Learning notes
advertisement
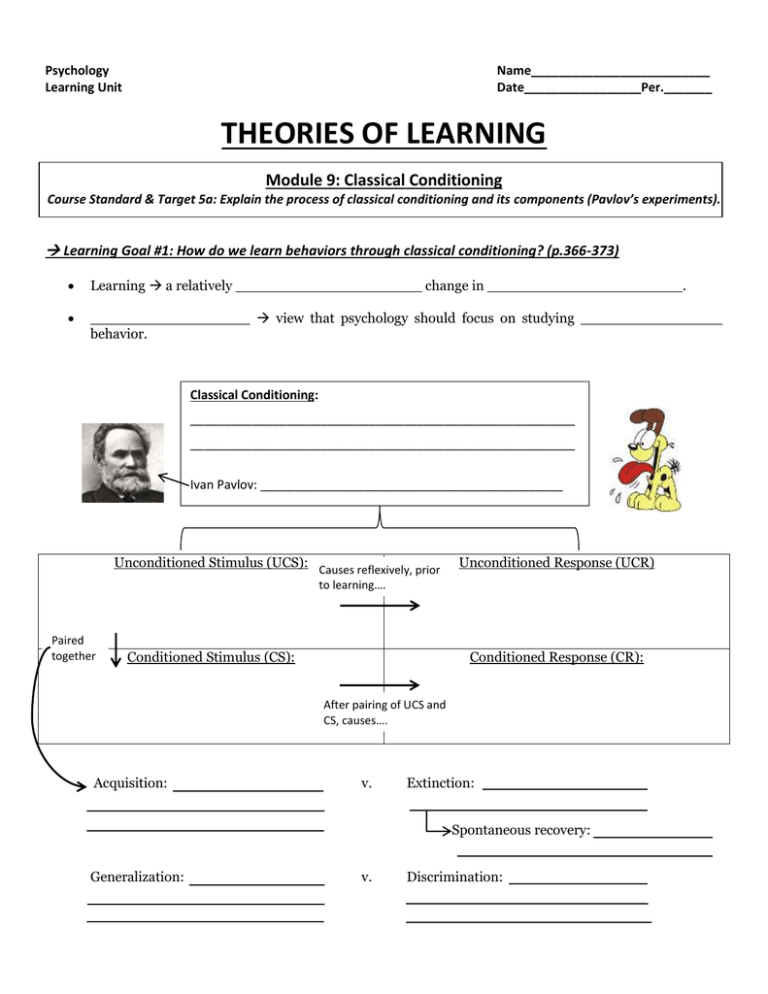
Psychology Learning Unit Name__________________________ Date_________________Per._______ THEORIES OF LEARNING Module 9: Classical Conditioning Course Standard & Target 5a: Explain the process of classical conditioning and its components (Pavlov’s experiments). Learning Goal #1: How do we learn behaviors through classical conditioning? (p.366-373) Learning a relatively _____________________ change in ______________________. __________________ view that psychology should focus on studying ________________ behavior. Classical Conditioning: ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Ivan Pavlov: ____________________________________________ Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): Causes reflexively, prior Unconditioned Response (UCR) to learning…. Paired together Conditioned Stimulus (CS): Conditioned Response (CR): After pairing of UCS and CS, causes…. Acquisition: v. Extinction: Spontaneous recovery: Generalization: v. Discrimination: Learning Goal #2 How did Watson demonstrate that fears can be learned through classical conditioning? (p.373-379) Generalization = Discrimination = John Watson’s “Little Albert” study What was the purpose? What was the US? UR? What was the CS? CR? *Higher-order conditioning: Learning Goal #3 What are some applications of classical conditioning in everyday life? (p.379-381) How does our thinking process influence classical conditioning? ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ How does biology influence classical conditioning? ________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Module 20: Operant Conditioning Course Standard & Target 5b: Describe the process and elements of operant conditioning (Skinner’s experiments). Learning Goal #4 How do we learn behaviors through operant conditioning? (p.386-393) Operant Conditioning: Reinforcement: Positive Reinforcement: Negative Reinforcement: Do we prefer immediate reinforcement or delayed reinforcement? WHY? Primary reinforcement: Secondary Reinforcement: Learning Goal #5 How does punishment influence behavior through operant conditioning? (p.393-395) Punishment: What are two outcomes or forms of punishment that can occur? 1) 2) What are some problems with punishment? Learning Goal #6 How can you vary operant conditioning to teach and maintain a behavior? (p.395-401) Shaping: Discrimination in Operant Conditioning: Continuous reinforcement: Partial reinforcement schedules: Fixed-interval schedule: Variable-interval schedule: Fixed-ratio schedule: Variable-ratio schedule: Learning Goal #7 How do our thinking processes and biology influence operant conditioning? (p.401-404) What is latent learning? What is a cognitive map? What happened when rats were not given reinforcement when going through the maze? What happened when reinforcement was later given upon completion of the maze? Overjustification effect: How does biology influence operant conditioning? Module 21: Observational Learning Course Standard & Target 5c: Evaluate the contexts in which observational occurs (Bandura’s experiments). Learning Goal #8 When and how do we learn by observation of others? (p.410-415) Observational learning: A ___________ is the person being observed; this person practices or repeats specific behaviors that the learner observes or models in a process called _________________. Albert Bandura’s study (identify the purpose, procedure, and results): Vicarious learning: We learn by observing others if what four conditions are met? 1) 2) 3) 4) What are mirror neurons and how do they influence learning? How do we learn anti-social behaviors through observational learning? How do we learn prosocial behaviors through observational learning? What does research show about media violence and real-life violence/aggression?








