Parts - share1
advertisement

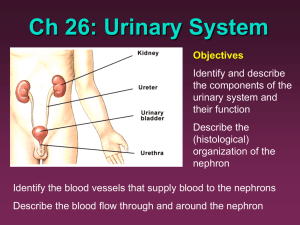
The Wonderful and Great Kidney By: Jamal McBroom Before learning about parts of Kidney lets learn what it is for. Excretion- The removal from the body of the waste products through Metabolic pathways Examples- Urinating, Defecation, Kidney also produces urine and excretes ammonium, urea, and are responsible for reabsorption of water, glucose, and amino acids. Bean shaped Reddish brown color Located on either side of the vertebral column just below the diaphragm in lower back where they are partially protected by the rib cage. Right kidney is slightly lower than left kidney Each kidney (left and right) is connected to a Ureter Is a duct that takes urine from kidney and transports it to the Urinary bladder. Urine is stored there until it is voided by body through the single Urethra(tubular structure that receives urine from bladder). Males urethra passes through penis, females opening of the urethra is ventral to that of the vagina It is the outer most region of the kidney and has a somewhat granular appearance. It also contains blood vessels and cortical collecting duct. Ultrafiltration occurs here as well Consists of six to ten cone-shaped sections called renal pyramids that lie on the inner side of the renal cortex. It is the innermost part of the kidney Nephrons are located here Hollow Chamber Urine is collected in here Urine is then carried to the urinary bladder by the Ureter. Also called Renal calculus Is a hard granule of phosphate, calcium, protein, or uric acid that forms in the renal pelvis. Many pass unnoticed Larger ones and jagged stones though can block renal pelvis or ureter causing intense pain and damage Each kidney is composed of over 1 million tiny tubules called nephrons. Nephrons produce urine in a kidney. Loceted primarily in renal cortex but some are located in renal medulla Is made of several parts Blind end of a Nephron pushed on itself to form a cuplike structure called glomerular capsule or Bowman’s capsule Outer layer is composed of squamous epithelial cells Inner layer composed of specialized cells that allow easy passage of molecules From glomerular capsule is the proximal convoluted tubule. It is lined by cells with many mitochondria and tightly packed microvilli. Then, Simple squamous epithelium appears in the loop of the nephron (loop of henle) Loop has descending and ascending limb. Its not over yet… More parts Next, Distal convoluted tubule. Several Distal convoluted tubule enter one collecting duct. Collecting duct transports urine down through the renal medulla and delivers it to the renal pelvis. Loop of Nephron and the collecting duct give the pyramids of the renal medulla their striped apperance Each Neprhon has it’s own blood supply. Renal Artery branches into numerous small arteries, which then branch into arterioles, one for each Nephron. Each arteriole (called an afferent arteriole), divides to form a capillary bed, the Glomerulus which is surrounded by the glomerular capsule. Glomerulus drains into an efferent arteriole, which subsequently branches into a second capillary bed around the tubular parts of the nephron. These capillaries are called peritubular capillaries. These capillaries lead to venules that join to form veins leading to the renal vein, a vessel that enters the inferior vena cava