PP review questions!
advertisement

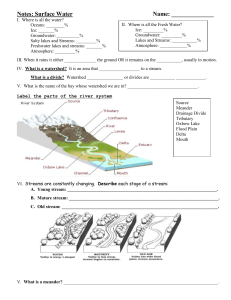
Streams & Rivers Q. What is runoff? A. Water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground. Wetlands Q. Why are the Everglades worth preserving? A. Many endangered species live there. Name That Word! Q. The area of soil in Q. An underground which the pores layer of rock or are totally filled sediment that with water. holds water. A. saturated zone A. aquifer Streams & Rivers Q. Nature of the ground surface, rate of rainfall, slope of the land (flat or hilly)… what do these factors determine? A. Whether water soaks into the ground or flows over as runoff. Groundwater Q. Where can you find groundwater? Be specific. A. In the saturated zone, permeable layer, or at the water table Name That Word Q. A ridge of land Q. The land area that separates one that supplies watershed from water to a river another. system. A. divide A. watershed Name That Word Q. A smaller stream or river that feeds into a main river. A. tributary Q. A river and all of its tributaries. A. river system Name That Process Q. Process by which soil and fragments of rock are deposited in a new location. A. deposition Name That Word! Q. Materials that allow water to easily pass through them. Q. What are two ways that water comes to the surface naturally? A. springs & geysers A. permeable Name That Section! Q. Which Aquifer, A or B, is more likely to produce an artesian well? A. B Streams & Rivers Q. Slope, volume of water, and shape of channel. A. Factors affecting the speed of a river. Name That Section of the River! Q. The many small Q. The river streams that meanders come together at through this flat the source of the section of land. river. A. headwaters A. flood plain Name That Word! Q. The top of the saturated zone. A. water table Q. Materials that water cannot pass through easily. A. impermeable Name That Word Q. What is shown in the picture? A. oxbow lake Name That Section! Q. What is located at letter A? A. headwaters Name That Process Q. Process by which fragments of soil and rock are broken off from the ground surface and carried away. A. erosion Name That Section! Q. What is located at letter D? A. tributary Stream and Rivers Q. If there is an increase in the amount of water in a river, how does this change the speed of the river? A. The river will flow faster. Name That Section! Q. What is located at letter E? At F? A. oxbow lake and meander Name That Word Q. What happens when the volume of water in a river increases so much that the river overflows its channels? A. flood Groundwater Q. If you would like to obtain groundwater when you drill a well, where should you drill to? A. into an aquifer or below the water table Name That Word! Q. A long ridge Q. A barrier across formed by deposits a river that may of sediments redirect the flow alongside a river of a river to other channel. channels or store the water in an artificial lake. A. levee A. dam Name That Word Q. An area of land covered with a shallow layer of water during some or all of the year. A. wetland Name That Word! Q. New water that enters an aquifer from the surface. A. recharge Q. A well in which water rises because of pressure within the aquifer. A. artesian well Rivers and Streams Q. How is an oxbow lake related to a meander? A. When the river breaks through the ends of a meander, the cut off body of water that remains is the crescent shaped oxbow lake. Wetlands Q. How do wetlands help control flooding? A. By absorbing extra runoff from heavy rains.