Intro to Short Stories
Introduction to the
Short Story
CLE 3002.8.2 Understand the characteristics of various literary genres (e.g., poetry, novel, biography, short story, essay, drama).
Definition: What is a short story?
• A short story is a work of fiction that focuses on one important event in the lives of a small number of central characters and that can usually be read in one sitting.
Definition: What is a short story?
• A short story is a work of fiction that focuses on one important event in the lives of a small number of central characters and that can usually be read in one sitting .
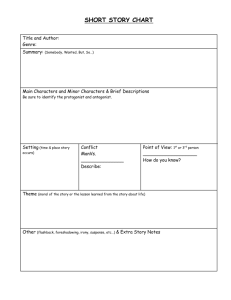
A short story has six basic elements:
• Plot
• Setting
• Conflict
• Character
• Point of View
• Theme
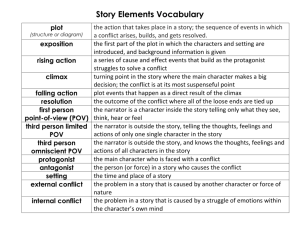
Plot = the framework of a story
• Plot is the arrangement of related events that makes the story hang together.
• Plot can also be referred to as the structure of a short story.
Structure concerns how the story is told.
The plot or structure of a short story has four basic parts:
• Exposition: introduces the characters, setting, and background situation of the story.
• Exposition can also be called the
Basic Situation of the story.
The plot or structure of a short story has four basic parts:
• Complication: introduces complications and obstacles that increase the tension of the story conflict.
The plot or structure of a short story has four basic parts:
• Climax: that moment in the story when tension rises to its highest point and the conflict comes to a head.
The plot or structure of a short story has four basic parts:
• Resolution: describes how the conflict is finally resolved and the story comes to an end.
• Resolution of conflict is also called the denouement of a story.
Conflict: the “story problem” that must be resolved.
• also called the “overall conflict” or the “central conflict”
4 Kinds of Conflict
• Man vs. Man
• Man vs. Self
• Man vs. Nature
• Man vs. Society
2 Types of Conflict
• External
• Internal
• External = a character struggles with a force outside himself or herself.
• Internal = a character struggles within his or her own mind with emotions, decisions, etc.
Characters
“In the best stories, characters come alive. We care about their dreams, fears, and frustrations, just as if they were real people in our lives.”
Characters
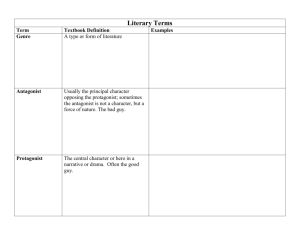
• Protagonist - ?
• Protagonist – main character / clearly central to the story with all major events having some importance to him or her.
Characters
• Antagonist - ?
• Antagonist – any character who opposes or struggles against the protagonist.
• Question: Does the antagonist always have to be a character (a person) in the story?
• Main
• Major
• Minor
Characters
• Dynamic
• Static
• Flat
• Round
Characterization: the process by which authors communicate their characters to the readers
• Direct characterization
• Indirect characterization
Point of View – the perspective from which a story is told
• First Person Point of View –
• Third Person Omniscient Point of View
• Third Person Limited Point of View
• Third Person Objective Point of View
Reader
First Person PoV
Narrator
Third Person Omniscient
PoV
Narrator
Reader
Third Person Limited PoV
Narrator
Reader
Third Person Objective
PoV
Narrator
Reader
Theme – the message the author intends to communicate by telling the story
• Can there be more than one theme found in a short story?
• A story’s themes are often universal truth’s, which are suggested by the specifics of a story.
Literary Elements used in short stories
• Foreshadowing – ?
• Foreshadowing – the use of clues that tell the reader what is going to happen as the story unfolds.
– Foreshadowing is often used as a device by which the writer uses to arouse the reader’s interest and increase suspense.
Suspense
• Suspense - ?
• Suspense – the uncertainty or anxiety that a reader feels about what is going to happen next in a story.
Suspense – a question?
• Why do writers use suspense in short stories?
• Answer: to hold the reader’s interest