Ba(OH)2
H2 /Ni
CH3
CH3
CH3-C-CH2-CH-CH3
OH
CH3 O
CH3-C-CH2-C-CH3
OH
H / warm
OH
O
CH3-C=CH-C-CH3
8]Aldol condensation:
O
H
no reaction
2
O
O
H
H3C
H
OH-
O
OH
C-CH2-CH
H
8]Aldol condensation:
O
2
CH3
O
C-CH2-C
OH
NaOC2H5
-H2O
heat
CH3 O
C=CH-C
O
+ CH3CH2CHO
dil OH-
OH
CHCHO
CH3
Carboxylic acid
R-COOH
Aliphatic (carboxylic cid)
Ar-COOH
aromatic (benzoic acid)
Nomenclature :
1)
replace
ane
by
-ic acid
No. C Formula
IUPAC
Common
1
2
3
4
5
Methanoic acid
Ethanoic acid
Prpanoic acid
Butanoic acid
Pentanoic acid
Formic acid
Acetic acid
Prpionic acid
Butyric acid
valeric acid
2-hydroxy ben. a
Salicylic acid
HCOOH
CH3COOH
CH3CH2COOH
CH3(CH2)2COOH
CH3(CH2)3COOH
OH
COOH
COOH
Benzoic acid
2) Longest continuous chain
CH3CH2CHCH2CH2COOH
CH3
4-Methyl hexanoic acid
C-C-C-C-C-COOH
CH3CH2CHCH2CH2COOH
CH3
γ-Methyl hexenoic acid
CH3 CH3
CH3-CH-CH-COOH
commmone:
IUPAC:
CH3-CHBr-CHCl-CO2H
-- Dimethyl butyric acid
2,3-Dimethyl butanoic a
3-Bromo-2-chlorobutnoic acid
3) In cyclic ring ------ cycloalkane carb. a'
COOH
COOH
COOH
cyclopropane
carb.ac.
cyclobutane
carb.ac.
COOH
COOH
cyclopentane cyclohexane
carb.ac.
carb.ac.
32-Cyclohexene carboxylic acid
4) Aromatic acid by common name
CO2H
CO2H
OH
benzoic acid
Salycilic acid
O- hydroxy benzoic acid
CO2H
CO2H
CO2H
(comm.) Phthalic a'
CO2H
(comm.) Terephthalic a'
Physical properties:
1] They form hydrogen
2] comp. 1-7 soli in H2O .
3] mor than 7 carbon less soli. (bec. R increased)
4] Aromatic acids insoluble. In H2O
5] BP. Acid > Alcohol
Acidity
COOH
OH
COOH
OH
inc acidity
Deac. gps inc. acidity
COOH
COOH
>
NO2
Acti gps dec. acidity
NO2
>
NO2
COOH
COOH
>
>
inc. acidity
CH3
COOH
OH
HCOOH > CH3COOH > CH3CH2COOH > CH3 CH2 CH2COOH
More acidity
Substitution with halogen :
CH3CH2COOH
CH3CH2COOH
<
<
CH2Cl-CH2COOH
CH2ClCOOH
<
More acidity
(more acidic)
CHCl2COOH
<
CCl3COOH
Preparation of carboxylic acid
1] Oxidation
a) 1 alcohols & Aldehydes
CH3CH2OH
KMnO4 / H+
CH2OH
KMnO4 / H+
or K2Cr2O7 /H+
CH3CHO
heat
CH3COOH
COOH
CHO
heat
Cu / Heat
or CrO3 / pyridine
R-CHO
RCH2OH
K2Cr2O7 / H+
or KMnO4 / H+
RCOOH
b) of alkyl benzene
CH3
COOH
KMnO4 / H+
OCH3 or K2Cr2O7 /H+
NO2
OCH3
NO2
CH3
KMnO4 / H+
or K2Cr2O7 /H+
CH2CH2CH3
COOH
COOH
KMnO4 / H+
or K2Cr2O7 /H+
2)Hydrolysis of nitriles
H+
R-X + NaCN
RCN +H2O
R-COOH
heat
OH
(K,Na,..)
RCOO
1)Li AL H4, ether
2)H3O or H2 / Pt
CH3CH2Cl
1)NaCN
CH2Cl
CH3CH2CN + H2O 2) H
heat
CH2CN
1)NaCN
(K<Na..)
RCH2NH2
amine
CH3CH2CO2H
CH2CO2H
2) H
+ H2O
heat
3] Carbonation of Grignard reagent:
R-Mg X
CH3-Mg Br
1) CO2
1)CO2
R-COOMgX
2) H3O
RCOOH
2) H3O CH COOH
3
CH3-COOMgBr
+ Mg(OH)Br
COOH
Mg Br
1)CO2
2) H3O+
Reactions of acids
1)Salt formation:
it react with strong base & we can use Ca or K
RCOOH + KOH
RCOOH + NaOH
It reacts with weak base
RCOOH + NaHCO3
RCOOK + H2O
RCOONa + H2O
sodi. acetate
RCOONa + CO2 + H2O
Sodium bicarb. Can be used to distinguish between
carboxylic acid and phenols
OH
+ NaHCO3
NO reaction
2) Formation of Easter:
R'-OH / H+
R-COO-R' + H2O
heat
OH
OH
CH3CH2OH
COOC2H5
H+ / heat
COOH
RCOOH
3) Formation of amide:
RCOOH
CH3COOH
NH3 or R-NH2 ,heat
NH3 , heat
R-CONH2
CH3-CONH2
4) Formation of acid anhydride:
O
O
H2SO4
R-C-O-C-R
2 RCOOH
O
O
H2SO4
2 CH3CH2COOH
CH3CH2-C-O-C-CH2CH3
5) Formation of acid chloride:
2 RCOOH
2 CH3COOH
SOCl3 , PCl3
or PCl5
SOCl3 , PCl3
or PCl5
2
O
R-C-Cl
2
O
CH3-C-Cl
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid derivatives
When Oxygen of Carboxylic acid is replaced with Nu.-----Carb. a' deriv
O
R
OH
O
O
Nu
R
O
R
O
Cl
Acid chl.
R
O
OR' R
Ester
Nu
Ar
O O
N
Amide
R-C-O-C-R R
Acid anhydride
O
O-(K or Na)
Salts
1] Salt:
O
H3C
Com.
IU.
O- Na
Sodium acetate
,K
from Acet.a'.
h
Sodium etanoate
from Ethan.a'.
2] Acid chloride
O
CH3CH2
Cl
I (Com.) Proanyl chloride from propanoic a'
Propionyl chloride
from propionic a'
Com. (I)
O
Cl
Benzoyl chloride
4] Ester:
The alkyl gp. Named 1st then the name of parent acid with ending –
ate in place of -ic acid
O
Com. (I)
O
H
OCH2CH3
CH3
from acetic a'
I (Com.) Ethyl ethanoate
from ethanoic a'
(I)
Methyl methanoate
from mthanoic 'a
(Com.) Methyl formate
from formic a'
OCH3
O
O
O
O-CH3
Methyl benzoate
Ethyl acetate
OCH
OH 3
CH3 O-CH=CH2
Vinyl acetate
Methyl salisylate
O
O-C-CH3
(I)
Phenyl ethanoate
(Com.) Phenyl acetate
O
CH2-O-C-CH3
(I)
Benzyl ethanoate
(Com.) Benzyl acetate
4]Amides:
-oic acid or -ice a' by
–amide .f 1 or 2 subst. on
nitrogen we say N-subs. or N,N-disubs. (sub. Name 1st )
O
O
NH2
R
O
Or
Ar
O
C-NH2
Benzamide
O
C-N
NH2
CH3CH2
CH3
N,N-Dimethyl benzamide
Propanamide
O
C-N
CH3
(I)
NH2
CH3
C2H5
(I)
N,Ethyl-N-methyl benzamide
4] Acid anhydride:
replacing
O
-acid with
O
O
anhydride
O
Ar C-O-C-R
R C-O-C-R
O
O
CH3 C-O-C-CH3
Ethanoic anhydride
O
CH3CH2 C-O-C-CH2CH3
O
O
(I) Propanoic anhydride
(C) Propionc anhydride
O
O
O
O
C-O-C-
Succinic anhydride
Z
Benoic
anhydride
Order of reaction:
R-CO-Cl >
Acid chloride
R-(CO)2O-R >
Acid anhydride
RCO2R >
Ester
RCO2H > RCONH2
Acid
Amide
Reactions of acid derivatives
a) Acid chlorides:
H2O/ H+
O
R-C-OH + HCl
R'OH
O
R-C-OR' + HCl
NH3
O
R-C-NH2 + HCl
R'NH2
O
R-C-NHR' + HCl
R'2NH
O
R'
R-C-N
R'
O
R-C-Cl
Reduction:
O
R
1) Li Al H4 / ether
Cl
2) H3O
+ HCl
R-CH2OH
B] Acid anhydride:
H2O/ H+
2
O
R-C-OH
acid
R'OH
O
O
R-C-O-C-R
O
R-C-OR' + RCOOH
Ester
O
R-C-NH2
NH3
+ RCOOH
Amid
R'NH2
O
R-C-NHR' + RCOOH
R'2NH
O
R'
R-C-N
R'
+ RCOOH
O
O
O
O
OH
R
R
O
COOH
COOH
CH3
CH3
CH3
+CH3-COOH
acetyl salisilic acid + acetc acid
Reduction:
O
O
R
O
R
1) Li Al H4 / ether
2) H3O
2 R-CH2OH
C] Esters:
RCOOR' + H2O
RCOOR' + R''OH
RCOOR' + NH3
H+
H+
H+
RCOOH + R'OH
RCOOR'' + R'OH
RCONH2+ R'OH
Reduction:
RCOOR'
1)Li Al H4 / ether
RCH2OH+ R'OH
2) H3O
CH3-CH2COOCH3 1)Li Al H4 / ether CH3CH2CH2OH+ CH3OH
2) H3O
R-C-OO-R'
1) 2 R'' Mg X
2 ) H3O / H+
OH
R-C-R''
R''
+ R' OH
d] Amide:
O
R-C-NH2
+ H2O
O
R-C-NH2
Reduction:
O
R-C-NH2
O
R-C-NHR'
O
R'
R-C-N
R'
Dehydration:
O
CH3-C-NH2
NaOH
O
R-C-ONa + NH3
/ heat
1) Li Al H4 / Ether
2) H3O
R-CH2NH2
1) Li Al H4 / Ether
2) H3O
R-CH2NHR'
1) Li Al H4 / Ether
R-CH2NR'2
O
R-C-NH2
Hoffman degradation:
O
R-C-OH + NH3
H+
2) H3O
P2O5
- H2O
R-CN
O
Br2/ NaOH
RCH2-C-NH2
or NaOBr
Br2/ NaOH
CH3NH2
nitrile
R-CH2NH2
Amines
-Intermediate in organic chemistry reactions
-Amino acids (proteins DNA, RNA)
-Alkaloids and drugs
Structure and classification of Amines:
It is derived from ammonia by replacing 1,2 or three H
by alkyl or aryl gp.
-Aliphatic amines contain only alkyl gps. bonded
directly to nitrogen atom.
-Aromatic – one or more aryl gps. bonded to N.
Aliphatic amines
H
H
H
N
H
H
Ammonia
N
N
CH3
H
H
CH3 CH3
N
CH3 CH2-
Alphatic amines
Aromatic amines
H
H
N
N
H
CH3
-1 , 2 &3 or quaternary ammonium salt according to
(R) or (Aryl) gp. attached to N atom.
H
N
H
H
R
R
N
R
R
N
R
R
R
R
N
R
+
R
X
Nomenclature of amines
1] Simple aliphatic by alphabetical order to gp.
Attached to N and adding -amine
H
H
H
H
N
N
N CH3
CH3
CH3
CH3 C2H5
Mathyl amine
ethylmethylamine
dimethylamine
N
H
-CH2
CH3
Benzylmethyla
mine
H
N
N
H5C2
Tri methyl amine
N
C2H5
Di ethyl amine
CH2CH2CH3
N
CH3 C2H5
Ethyl methyl propylamine
H5C2
C2H5
Diethyl isopropyl amine
C2H5
N C H
2 5
C2H5
Triethylamine
2] Complicated amine we consider (NH)as substituent
& it's position will take the lowest possible number.
CH3
NH2
CH3-CH2-CH-CH2CH-CH3
3-Amino-5-methylhexane
NH2-CH2-CH2-NH2
1,2-Diamino ethane(I)
Ethylene diamine
NH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2
5
1,6-Diaminopentane(I)
5
pentamethylene diamine(C)
NH2CH2CH2OH
2-Amino ethanol
O
NH2CH2CH2CH2OH
3-Amino-1-propanol
NH2
5-Amino-2-hexanone
NH2
NH2
Amino cyclohexane(I)
Cyclohexyl Amine(C)
O
cyclo
2-Amino pentanone
3] Amine salt by replacing Amine by ammonium
CH3
CH3
N
CH3
+
Cl
-
N
CH3
CH3
NH2
NH2
NHC2H5
OH
NO2
P-Nitroaniline
Br
-
Ethyl methylammoinum bromide
4]Aromatic amine
Aniline
C2H5
H
Tetramethyl ammoinum chloride
NH2
+
H
NHCH3
C2H5
N-C2H5
e
P-Aminophenol
P-Hydroxyaniline
N-Ethyl aniline
N-mthyl aniline
N,N-Diethyl aniline
CH3
N-C2H5
NHN- Diphenyl amine
N-Phenyl aniline
N-Diphenyl aniline
N-ethyl-N-methyl aniline
Physical properties:
- Amines are solutions are basic (ammonia or died
fish odor)
- 1-3(methyl, dimethyl trimethy) are gases (aliphatic
only)- 1 , 2 amine can form H bond So their MP > alkane
of similar M.Wt
(B.P
Amine > Alkane)
Basicity of amines:
-Amines basic because N has non bonded pair of
electrons which can be donated to an acid to form
ammonium salt.
- base strength depend on the degree of substitution on N.
- More basic CH3-NH-CH3 > NH2-CH3 > NH3
- Activating gps. Increase basic properties.
- RNH2 > ArNH2
aliphatic more basic than
aromatic
- Amine > RCONH2 (Amide) less basic from amine
NH2
NH-CH3 NH2
NO2
NH2
NO2
NO2
NH2
OH
CONR
Preparation of amines:
1] Reduction of:
a) nitro compounds
CH3CH2NO2
Sn/HCl
NO2
Sn/ HCl
or Fe/ HCl
RNO2
RNH2
CH3CH2NH2
NH2
b) Of Amide
O
R-C-NH2
Sn/conc HCl
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
O
R-C-NHR 1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
O
1)LiAl H4 / ether
R-C-NR2
2)H3O+
NO2
Sn/ conc. HCl
or Fe/ HCl
CH3
R-CH2-NH2
NH2
CH3
1o amine
R-CH2-NHR
2o amine
R-CH2-NR2
3o amine
R-C=NH
c) Of Imines
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
R-CH2-NH2
d) Of Oxime:
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
R-C=NOH
R
R-C=NOH
H
R-C=N
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
e)Of nitriles
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
CH2CN
H3O+, heat
R-CH-NH2
R
R-CH2-NH2
R-CH2-NH2
CH2CH2NH2
CH2COOH
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
CH2CN
H3O+, heat
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
CH2CH2NH2
CH2COOH
CH2NH2
CN
H3O+, heat
CH2Br
CH2CN
1)LiAl H4 / ether
2)H3O+
COOH
RCH2CH2NH2
CH2COOH
NaCN
H3O+, heat
2] Alkylation of Ammonia
RNH3X
NH3 + RX
CH2CL
NH3 +
OH
CH2NH-CH3
CH2NH2
NaOH
RNH2
CH3Cl
NaOH
+ HCl
CH2N-CH3
CH3 NaOH
CH3Cl
CH3NH2 + CH23Cl NaOH
CH3NHCH3 + HCl
3] Hofmann degradation of amides
O
Br2/ NaOH
RCH2-C-NH2
or NaOBr
O
CH3C-NH2
acetamide
Br2 / NaOH
or KOH / Br2
R-CH2NH2
CH3-NH2 +NaCO3+NaBr+ H2O
(methyl amine)
O
CH2-C-NH2
+ NaOBr
phenyl acetamide
CH2-NH2
Br2 / NaOH
or KOH / Br2
benzyl amine
Reactions of amines
1] With acid chloride
acid chloride react with 1 & 2 amine only(no 3 )
O
RNH2 + R'-C-Cl
O
R'-C-NH-R
NaOH
O
NH-C-R
NH2
O
+ R-C-Cl
+HCl
NaOH
+HCl
Acylation or amide formation
R'-NHR'
NH
N
H
O
+ R-C-Cl
O
+ CH3-C-Cl
NaOH
NaOH
O
+ CH3-C-Cl
O
R-C-NR'2
O
C-CH3
N
O
C-CH3
N
NNCl
NaNO2 +2HX
N2Cl
or
0-5 C
diazonium salt
NH2
or
R-NH2
O
NH-C-CH3
(CH3-CO)2O
acid anhydride
+ CH3COOH
NH2
Br
Br
or RNHCOCH3
Br2 / H2O
NH-CH3
Br
CH3 Cl / NaOH or (KOH)
(only with 1 and 2 amine)
+HCl
Alkylation
HCl
Reactions of Diazonium salt:
NNCl
NH3Cl
salt formation
NHCH3
NaOH/H2O
N=NNH-CH3
+ HCl
yellow azocompound
NNCl
Cu2(CN)2
NNCl
NaNO2
NNCl
KI
CN
+ N2
NO2
+ N2
I
+ N2
NNCl
H3PO2
NNCl
CH3OH
+ N2
OCH3
+ N2
+H2O
NNCl
H3O+ / heat
or H2O /H+
OH
NNCl
HBF4 / heat
F
+ N2
+ N2
NNCl
Cu2Br2
NNCl
Br
+ N2
OH
o
o C , NaOH
N=NOH
+HCl