Moss Life Cycle - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

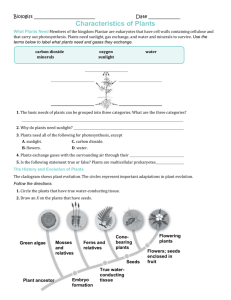
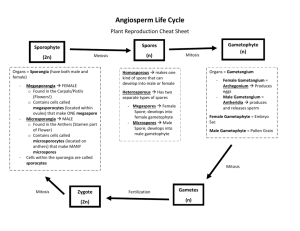
Moss Life Cycle Alternation of generations Zygote created from egg & sperm Alternation of generations Zygote divides by mitosis to create adult sporophyte Alternation of generations Haploid spores created by meiosis Alternation of generations Haploid spores released into air Alternation of generations Female gametophyte creates eggs Spore grows into male or female gametophyte Male gametophyte creates sperm Alternation of generations Sperm & egg create diploid zygote Alternation of generations Cycle repeats Group 1: Seedless, Nonvascular Plants • Most primitive of plants • Live in moist environments – Swimming sperm • Examples: – Liverworts – Hornworts – Mosses Mosses • Because nonvascular: Grow low to ground – Water transported by simple diffusion • Lack true leaves – only 1 cell thick • Rhizoids anchor into soil • Early inhabitant of new ecosystems (succession) Moss Life Cycle • Gametophyte stage – Dominant stage; Haploid – Looks like mat of green shag carpet Moss Life Cycle • Gametophyte stage – Dominant stage; Haploid – Looks like mat of green shag carpet • Antheridium: produces male sperm Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Moss Life Cycle • Gametophyte stage – Dominant stage; Haploid – Looks like mat of green shag carpet • Antheridium: produces male sperm • Archegonium: produces female egg Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Moss Life Cycle • Gametophyte stage – Dominant stage; Haploid – Looks like mat of green shag carpet • Antheridium: produces male sperm • Archegonium: produces female egg – Sperm swims through water to fertilize egg Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Moss Life Cycle – Dominant stage; Haploid – Looks like mat of green shag carpet • Antheridium: produces male sperm • Archegonium: produces female egg zygote Male gametophyte (creates sperm) • Gametophyte stage – Sperm swims through water to fertilize egg Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Moss Life Cycle • Gametophyte stage – Dominant stage; Haploid – Looks like mat of green shag carpet • Antheridium: produces male sperm • Archegonium: produces female egg stalk zygote – Sperm swims through water to fertilize egg • Sporophyte stage – Stalk grows out of the zygote Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Moss Life Cycle • Gametophyte stage – Dominant stage; Haploid – Looks like mat of green shag carpet • Antheridium: produces male sperm • Archegonium: produces female egg capsule stalk zygote – Sperm swims through water to fertilize egg • Sporophyte stage Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) – Stalk grows out of the zygote – Haploid spores created inside capsule by meiosis Moss Life Cycle capsule stalk zygote .. • Gametophyte stage – Dominant stage; Haploid – Looks like mat of green shag carpet • Antheridium: produces male sperm • Archegonium: produces female egg – Sperm swims through water to fertilize egg • Sporophyte stage Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) – Stalk grows out of the zygote – Haploid spores created inside capsule by meiosis – Spores released and grow into new gametophytes See appendix B in your text book Moss Life Cycle capsule stalk zygote Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Male gametophyte . (creates sperm) Female gametophyte . (creates eggs) See appendix B in your text book Moss Life Cycle capsule stalk zygote Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) See appendix B in your text book Moss Life Cycle capsule stalk zygote Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) See appendix B in your text book Moss Life Cycle capsule stalk zygote Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Moss Life Cycle capsule stalk zygote sporophyte zygote Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Moss Life Cycle capsule stalk . zygote sporophyte Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Male gametophyte (creates sperm) Female gametophyte (creates eggs) Moss Life Cycle Place the steps of the moss life cycle in order, from the step started for you: __ 1___ Spores land. 5 _______ Diploid sporophyte will grow from zygote. 3 _______ Through water, sperm swim from antheridium (male gametophyte) to archegonium (female gametophyte). 2 _______ Moss gametophytes grow near the ground. 6 _______ Sporophyte will create and release spores. 4 _______ Fertilization occurs. Plant Life Cycle Comparisons Plant type Sporophyte Gametophyte Dominant? Moss Stalk with cup (capsule) at tip, which is where spores are produced. More familiar, carpet-like plant that produces specialized gametes GAMETOPHYTE Fern More familiar, leafy plant with clusters of spore producing sacs (sori) Haploid plant body (prothallus) is size of a finger nail, produces both male and female parts SPOROPHYTE Conifer More familiar- like pine trees, produces male and female cones that produce spores Pollen grains are male gametophytes sperm, female gameotphytes are microscopic eggs SPOROPHYTE Review 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Label the parts of the diagram. Using the picture answer the following: • Where are spores created? • Name the haploid stage. • Which grows from the zygote? How are the antheridia and archegonia different? Similar? Meiosis begins which stage of plants? Fertilization begins which stage of plants? How are haploid spores created?