Bio 11 Plants Lesson 4 Nonvascular Plants Student Notes KEY
advertisement

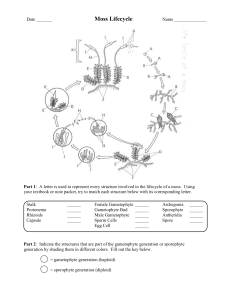
BIOLOGY 11 NONVASCULAR PLANTS General Characteristics ____________________ is the dominant generation Do not have true _______________, _______________ or _______________ Flagellated _______________ swim in a thin film of water to the egg zygote develops into a _______________ that is attached to the gametophyte shoot for _______________ Spores dispersed by the _______________ Low lying plants lack efficient means to transport _______________ very high Division Anthocerotophyta (Hornworts) Grow as a thin _______________ or ribbon-like _______________ 1 to 5 cm in diameter Chloroplasts fused with other organelles to for a _______________ manufactures and stores food (_______________ characteristic) Division Hepatophyta (Liverworts) 10 000 species Have a _______________ appearance Asexual reproduction is by _______________ on the surface of the thallus Gemmae are groups of cells that can become detached and grow into a ____________________ Sexual reproduction involves male and female ____________________ Division Bryophyta (Mosses) 12 000 species Most found in damp, shaded locations require _______________ for sexual reproduction Can reproduce asexually by ____________________ Sporophyte is dependant upon the more conspicuous ____________________; that means it is the gametophyte generation that ____________________ and the sporophyte generation draws its nourishment from the gametophyte generation Moss Life Cycle Also called a capsule Adaptations & Uses of Nonvascular Plants Able to colonize bare _______________ where they help to break down that rock into _______________ Dead mosses in bogs (ex: Sphagnum moss) do not decay called _______________ or _______________ moss Used in gardens to improve _________________________ capacity of soils