Rivers_description
advertisement

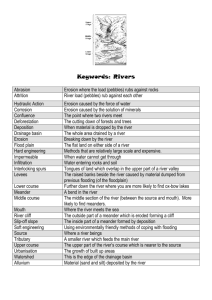
Rivers KEY WORDS AND TERMS: Erosion Transport Deposition River basin Tributary Source Mouth Confluence Meander Flood plain Oxbox lake Waterfall Upper, middle and lower course How do rivers alter the landscape? Moving water has energy. The faster it moves the more energy it has. Rivers have energy, and they can wear things down, move things and carry them along as they flow. We call this the work of the river. The faster a river flows, the more energy it has and the more work it can do. Streams and rivers alter the landscape by redistributing material through the three processes of erosion, transportation and deposition, The river erodes mud, soil and other material from places, transports it down stream and deposits somewhere else. This changes the shape of the landscape. Creating meanders and oxbow lake In this picture, soil and mud is being eroded from various points on the bank. It’s being transported in the direction of the white arrows and deposited downstream (the sandy patches). This is changing the course of the river This picture shows the same river many many years later, the erosion and deposition have created such a deep meander that it has nearly formed a circle Eventually, the river erodes so much that it cuts off part of the meander and creates an oxbow lake Write the correct tem next to its definition. Then write its translation. Term Definition Translation of term is a small stream or body of water that flows into a larger body of water. the landform occurring at the river mouth, where the river meets the sea. where a river joins another river basically the end point of the river, where it flows into either the sea, a lake, or a larger river bends or turns in watercourse or river. the land that water flows across or under on its way to a river. the original point from which the river flows a crescent-shaped lake lying alongside a winding river flat and dry land that's alongside a stream, river or lake and ends up covered by water during a flood The Course of a River A river flows through a piece of land called a ‘River Basin’. The river basin is all the land that is drained of water by a river and the streams that flow into it. Below are some of the features you will find in a river basin. This is the Long Profile of a river – in 3 sections which each have their own features. UPPER COURSE – The course is a steep slope The start of a river is its source, which could be melting snow or ice or spring (water bubbling out of the ground). The source of a river is usually in upland areas such as mountains or hills. Small streams flow downhill from the source and join other streams until they form the main river of a river system. The streams are the tributaries of the main river. In upland areas, water in streams and rivers is very fast-flowing, cutting and eroding the land to form valleys, and features such as waterfalls. MIDDLE COURSE – The course is less sloping than before Where two streams join, or a stream joins a river, this is called a confluence. When the ground becomes flatter, the river slows down and starts to swing from side to side, this is called meandering. The large bends it makes are called meanders. Sometimes, these large bends become cut off from the main river, and ox bow lakes are formed. LOWER COURSE – The course is slightly sloping or practically flat The river widens and starts to cross a flood plain. This is a wide, flat area either side of the river. It is used for flooding. The end of a river, where it flows into the sea or sometimes a lake, is called its mouth. The area where the river meets the sea (the tidal part of the river) is called the estuary. A delta may be formed near the mouth of the river, if the land is very flat and the river is very slow-flowing and carrying a lot of sediment. Comprehension Questions 1. What is the name for the beginning of the river? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. Where does the water come from at the start of a river – name 2 places? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3. Put these features in the order you’d expect to find them in a river: SOURCE ………………………… MOUTH FLOOD PLAIN WATERFALL MEANDER ………..……………… ………………………… ……………………………. …………………………. 4. Match the letter to the feature Mouth Source Gorge Meander Waterfall Tributary 5. A confluence is a a) A small river that feeds into a big river b) The join of two rivers c) A type of valley formed by erosion 6. Circle the features that can happen at the end of a river: Delta Meander Plunge pool Mouth Tributary Lake Estuary Confluence