Elements of Literature Vocabulary

Elements of Literature:
Think like a Reader and Writer
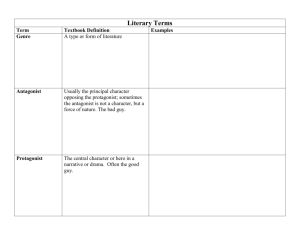
Genre
• Genres are the categories in which literature can be classified.
– Science fiction
– Fantasy
– Historical Fiction
– Mystery
– Traditional Literature
Protagonist and Antagonist
• The protagonist is the main character in the story.
• The antagonist is the character or force working against the main character.
Traditional Literature Character Types
• Magic Helper
• The Wise Sage
• The Trickster
• The Fool
Dialogue and Dialect
• Dialogue is when characters are speaking.
• Dialect is the specific way characters speak.
• Authors use dialect to make characters more realistic for the reader.
Point of View
• Point of View is the perspective from which the events in the story are told.
– 1 st Person: The narrator is a character in the story.
– 3 rd Person Limited: The narrator is not a character in the story, but is able to reveal the thoughts and feelings of one character in the story.
– 3 rd Person Omniscient: The narrator is not a character in the story, but describes the thoughts, feelings, and actions of many characters in the story.
Setting
• The setting is where and when parts of the story take place. (Culture and time period can be very important.)
Conflict
• A conflict happens when two opposing forces meet.
• Authors use conflict to move the plot forward and sometimes reveal the theme.
• Internal Conflict :
– Person vs. Self
• External Conflict:
– Person vs. Person
– Person vs. Nature
– Person vs. Society
Plot
• The plot is the basic sequence of events in a story.
• Plot patterns include these parts:
– Exposition: the beginning of the story
– Rising Action: conflicts/complications in the story are introduced and possibly resolved.
– Climax: the main conflict reaches peak tension and is resolved
– Denouement (Falling Action and Resolution): The story is wrapped up.
Plot Diagram
Symbolism
• The use of symbols to represent important ideas in the story.
Theme
• The central message or idea in a work of fiction.
Stranger Danger!
Common Plot Patterns
• The Hero’s Journey
• Rags to Riches
Turning Points
• A minor turning point happens when an event in the story changes the direction of the story.
– Example: When Harry Potter decides to go to school at Hogwarts.
• The climax of a story is the major turning point.
Flashback
• Interruptions in the story’s sequence of events which take the reader back to an earlier time.
• A flashback allows the reader to understand something that happened in the past.
Foreshadowing
• Clues that the author gives you about what is going to happen later in the story
Mood
• Mood is the atmosphere or feeling created by the writer using imagery, word choice, setting, voice, theme, etc.
The Rule of 3 or 7
• Things grouped in 3 or 7 create a more memorable and satisfying pattern.
• Characters, events, words or phrases, objects . . .