©2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Financial Analysis
Financial statement analysis is
the process of applying
analytical tools to a company’s
financial statements to
understand the company’s
financial health and requires:
Financial
information
Standards
of
comparison
Analysis
tools
Standards of Comparison
Prior Year of • Often called
intracompany
the Same comparison
1
Company (horizontal analysis)
Benchmark • Often called
intercompany
2
Among
comparison (vertical
Competitors analysis)
• Industry benchmarks
3 Industry
can be obtained from
Standards financial websites.
Analysis Tools
Horizontal
1 Analysis
2
3
• comparison of a
company’s financial
results across time.
Vertical
Analysis
• comparison of
financial balances to
a base account from
the same company.
Ratio
Analysis
• comparison of
different balances
from the financial
statements.
Horizontal Analysis
Horizontal analysis is an analysis technique that calculates the
change in an account balance from one period to the next and
expresses that change in both dollar and percentage terms.
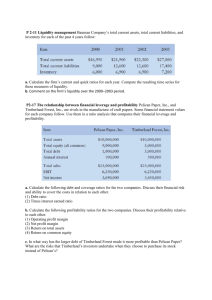
Balance Sheet – Horizontal – Best
Buy (2010)
Best Buy ($ in millions, except
per share amounts
2010
2009
$ Change
Current Assets:
Cash and cash equivalents
1,103
1,826
(723)
Receivables
2,348
2,020
328
Merchandise Inventories
5,897
5,486
411
Other current assets
1,125
1,234
(109)
Total Current Assets
10,473 10,566
(93)
$ Current
- $ Base
2,020 = (247)
Property
andYear
Equipment,
netYear = $2,348
3,823 – 4,070
Goodwill $ Base Year
2,454
2,452
2
$2,020
Other Assets
1,099
1,214
(115)
Total
Assets = $2,348 – 2,020 = $32817,489 18,302
(453)
$ Change
% Change
(39.6%)
16.2%
7.5%
(8.8%)
(0.9%)
(6.1%)
0.1%
(9.5%)
(2.5%)
16.2%
Vertical Analysis
Vertical analysis is an analysis technique that states each account
balance on a financial statement as a percentage of a base amount on
the statement.
Balance Sheet Vertical – Best Buy (2010)
Asset accounts are stated as a percentage of Total Assets
(set at 100%). For example, on 31/12/2010, Receivables is
13.2% of Total Assets (calculated as $2,348 ÷ $17,849).
Profitability Analysis
Profitability Ratios – importance of Profitability
• Indicates the ability to
make required
Creditors principal and interest
payments.
• Indicates related stock
Stockholders price increases or
dividends paid.
Managers
• Indicates potential for
bonuses and incentive
plans linked to
performance.
Liquidity Analysis
Liquidity ratios assess the ability of a company
to meet its immediate or short-term financial
obligations. Failing to do so can result in additional
expenses and, ultimately, bankruptcy.
Liquidity Ratios
Solvency Ratios
Solvency focuses on capital structure and
assesses the extent of borrowing needed.
• Solvency refers
to a company’s
ability to satisfy
its long-term
obligations.
Debt to
Assets
Ratio
Times
Interest
Earned
Debt to
Equity
-
Solvency Analysis
DuPont Analysis
A DuPont analysis
provides insight into how a
company’s return on
equity was generated by
decomposing the return
into three components:
•operating efficiency,
•asset effectiveness, and
•capital structure.
DuPont Calculation
The higher the ratio, the more
efficient a company is in turning
sales into profits.
The higher the ratio, the more
effective a company is in generating
sales given its assets.
The higher the ratio, the more a
company is financing its assets with
debt rather than equity (riskier).
This is the leverage multiplier.
Benefit of DuPont Analysis
One of the main benefits of a DuPont
analysis is the ability to ask what-if
questions.
???
What if Best Buy was able to
squeeze out another $.02 of
profit on each dollar of sales?
How would that affect the
return to owners?
Answer: 2008 return
would increase to 0.407 (0.042
X 2.84 X 3.41).
What if the market for electronics
took a significant downturn and
Best Buy was only able to generate
sales of 1.5 times assets on hand?
Would that significantly affect the
return to investors? Answer: 2008
return would fall almost in half to
0.113 (0.022 X 1.50 X 3.41).
End of Chapter 12