Proteins: Structure, Function, and Amino Acids Study Guide
advertisement

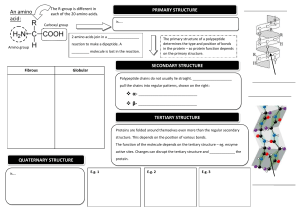
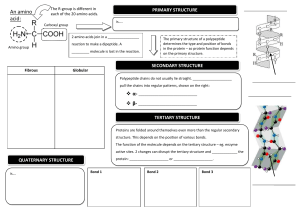
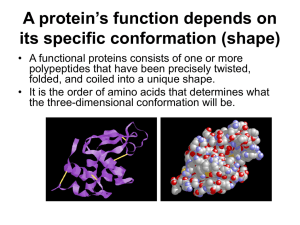
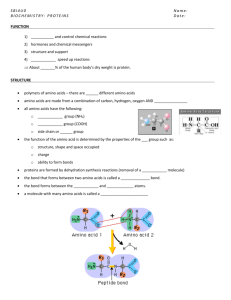
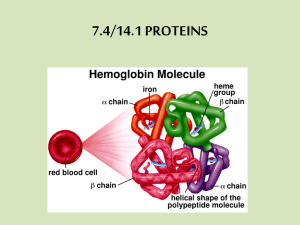
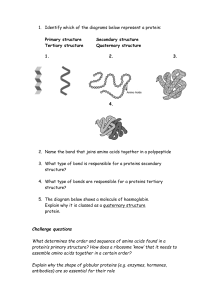
PROTEINS type Function Example Enzymatic Catalyse chemical reactions Digestive enzymes Defensive Protect against disease. Antibodies Storage Storage of amino acids Casein, Ovalbumin Transport Transport of substances Haemoglobin Hormonal Coordination of an organism’s activities Receptor Response to chemical stimuli Contractile & motor Structural Insulin Receptors in nerve cells Movement of cilia, flagella, muscles Actin, myosin Provide support & framework Keratin, elastin, collagen Amino acids Amino group + carboxyl group + hydrogen atom + R group/side chain (differentiate) Non polar – hydrophobic (methionine, tryptophan, glycine) Polar – hydrophilic (serine, tyrosine, cysteine) Negative – acidic (aspartic acid, glutamic acid) Positive – basic (lysine, arginine, histidine) Peptide bond – covalent bond from a dehydration reaction between carboxyl group of one protein and amino group of the other protein Interactions in proteins – • • • • Hydrogen bonds – between strong polar groups, weak, folding & coiling of polypeptide chains, break easily & reform Ionic bonds – between strongly positive & negative amino acids, strong but uncommon Weak hydrophobic reactions – weak, occur between nonpolar R groups Disulphide bonds – strong but rare, hold the folded polypeptide chain together, between two cysteine molecules Structures – • • • • Primary – sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain Secondary – polypeptide chain forms localized 3D structures held together by H bonds (Alpha helix & Beta pleats) Tertiary – overall 3D shape of proteins held together by hydrophobic, disulfide, ionic & H bonds (globular proteins) Quaternary – two or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecule (haemoglobin, collagen) Protein folding – functional proteins are folded, twisted & coiled with the aid of chaperonins, chaperonins keep the polypeptide segregated from disruptive chemicals in the cytoplasm while it spontaneously folds. Denaturation – the bonds & interactions in a protein are destroyed, causing it to unravel & lose its natural shape, due to alterations in its environment. Denaturation causes – chemicals that disrupt the bonds, excessive heat, transfer from aqueous medium to nonpolar solvent Reversible – warming milk, Irreversible – frying egg