Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry at Loyola
advertisement

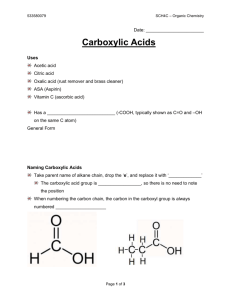
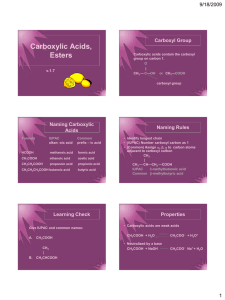
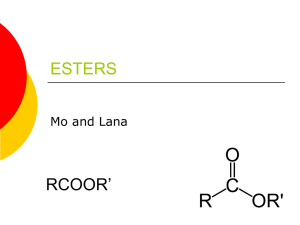
1.6 Carboxylic Acids and Esters Learning Goals … … name and draw carboxylic acids … name and draw esters Carboxylic Acids • contain the carboxyl group located at the end of a parent chain General formula: O R–C R-COOH OH • name carboxylic acids by replacing the – e with – oic acid • number chain so that the carboxyl group is at position #1 CH3 O II C OH ethanoic acid (acetic acid) CH3 CH3 – C – CH2 – C = 0 CH3 3,3-dimethylbutanoic acid OH 4-methylpentanoic acid benzoic acid H2C C O OH phenylethanoic acid Properties of Carboxylic acids • polar and weakly acidic • hydrogen bonding can occur between molecules and with water • very high boiling points due to strong Hydrogen bonds • often have unpleasant odours • the –OH group does NOT behave like the basic hydroxide ion – only the H+ ion is lost in solution to form an acid Esters General formula: O II R–C OR’ R-COOR’ O II R–C main chain OR’ alkyl group To name an ester: 1. Name the alkyl group attached to the O, indicate position # 2. Name the parent chain which includes the C=O group, replacing the ending with –oate 3. Put the 2 names together (but as separate words) O II CH3CH2CH2C-O-CH2CH3 O II H C-O-CH2CH2CH3 ethyl butanoate 1-propyl methanoate Note: main chain does not have to be the longest chain CH3CH2COOCH2(CH3)CH2CH3 O II CH3CH2C-O-CH2CH2CH3 CH3 2-butyl propanoate 2-butyl methylpropanoate Properties of Esters • polar • low boiling points • ester groups are found in fats and oils • often produce pleasant odours and tastes, such as in fruits. As a result, they are often used for perfumes and artificial flavours Self Check How prepared am I to start my homework? Can I … … name and draw carboxylic acids … name and draw esters HOMEWORK p48 #1, 2 p50 #1, 2 p55 #1,2