Water - Hepler Science
advertisement

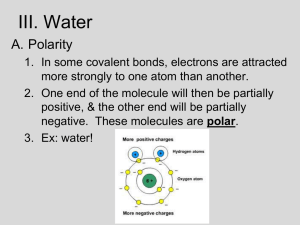
Water Probably the most important compound in organisms water makes up 70 - 95% of most organisms allows molecules to move and interact with one another transports materials in plants and animals (blood, plant sap) Water is polar Polar molecule - molecule with an unequal distribution of charge has a negative end and a positive end Charged ends of water molecules are attracted to each other the attraction of opposite charges of hydrogen and oxygen atoms forms a weak bond - hydrogen bond Water is cohesive Water is held together by hydrogen bonds drop holds together water being soaked up pulls more water up with it Water resists temperature change water requires high heat to increase its temperature Why is this important to cells? Water helps cells maintain a steady environment (homeostasis) Mixtures • Mixture - combination of substances in which each substance retains its own properties • ex. Salt and pepper • Solution - a mixture in which one or more substances is dissolved in another substance • evenly distributed • ex. Sugar dissolved in water • Solute - substance that is dissolved • ex. Sugar (Kool-Aid) • Solvent - substance in which the solute is dissolved • ex. water Acids and bases • pH - measure of how acidic or basic a solution is • pH ranges from 0(most acidic) to 14 (most basic) • 7 is neutral • Acid - substance that forms + hydrogen ions (H ) in water • Hydrochloride (HCl) forms + H and Cl ions in water • hydrochloric acid • Acids have a pH below 7 • Base - substance that forms hydroxide ions (OH ) in water • Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) + forms Na and OH ions in water • Bases have a pH above 7 Acid or base Ammonia (Windex) Base (pH 11) Vinegar Acid (pH 3) Egg Base (pH 8) Tomato Acid (pH 4) Milk Acid (pH 6) Water (pure) Neutral (pH 7)