UNIT 3: Psychological Testing
advertisement

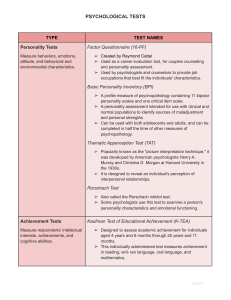
Psychological Testing Unit 3 Reliability: Is the test consistent? Do you get the same result under any circumstance? Test-retest Validity: Does the test measure what it is supposed to? The longer = more valid Standardization: (IOWA, LEAP, ACT) Tests are given and scored the same way every time Establishes a norm, or the average score, made by a large group of people Percentile System: “grading on the curve” *Scores are placed in order from highest to lowest and are assigned a percentile Measurement Tests 1) 2) 3) Achievement tests measure people’s skills & the knowledge they have in specific academic areas Aptitude tests (taken before training) measure specific abilities or skills; determine whether a person is likely to do well in a field ex. SAT Interest Inventories determine whether their interests are similar to people in line of work Ex. Kuder Preference Record & Strong-Campbell Interest Inventory I. INTELLIGENCE TESTING: Intelligence: the ability to acquire new ideas and new behavior and to adapt to new situations Gardner’s Theory of Intelligence: *Came up with 8 types of intelligences 1. Verbal: speaking 2. Logical-mathematical: formulas & theories 3. Spatial: ability to find your way around an environment 4. Musical: ability to create and perceive pitch and rhythm patterns 5. Body-kinesthetic: body movement (athletics) 6. Interpersonal: communication with others 7. Intrapersonal: knowledge of oneself 8. Naturalist: a person’s ability to identify and classify patterns in nature IQ Scores (Intelligence Quotient): dividing a child’s mental age (the average age of those who also received the same score as that child) by chronological age (actual age) and multiplying by 100 IQ = Mental Age x 100 Chronological Age *average score is 100; >100 (intelligent); <70 (handicapped) *2% score @ or above 130 II. PERSONALITY TESTING: *used to identify personality characteristics and to identify problems and psychological disorders *personality includes a person’s characteristics, habits, preferences, and moods A) TYPES OF OBJECTIVE TESTS: forced-choice tests; must select from possible answers; (-) must rely on a person’s selfreports (1) MMPI: Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (1930s & 1940s) *this test has 567 statements to which the person can respond true, false, or cannot say *EX: I like tall women; I am envied by most people; I am seldom troubled by headaches *reveals habits, fears, delusions, and symptoms of disorders (2) Meyers-Briggs Test: • characterizes personality into 4 scales • Description 1. Extrovert vs. introvert: out-going or keep to yourself 2. Intuitive vs. sensing: sensing something without knowing why or seeing to believing 3. Feeling vs. thinking: heart or mind 4. Judging vs. perceptive: organized, structured, or flexible (B) TYPES OF PROJECTIVE TESTS: respond freely; no written choices to choose from; presented with ambiguous stimuli or sentence fragments…ex. “When I see myself in the mirror, I…” (+) flexible, relaxed atmosphere (1) Rorschach Inkblot Test: 10 cards with inkblot designs (5 black and gray; 2 with red; 3 mixture of colors) show inkblot and person says what they see; no right or wrong answers Types of Projective Tests cont. (2) TAT…Thematic Apperception Test Developed by H.A. Murray 20 figures in ambiguous situations p. 469 One key is to see if the subject identifies with hero of the story or minor characters