Chapter 5: Managerial Ethics & Corporate Social Responsibility
advertisement

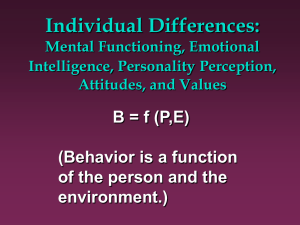
Chapter 10 Understanding Individual Behavior Attitudes: The ABC Model Affect » Feelings for an object Behavioral Intentions » Potential Behavior toward it Cognition » Beliefs about it Other Attitudes Job Satisfaction Enjoyment of your specific job Organizational Commitment Positive feelings, Pride, Loyalty, etc. concerning the organization as a whole Organizational Citizenship Behaviors to help the organization that are outside of one’s job duties Attitude Change Techniques Persuasion » Cognition -> Behavior Conditioning » Affect -> Cognition -> Behavior Cognitive Dissonance Production » Behavior -> Cognition Perception “The link between the person and the environment” Broadly defined, includes Social Perception (impressions of people) Perception Why are perceptions often distorted? » Why do people not always perceive things as they are? » Why do people perceive things differently? – Different people – Same person at different times Sources of Perceptual Distortions/Differences Selectivity (perceiving only part of envir. or attending to some parts more than others) » External Factors (i.e., in physical envir.) – Similarity – Size – Nearness – Motion » Internal Factors – Experience – Motivation Sources of Perceptual Distortions/Differences Closure (adding to your perception) » Stereotyping » Halo Effects » Attribution Attributions Perceived causes of behavior Major concern: whether caused by internal or external factors (the person or the environ.) Our judgments based on 1) whether a person acts like other people do and 2) whether a person does something repeatedly and in a variety of situations Common Attributional Errors Fundamental Attribution Error » We Perceive others’ behaviors as more Internally caused than they are Self-Serving Bias » We perceive our own: –Success as Internal –Failure as External Personality Internal State Uniqueness Consistency Stability Personality Theories Developmental Stage (Psychodynamic) » (Freud, etc.) Trait-Based (“Big Five”, etc.) » e.g., Neurotic, Extraversion, Authoritarian (Eysenck) Motive-Based » e.g., Achievement, Affiliation, Power (McClelland) Belief-Based » e.g., Internal vs. External Locus of Control (Rotter) Locus of Control » People who believe that individuals are in control of their own lives have an Internal locus of control. » People who think that forces beyond their control dictate what happens to them have an External locus of control. Emotional Intelligence Dimensions 1) 2) 3) 4) Knowing one’s own emotions Controlling one’s emotions Recognizing others’ emotions (Empathy) Social Skill - Controlling others’ emotions Emotional Intelligence Author Daniel Goleman says incompetence in management occurs more often from lack of EQ than lack of IQ. EQ skills are essential in managing conflict Types of Learning Shaping » Learn by doing » Small, Reinforced Steps Modeling (Social Learning) » Learn by observing someone else » Consequences to Model are important Mental Ability General Intelligence (g factor) » Correlation with Job Performance Specific Intelligences (s factors) » Correlation with Job Satisfaction Testing Intelligence and Personality When using in selection and placement: Back up with validity studies. In General: » Intelligence - Moderate Validity » Personality - Low Validity Cognitive (ProblemSolving) Styles How do we gather information? » Sensing - Look at the facts, details. » Intuiting - Brainstorm, get a general overview. How do we choose between alternatives? » Thinking - Analyze objectively, reason. » Feeling - Consider the impact on people. Cognitive Styles Sensation / Thinking (ST) (e.g., technician) Intuitive / Thinking (NT) (e.g., planner) Sensation / Feeling (SF) (e.g., salesperson) Intuitive / Feeling (NF) (e.g., artist) Myers-Briggs Test Has 4 dimensions (incl. Sensation vs. Intuition and Thinking vs. Feeling) Also Includes: » Extraversion vs. Introversion » Judger vs. Perceiver – (decisive vs. flexible) The Myers-Briggs Framework Higher and lower positions in each of the dimensions are used to classify people into one of sixteen different personality categories. Consequences of Stress Psychological » moodiness, depression, emotional fatigue Physiological » cardiovascular diseases » ulcers, sexual dysfunction, headaches Behavioral » poor performance, accidents » absenteeism » workplace aggression Sources of Stress Experience » Job Conditions » Job Events » Life Events » Life Conditions Personal Characteristics » Personality » Coping Behaviors (These and other factors influence how people much stress people feel.) Sources of Stress Job Conditions » Intrinsic to the Job » Being in the Organization » Roles in the Organization » Career Development » Relations within the Organization » Organization interface with the outside Sources of Stress Intrinsic to the Job - Examples » Making decisions » Unstructured tasks » Constant monitoring » Repeated exchange of info with others » Dealing with the public » Unpleasant physical conditions Sources of Stress Job Events & Life Events » Even “good” things can be stressful, because change is generally stressful. Sources of Stress Life Conditions » Urban Stress Test –Measures: Population Change, Crowding, Education, Violent Crime, Unemployment, Per Capita Income, Birth Rate, Air Quality, Hazardous Wastes, Water Supply & Quality, Wastewater Treatment –Does not include: Climate, Cultural Offerings, NFL Football Sources of Stress Personality » Type A Behaviors –Highly Competitive –Impatient –High Job Involvement » Determinants of Type A Personality –Sensitive Nervous System –Demanding Parents (love contingent upon achievement) Coping with Stress DESCRIPTIONS Primary Prevention EXAMPLES Primary Prevention » Change how you do things to remove stressors from your life Secondary Prevention » Time management, skill enhancement, delegation, job redesign » Prepare yourself to withstand stressors Treatment » Treat the stress effects you already have Secondary Prevention » Exercise, diet, recreation, sleep, relaxation, meditation Treatment » Professional help, social support