Document
advertisement

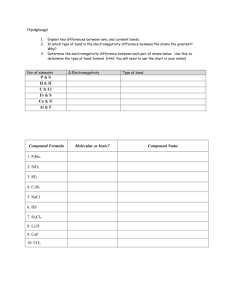
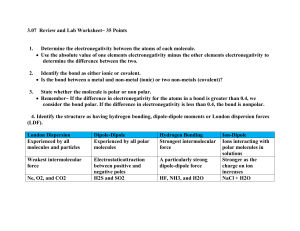
CHEMISTRY January 7, 2015 CHEMICAL BONDS SCIENCE STARTER • Log onto www.coursesites.com • 5 MINUTES ANNOUNCEMENT • LAB ON MONDAY • FINAL EXAM ON JANUARY 16 AND 20 • NO HOMEWORK ACCEPTED AFTER JANUARY 22, 2015 REVIEW • ELECTRONEGATIVITY IS THE ATTRACTION FOR ELECTRONS • ELECTRONEGATIVITY INCREASES ACROSS A PERIOD • ELECTRONEGATIVITY DECREASES DOWN A GROUP • ELECTRONEGATIVITY DOES NOT EXIST FOR NOBLE GASES ELECTRONEGATIVITY DIFFERENCE • Electronegativity differences determine the type of bonding that may occur. COVALENT BONDING • Usually, if the electronegativity between 2 atoms is less than 1.7 than the bond is a covalent bond. • For example: In CO2: – C has an electronegativity value of 2.6 and O has an electronegativity of 3.4. – The electronegativity difference is 3.4 - 2.6 which is 0.8. – Since 0.8 is less than 1.7, the bond is a covalent bond. IONIC BONDING • Generally, if the electronegativity difference is greater than 2.0, then the bond is an ionic bond. • For example: NaCl – Electronegativity value of Na = 0.9 – Electronegativity value of Cl = 3.2 – Electronegativity difference (high number - low number) = 3.2 - 0.9 = 2.3 – Since 2.3 is greater than 2.0, the bond is therefore an ionic bond IONIC OR COVALENT • If the electronegativity difference is between 1.7 and 2.0, then – if one of the atoms is classified as a metal, then an ionic bond exist – if both atoms are nonmetals, then a covalent bond exists. POLARITY • Definition - a separation of charge • Occurs in covalent bonds POLARITY DETERMINATION • Polarity is determined based on the electronegativity of the atom. • For example: HCl – Electronegativity value of H = 2.2 – Electronegativity value of Cl = 3.2 – Even though the pair of electrons are shared between H and Cl, the electrons are positioned closer to Cl than H because Cl has the higher electronegativity value. NONPOLAR • Nonpolar occurs when the electronegativity differences between the two atoms in a compound is less than 0.5. • Example : • F2 - each F atom has an electronegativity value of 4.0. So, the electronegativity difference is 0. As a result, F2 is nonpolar. Hence, F2 has a nonpolar covalent bond • CH4 – – – – Electronegativity value of C = 2.6 Electronegativity value of H = 2.2 Electronegativity difference = 2.6 - 2.2 = 0.4. Thus, CH4 is nonpolar and has a nonpolar covalent bond. DIPOLE • Definition of Dipole: difference in charge between the two atoms caused by a shift in electron density in the bond. DIPOLE • Bond polarity is measured by its dipole moment. • In other words, the electron density around the higher electronegative atom results in giving the atom a partial negative charge (designated as d-). The less electronegative atom has some of its electron density taken away giving it a partial positive charge (d+). • Example: HCl – Cl has the higher electronegativity value so Cl will have a greater electron density. As a result, Cl will have a partial negative charge while H will have a partial positive charge. DIPOLE DIAGRAM • Dipole moment for a polar covalent bond can be shown as in the example below. • For HCl, Cl has higher electron density. Thus, more of the electrons are positioned closer to the Cl. To illustrate this, draw the dipole arro • w as shown below. REMEMBER • The greater the electronegativity difference, the more polar the bond. • Example: – HCl vs. HF – HF has a greater electronegativity difference. Thus, HF will be more polar.