Plants - Warren County Schools
advertisement

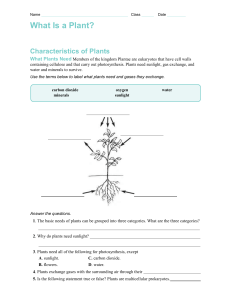
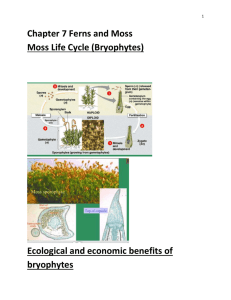
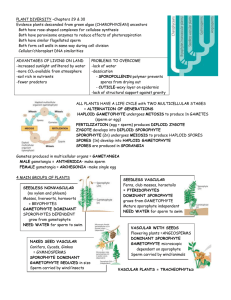
Plant Diversity Land Plants Evolved from Green Algae Occurred 500 million years ago Plants have enabled the life of other organisms on land Supply oxygen & provider of energy Evolutionary Evidence 1) Produce cellulose for cell walls in the same fashion 2) The peroxisomes have enzymes that reduce the effects of photorespiration 3) Sperm structure is related 4) Produce cell plates the same way 5) Genetic similarities Alteration of Generation 2 stages: 1) Gametophyte 2) Sporophyte In gametophyte stage: Gametes are produced Egg & sperm fuse to form a diploid zygote (sporophyte) Divides mitotically Sporophyte produces spores by meiosis The zygote develops within the tissues of the female Provides nutrients Referred to as embryophytes Anatomy Females = archegonia (single egg produced) Males = antheridia (many sperm produced) Moss Life Cycle Nonvascular (no xylem or phloem) Life cycle dominated by gametophytes Ferns & Seedless Vascular Plants First to grow tall Require water for fertilization Dominated by the sporophyte stage Seeded Plants 5 adaptations: 1) Reduced gametophytes - microscopic 2) Heterospory – 1 for male, 1 for female 3) Ovules & eggs – increases reproductive fitness 4) Pollen & sperm – Key adaptation to land 5) Seeds – protect the embryo Gymnosperms Naked seeds Usually found on cones Pines, spruces, firs, & redwoods Evolutionary Advances of the Pine Life Cycle 1) Ovulate cone bears ovules 2) Sporangia in pollen cone produce spores 3) Pollination 4) Haploid spore develops into female gametophyte to form eggs 5) Male gametophyte forms sperm 6) Zygote develops into embryo, ovule becomes seed 7) Seed germinates & embryo grows Angiosperms Seeded plants Contain flowers & fruit 250,000 species – 90% of all plants Flower: Sepals Petals Stamens – male reproduction Carpels – female reproduction Fruits Mature ovaries of the plant As seeds develop from ovules after fertilization, the wall of the ovary thickens to become fruit Fruits help disperse the seeds Evolutionary Advances of the Angiosperm Life Cycle 1) Haploid spores in anthers develop into pollen grains 2) Haploid spore in ovule develop into an egg 3) Pollination & growth of pollen tube 4) Zygote 5) Seed 6) Fruit 7) Seed germinates & embryo grows