Chapter 8.1: The Nervous System
advertisement

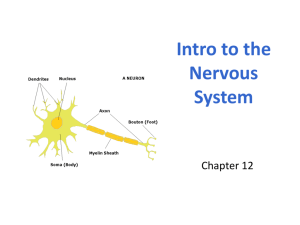
Monitors internal and external environment Integrates sensory information Coordinates all systems Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Intelligence, Memory, Emotion Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) All neural tissue outside the CNS Afferent Division Receptor to CNS Efferent Division CNS to muscles and glands Somatic Nervous System Control over skeletal muscle contractions Autonomic Nervous System Involuntary regulation Cell Body Large Nucleus No centrioles (used for division) Neurons cannot divide Can divide in nose (for smell) and in hippocampus (for memory) Nissl Bodies Rough ER and free ribosomes Several dendrites Receive signals Axon Usually only one/neuron Transmits signal Axon Hillock Where action potentials start Collaterals Branches off axon Synaptic terminals Site where neuron communicates with other cells Multipolar Neuron Two or more dendrites One axon Most common Control skeletal muscles Unipolar Dendrites and axon continuous Cell body off to one side Sensory neurons Bipolar neuron One dendrite One axon Sight, smell, hearing Sensory Neurons Receive information from receptors External receptors—touch, temperature, pressure and senses Proprioreceptors—position and movement of muscles and joints Visceral (internal) receptors—taste, deep pressure, pain Motor Neurons CNS to rest of body Interneurons Only brain and spinal cord Coordinate motor activity