Chapter 12 Powerpoint (Neural Tissue)
advertisement

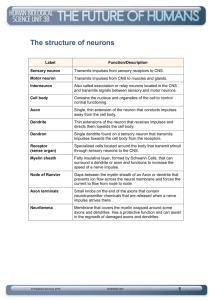
Ch 12-Nervous System 3% of your body weight 2 divisions • Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain & spinal cord • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)- nerves in rest of body Afferent- brings sensory information to CNS from peripheral tissues & organs Efferent- carries motor from CNS to muscles, glands, & adipose 1. Somatic NS- sensory receptors for senses, motor from skeletal 2. Autonomic NS- sensory for visceral, motor CNS to smooth & cardiac muscle & glands 1. Sympathethic- fight or flight 2. Parasympathetic- rest & digest Nervous Tissue • Neurons- structural & functional units - react to physical & chemical changes - send nerve impulses along nerve fibers • Neuroglia- supporting cells (protect, nourish, cleanup, regulate) Parts: Pg 376 1. cell body- nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm, rough ER called Nissl bodies 2. dendrites- receiving portions of neurons, usually not myelinated 3. axon- moves nerve impulses toward another neuron, muscle fiber, or gland Others: - joins cell body at axon hillock - first part called initial segment - axoplasm- cytoplasm - axolemma- plasma membrane - axon collateral- branch & axon terminal- end - Trigger zone- initial segment meets axon hillock, where impulse arises Synapse • site of communication b/w two neurons, must have at least 2 neurons for a reflex • Presynaptic cell-sends a message • Synaptic end bulb- tips of axon terminal • contain synaptic vesicles that store neurotransmitters *Separated by synaptic cleft* • Postsynaptic cell-receives the message • If receiving cell is a: muscle = Neuromuscular junction Gland = neuroglandular junction Structural Classes of Neurons • 1. Anaxonic- not distinguishing dendrite from axon • 2. Bipolar- 2 distinct processes(1 dendrite & 1 axon) • Rare- in special sense organs for sight, smell, hearing • small • 3. Unipolar- dendrites & axons are continuous, cell body inbetween • Peripheral nervous system, long • 4. Multipolar- 2 or more dendrites & an axon • Most common in CNS, control skeletal muscles, long Functions *SAME* 1.Sensory- “afferent neurons” (to brain), at the ends of neurons -gather info if something changes & convert to impulses • Interoceptors- inside • • systems (digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular) senses (deep pressure, pain) • Exteroceptors- outside • touch, temp, pressure, sight, smell, hearing • Proprioceptors- body position from muscles & joints 2. Integrate- “interneurons” (in brain), signals are sent to brain - create sensation, memory, produce thoughts 3. Motor- “efferent neurons” (away from brain), act upon impulses effectors- response structures (muscles & glands) Myelination • Myelin Sheath- multilayered lipid & protein covering, insulate the axon & increases speed - more myelin = faster impulse - Neurolemma- outer layer of Schwann cell, aids in regeneration of injury - Internodes-where myelin occurs - Nodes of Ranvier- gaps in myelin sheath Conduction- how it travels 1. Continuous- straight line 2. Saltatory- myelinated fibers, jumps, fastest Disorders of Myelin -all can lead to paralysis • Chronic exposure to heavy-metals (lead, arsenic, mercury) leads to demyelination • Diphtheria- from bacterial infection, toxin damages myelin, we have a vaccine • Multiple Sclerosis- affects axons in the optic nerve, brain, & SC • Loss of vision, problems with speech, balance, coordination • Can be progressive, 30-40yrs of age, more in women • Guillain-Barre Syndrome- autoimmune, demyelination of PNS • Weakness & tingling > paralysis • Triggered by virus • Most fully recover MShttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qgySDmRR zxY What’s the Matter? • White Matter- has myelin, axons • Gray Matter- little or no myelin - cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminals, neuroglia Neuroglia- Nourishes neurons • Separate/protect neurons • Provide framework for neural tissue • Regulate composition of interstitial fluid • Act as phagocytes Classification of Neuroglia of CNS 1. Astrocytes- (star), most numerous maintain blood-brain barrier, structural support, regulate ions, absorb & recycle neurotransmitters, form scar tissue 2. Oligodendrocytes- form myelin in CNS, structural framework 3. Microglia- janitors/police (eat bacterial cells & debris), smallest, least numerous 4. Ependymal- lines central canal of sc and ventricles of brain, regulate the composition of cerebrospinal fluid Classification of Neuroglia of PNS 1. Schwann- produce myelin in the PNS 2. Satellite- regulate exchange of material b/w neuronal cell bodies & interstitial fluid Neural Response to Injury Wallerian Degeneration- PNS • 1. fragmentation of axon & myelin occurs in distal stump • 2. Schwann cells form cord, grow into cut, & unite stumps • Macrophages engulf debris • 3. Axon sends buds into network of Schwann cells and then starts growing along cord of Schwann cells • 4. Axon grows CNS- more complicated • More axons are likely involved • Astrocytes produce scar tissue that can prevent growth • Astrocytes release chemicals that block growth How does a nerve impulse happen? Ion movements & electrical signals: • All plasma membranes produce electrical signals by ion movement • Transmembrane potential is particularly important to neurons • Main membrane processes: 1. Resting Potential- work it may do, difference in electrical charge • Inside- negative (K+), Outside- positive (Na+) & (Cl-) 2. Graded potential- temporary, change in resting potential caused by stimulus 3. Action potential- electrical impulse produced by graded potential propagated along axon to synapse 4. Synaptic activity- releases neurotransmitters producing graded potentials in postsynaptic cell membrane 5. Information processing- response of postsynaptic cell Electrochemical GradientsSum of chemical and electrical forces acting on ion across membrane Why is the inside -? 1. Negatively charged proteins inside the cell are too large to cross 2. it is easier for K+ to diffuse out than Na+ to enter Membrane channels Passive/Leakage channels- always open Active/Gated channels- open or close in response to stimuli • Chemically/Ligand gatedresponse to chemicals (hormones, neurotransmitters) • Ex: Ach receptors at neuromuscular junction • Voltage gated- response to changes in transmembrane potential • Mechanically gated- response to physical distortion of membrane surface by touch, pressure or vibration Action potential when a nerve detects a change 1. Resting state- all channels closed -Threshold- gates open 2. Depolarizing phase- Na channel opens and Na comes in - makes more positive 3. Repolarizing phase- Na channel closes, K channel opens and K flows out, makes more negative until 4. Resting state *exception- can go from #1 to Hyperpolarized = more negative -happens if K+ opens right away Refractory Period- short gap in time b/w impulses All or None – if nerve responds, it is completely http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ifD1YG07fB8 Neurotransmitters Excitatory-promote action potential Inhibitory- suppress action potential 1. Acetylcholine (Ach)- skeletal muscles 2. Norepinephrine- consciousness & attention, body temp 3. Dopamine- emotions, addictions, pleasure, subconscious motor function 4. Serotonin- senses, temperature, mood (lack of=depression), appetite 5. Glutamate & Aspartate- memory, learning, excitatory 6. GABA- inhibitory, anti-anxiety Neuromodulators • Other chemicals released by synaptic terminals • Similar in function to neurotransmitters • Alter rate of neurotransmitter release or change post-synaptic cell’s response • Opioids like endorphins- relieve pain Drugs & Addiction • Drugs can release two to 10 times the amount of dopamine that natural rewards do, and they do it more quickly and more reliably • brain responds by producing less dopamine naturally or eliminating dopamine receptors • Alcohol: increases GABA & decreases glutamate=increase in dopamine • Cocaine: inhibits removal of dopamine from synapses = “high” • THC: stimulates release of dopamine = euphoria, drowsiness, appetite • Ecstasy: targets serotonin receptors > mood Parkinson’s Disease • damage/degeneration of dopamine producing neurons • Usually after 50, more in men, can be genetic Symptoms: • Problems with balance and walking • Rigid or stiff muscles • Difficulty swallowing • Drooling • Slowed, quieter speech and monotone voice • No expression in your face (like you are wearing a mask) • Tremors Epilepsy • short, recurrent attacks of motor, sensory, or psychological malfunction • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6NcqQkKjqTI