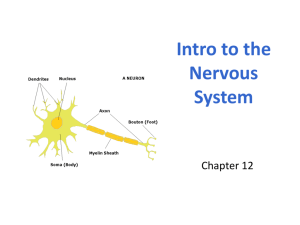
The structure of neurons
advertisement
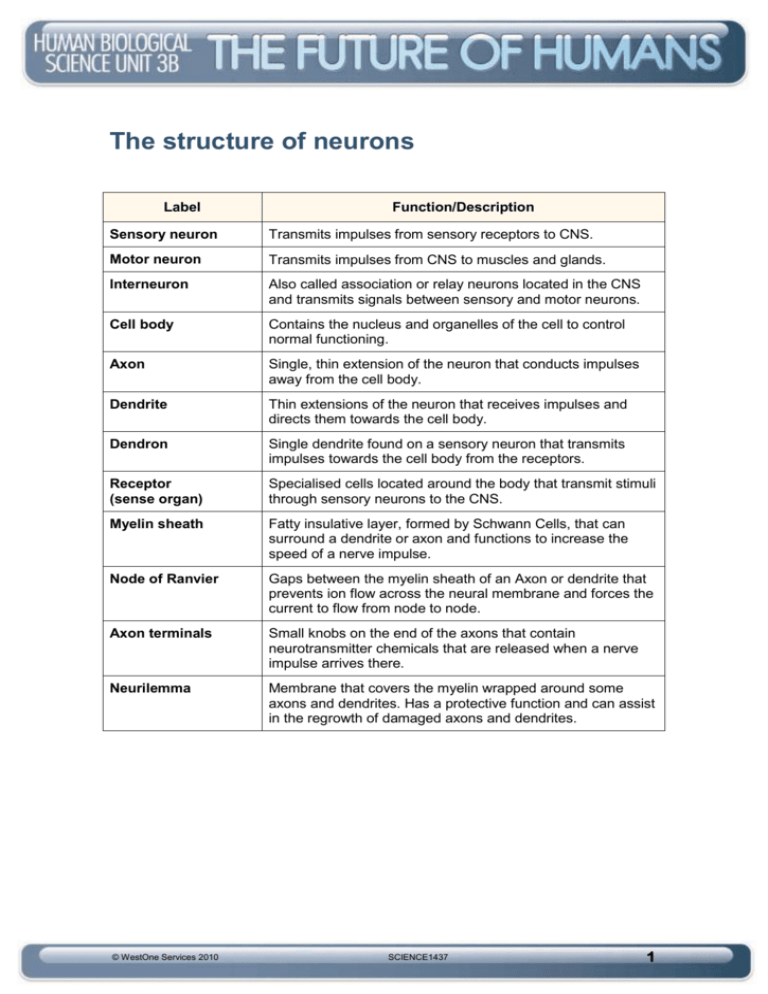
The structure of neurons Label Function/Description Sensory neuron Transmits impulses from sensory receptors to CNS. Motor neuron Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands. Interneuron Also called association or relay neurons located in the CNS and transmits signals between sensory and motor neurons. Cell body Contains the nucleus and organelles of the cell to control normal functioning. Axon Single, thin extension of the neuron that conducts impulses away from the cell body. Dendrite Thin extensions of the neuron that receives impulses and directs them towards the cell body. Dendron Single dendrite found on a sensory neuron that transmits impulses towards the cell body from the receptors. Receptor (sense organ) Specialised cells located around the body that transmit stimuli through sensory neurons to the CNS. Myelin sheath Fatty insulative layer, formed by Schwann Cells, that can surround a dendrite or axon and functions to increase the speed of a nerve impulse. Node of Ranvier Gaps between the myelin sheath of an Axon or dendrite that prevents ion flow across the neural membrane and forces the current to flow from node to node. Axon terminals Small knobs on the end of the axons that contain neurotransmitter chemicals that are released when a nerve impulse arrives there. Neurilemma Membrane that covers the myelin wrapped around some axons and dendrites. Has a protective function and can assist in the regrowth of damaged axons and dendrites. © WestOne Services 2010 SCIENCE1437 1