Evidence of Evolution Fossil Record Fossil Record Practice
advertisement

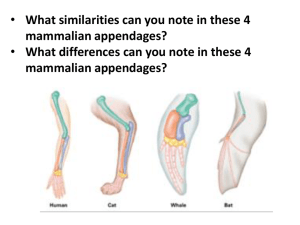
15.2 Evidence of Evolution Evidence of Evolution Section 15.2 Fossil Record Practice Fossil Record · tells us the age of the fossil, where it lived, and what the environment was like when it was alive · more primitive species in bottom (older) layers · more complex species in the upper (newer) layers · shows how species have changed over time Homologous Structures · features that are similar in structure but appear in different organisms and have different functions · suggests common descent (ancestor) F E D C B A 1. What major change in environment occurred after layers D and E? 2. What inferences can you make about lifeforms when layer A was deposited? 3. If radioactive dating dates the rocks in layer C as 450 million years old, what can you infer about the age of the fossils in layer C? Layer B? Layer D? Analogous Structures · structures that perform similar function but are NOT similar in origin · organisms do NOT share a common ancestor Structural Patterns · some organisms have structures that seem to lack useful function, or no longer have a useful function · vestigial structures - underdeveloped or unused structures ex. appendix, snake hip bones, goosebumps 15.2 Evidence of Evolution 1 Which type of structure suggests a common ancestor? 2 Fins of a fish and flippers of whale look similar, but evolved separately. They are an example of A analogous B vestigial A analogous structures C homologous B vestigial structures D reciprocal C homologous structures D reciprocal structures 3 Whale hip bones are an example of A analogous structures B vestigial structures C homologous structures D reciprocal structures Embryology · embryos look similar in early development · similar features in very different organisms suggests evolution from a distant common ancestor ex. gill slits DNA and Macromolecules · DNA analysis - the more related two organisms are the more DNA they share in common · related organisms have proteins with similar amino acid sequences...similar DNA human hemoglobin and gorilla hemoglobin vary by 1 amino acid Geography · island species resemble species on nearest mainland · species move or migrate · develop adaptations to their new environment ex. Darwin's finches 15.2 Evidence of Evolution Adaptation · a feature that allows an organism to better survive in its environment · can lead to genetic change in a population over time · increases an organism's fitness ex. camouflage, mimicry 4 MATA: An adaptation... A allows an organism to better survive in its environment B causes mutations C D Fitness · ability to survive and reproduce can lead to genetic changes over time increases fitness 5 MATA: Which of the following suggests a common ancestor? A embryology B homologous structures C similar proteins D analogous structures