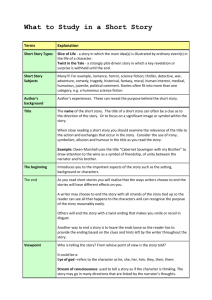
Literary term definitions
advertisement
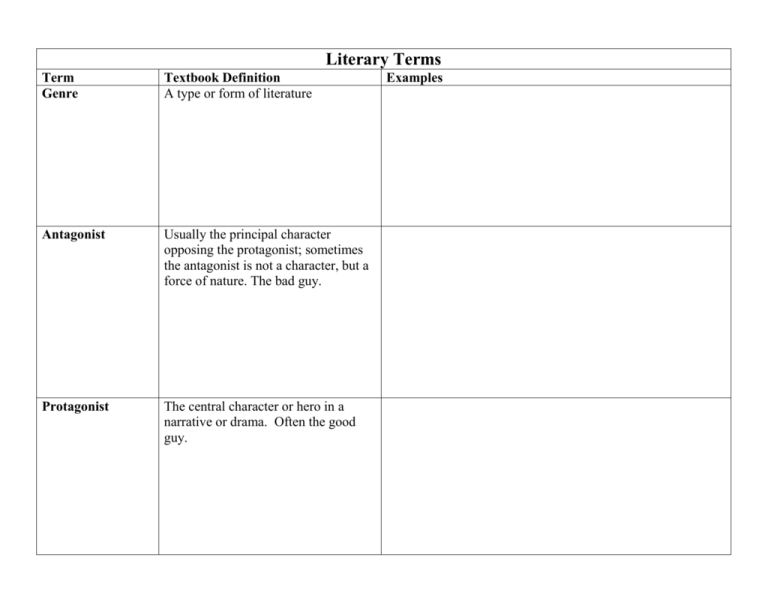
Literary Terms Term Genre Textbook Definition A type or form of literature Antagonist Usually the principal character opposing the protagonist; sometimes the antagonist is not a character, but a force of nature. The bad guy. Protagonist The central character or hero in a narrative or drama. Often the good guy. Examples Character The people, animals, or imaginary creatures who take part in the action of a story or a novel. Round- three dimensional characters or characters that are fleshed out. You know a lot about these characters as they are usually main characters. Flat- these characters are not as well developed. You don’t know much about them and they are usually minor characters. Static-characters that do not change throughout the course of the story or novel. Dynamic- characters who are transformed or undergo a change as the work of literature progresses. Plot Chain of events; story line Exposition The beginning of the story, which sets the tone, establishes the setting, introduces the characters, and gives the reader important background information Rising Action Events in a story that move the plot along Climax The turning point; the moment when the reader’s interest and emotional intensity reach the highest point Falling Action Also referred to as resolution of the conflict, where loose ends of the plot, or story, are tied up Setting Details related to location, time, and historical context Flashback A conversation, episode, or event that happened before the beginning of the story and often interrupts the chronological flow of the story. Foreshadowing Hints or clues that indicate events and situations that will occur later in the plot Irony A contrast between appearance and reality—usually one in which reality is the opposite of what it seems. Verbal-when someone knowingly exaggerates or says one thing and means another. Dramatic- the reader or viewer knows something that a character does not know. Situational-contrast between what a reader or character expects and what actually exists or happens. Narrative Point of View – who is telling the story 1st Person-The narrator is a character in the story. Narrator uses “I” and “me.” 3rd Person-The narrator is someone outside of the action, not a character writing the story. Characters are referred to by name or by the pronouns he, she, they. Symbol/Symbolism A person, place, an activity or an object that stands for something beyond itself. Theme The main idea or central message in a work of fiction. It is a perception about life or human nature that the writer shares with the reader. Tone The attitude a writer takes toward a subject Mood Mood depends on the tone. The feeling or atmosphere that the writer creates for the reader. Diction A writer’s or speaker’s choice of words and arrangement of these words in a sentence. Conflict A struggle between opposing forces Internal: man vs. himself External: man vs. man man vs. nature man vs. society