Evidence of Evolution
advertisement

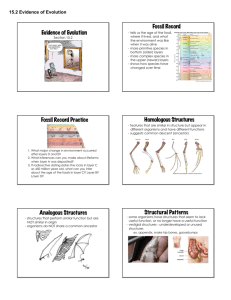
Evidence of Evolution Part II The study of living organisms reveals secrets of ancestry Theory of Evolution All life on Earth descended from a common ancestor Life originated as a simple form, and became more diverse and complex over time Evidence in Organisms “Evolution proceeds by modifications of organisms which already exist” Evidence in Organisms I. Homologous Structures * Definition * Examples (Can you give detailed descriptions of homologous bones?) I. Homologous Structures Homologous Structures Evidence in Organisms II. Similarities in Embryonic Development • All animals: cleavage, morula, blastula, layering after blastula (gastrula) • All Vertebrates: What did you observe? Similarities in Embryonic Development The limbs of all tetrapods develop from limb buds in similar ways (see below). Similarities in Embryonic Development How evidence of Evolution? Evidence in Organisms III. Vestigial Structures • definition: • Examples: • • • • Eyes on blind cavefish Human coccyx (tailbone) Femurs on pythons, whales Wings on a Kiwi bird • How evidence of evolution? Evidence in Organisms What evidence suggests that life forms today share a common ancestor? Animal life: – Bone homology – Embryological comparisons All life: – Biochemical evidence DNA/Proteins Energy reactions Question Why do scientists believe that all life on Earth descended from a SINGLE common ancestor? Why don’t we think that several “trees of life” exist? (One for vertebrates, one for invertebrates, one for plants, one for fungi, etc?) ANSWER D –N A II. Evidence in Organisms Evidence that Life forms change over time Vestigial Structures – Definition – Examples Artificial Selection Peppered Moth