hydrolysis of esters
advertisement

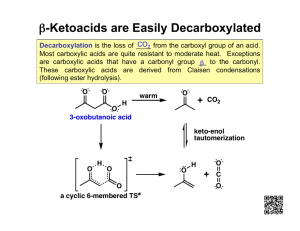
After completing this lesson you should be able to : • Esters can be hydrolysed to produce the parent carboxylic acid and parent alcohol. • Given the name of an ester or its structural formula, the hydrolysis products can be named and their structural formulae drawn. • In a hydrolysis reaction, an ester is split apart by a water molecule. • Describe the difference between dilute acid catalysed hydrolysis of an ester and using a strong alkali, such as NaOH(aq) or KOH(aq). COPY • Breakdown of an ester by water. • Process sped up by catalysis • Can use a dilute acid to catalyse (H2SO4) • Alkali catalysts (e.g. sodium hydroxide) can also be used but instead of producing carboxylic acid a carboxylate salt is formed. • Alkaline hydrolysis goes to completion & hence is usually preferred. COPY Hydrolysing Esters Condensation Alcohol + Carboxylic Acid Ester + Water Hydrolysis Alcohol + Carboxylic Acid Ester + Water The ester is split up by the chemical action of water, hydrolysis. The hydrolysis and formation of an ester is a reversible reaction. O R C O R + H Bonds broken Ester + Water + O O H R C O O R H H Bonds formed Carboxylic Acid + Alcohol COPY • Anti-bumping granules ensure even boil and provide uneven surface for bubbles of gas to form. • you heat reactants under reflux if the organic compound you are heating is volatile (that is it goes to the gaseous state very easily under heat). • When you heat reactants, you turn them back into a liquid so they don’t escape from your reaction vessel. Reactants are turned back into a liquid by having a condenser at the top of the apparatus. So you’re 'fluxing' between the two states, gaseous and liquid. Alkaline hydrolysis COPY Alkaline hydrolysis of an ester has two main advantages over acid-catalysed hydrolysis. 1) Alkaline hydrolysis is not reversible and hence there should be a higher yield. 2) It is usually easier to separate the products when alkaline hydrolysis has been used. COPY …After separating your carboxylate salt via distillation you can displace the sodium using a strong acid to obtain the parent acid of the ester. If sodium hydroxide is used a sodium salt of the acid is formed. If this is reacted with a strong acid (eg. Hydrochloric acid) the acid can be displaced from the salt RCOO- Na+ + Carboxylate Salt + hydrochloric acid HCl RCOOH acid + NaCl + sodium chloride In hydrolysis reactions large molecules are broken down into smaller molecules by water. Esters can be hydrolysed to produce the parent ................... .......... and the parent .................... . ESTER + WATER ⇌ ACID + ALCOHOL An alkali is often used to catalyse the reaction and the mixture heated under reflux. If sodium hydroxide is used a sodium salt of the acid is formed. If this is reacted with a strong acid (eg. Hydrochloric acid) the acid can be displaced from the salt HCOO- Na+ Sodium methanoate + + HCl hydrochloric acid HCOOH methanoic acid + + NaCl sodium chloride Past paper question 2015 Esters hydrolysis COPY Ester hydrolysis, especially by alkali, is an important process in the manufacture of soap from fats and oils. This will be looked at in the next subtopic (B). Prevention of ester hydrolysis COPY • Prevention of ester hydrolysis is also important in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. • As esters are found in these products, if they hydrolyse easily then the property of the products will change. • Expiry dates are predicted, along with other factors, to take account how quickly the product is likely to hydrolyse. • When the acid is produced upon ester hydrolysis it can have an undesirable smell. COPY Extension material - Higher Properties of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylate salts are often used as preservatives and flavor enhancers in soups and seasonings. Sodium propionate, a preservative, is added to cheeses, bread, and other bakery items to inhibit the spoilage of the food by microorganisms. COPY Polarity of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids are strongly polar because they have two polar groups: • hydroxyl group (—OH) • carbonyl group (C O) COPY Solubility in Water Carboxylic acids • form hydrogen bonds with many water molecules • with one to four carbon atoms are very soluble in water As the number of carbons increases, the solubility of the carboxylic acid in water is reduced. Acetic acid forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Solubility in Water COPY Acidity of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids • are weak acids • ionize in water to produce carboxylate ions and hydronium ions • can lose a proton because two oxygen atoms in the carboxylate ion stabilize negative charge Study Check Write the balanced equation for the ionization of butanoic acid in water and identify the carboxylate ion. Solution Write the balanced equation for the ionization of butanoic acid in water and identify the carboxylate ion. O O CH3 —CH2—CH2—C—OH Butanoic acid - CH3 —CH2—CH2—C—Ocarboxylate ion (butanoate) + H3O+ Neutralization of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acid salts • are a product of the neutralization of a carboxylic acid with a strong base, such as NaOH or KOH (carboxylic acid salt) • are used as preservatives and flavor enhancers Carboxylic Acid Salts The carboxylate ion is named by replacing the ic acid ending of the acid name with ate. COPY Carboxylic Acid Salts Carboxylic acid salts • are ionic compounds with strong attractive forces between ions • are solids at room temperature • have high melting points • are usually soluble in water Carboxylic Acid Salts Carboxylic acid salts are used as preservatives and flavor enhancers such as • sodium propionate, which is used in cheese and breads • sodium benzoate, which inhibits growth of mold and bacteria and is added to fruit juices, margarine, relishes, salads, and jams • monosodium glutamate, MSG, which is added to meats, fish, vegetables, and baked goods to enhance flavor Study Check Write the equation for the reaction of propanoic acid with NaOH. Solution Write the equation for the reaction of propanoic acid with NaOH.