Cell Membrane
advertisement

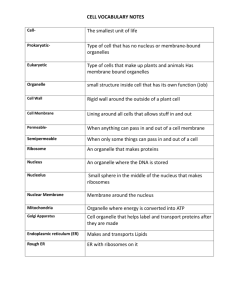
09-21-11 1) True/False: Chloroplast are found in plant cells. True 2) What is the nucleus’ main job? The “brain” of the cell—control the cells inner workings Agenda 1) Warm-Up 5 min 2) Cell Theory Notes II 25 min 3) Cell Organelle WS II 25 min Organism Organ Tissue Cell Biology Cell Organelle The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in the human body. It can be specialized to do many things. Just as the objective of Santa’s shop is to make toys the objective of a cell is to make proteins. What might the function of this cell be? The cell consists of a mass of cytoplasm surrounded by a cell membrane. The cytoplasm contains tiny structures called organelles. Each organelle performs a specific function for the cell. The Organelles Large organelle surrounded by a double layered nuclear membrane. It contains chromatin, made of DNA, which controls the cells activities. (Santa’s List) Chromatin Nucleus Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Nucleolus (Ribosome Factories) Found in nucleus. Dark area that is important in making ribosomes. Where amino acids are assembled to form proteins during protein synthesis. Located on the ER or floating in the cytoplasm. A network of passageways made from membranes that transports proteins around the cell. Rough ER has ribosomes. Smooth ER has no ribosomes. Endoplasmic Reticulum A series of saclike membranes where proteins are packaged, stored, and shipped off to their destinations. Rod-shaped organelle, covered by a double membrane, where cellular respiration takes place. Burn sugar (glucose) to make energy (ATP) Mitochondria Chloroplasts (plant cells only: Solar Power) Double membrane sacs that contain Chlorophyll. It can take light energy and convert it into sugar (glucose) by Photosynthesis. Vesicles(Sacs) filled with digestive enzymes and acid. They break down and recycle old organelles in the cell. Vesicles (Sacs) filled with enzymes that break down toxins in the cell . A net-like framework that gives the cell its shape. Composed of threadlike proteins called microfilaments, microtubules. Cytoskeleton Two small cylinders made of protein microtubules that help the cell divide during mitosis and meiosis. Short hair-like structures that wave and create currents to move fluids past a cell. Cilia on a Paramecium Long, hair-like structures that move a cell through a fluid. Flagella Semipermeable barrier that controls what enters and leaves the cell Cell Wall (plant cells only) Rigid layer of cellulose outside the membrane that supports plant cells. Cell Wall Vacuoles (water tower of cell) •Stores water and dissolved mineral cells. In plants there is one large central vacuole. Plant Cell Animal Cell The goal of Santa’s shop is to make The goal of a Cell is to toys make proteins DUE TODAY: • Organelle Color WS “It’s never to late to be what you might have been.” George Ellis DUE NEXT CLASS: • Cell WS