Principles
of
Corporate
Finance
Chapter 28
Managing
International Risks
Ninth Edition
Slides by
Matthew Will
McGraw Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
28- 2
Topics Covered
Foreign Exchange Markets
Some Basic Relationships
Hedging Currency Risk
Exchange Risk and International Investment
Decisions
Political Risk
28- 3
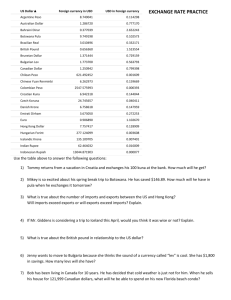
Exchange Rates
April 16, 2007
Forward Rate *
Spot Rate * 1 Month 3 Months 1 Year
Europe
EMU (euro)
Norway (krone)
Sweden (krona)
Switzerland (franc)
United Kingdom (pound)
Americas:
Canada (dollar)
Mexico (peso)
Pacific/ Africa:
Hong Kong (dollar)
Japan (yen)
South Africa (rand)
South Korea (won)
1.3549
5.9566
6.8028
1.213
1.9901
1.3565
5.9514
6.7915
1.2099
1.99
1.3595
5.9436
6.7705
1.2038
1.9892
1.3689
5.9377
6.7041
1.1812
1.9811
1.1309
10.9892
1.1298
11.0055
1.1278
11.0408
1.1208
11.2274
7.8129
1119.795
7.0942
903.55
7.8071
119.33
7.116
929.85
7.7916
118.397
7.162
928.45
7.7429
114.571
7.3807
923.65
28- 4
Foreign Exchange Markets
Exchange Rate - Amount of one currency needed
to purchase one unit of another.
Spot Rate of Exchange - Exchange rate for an
immediate transaction.
Forward Exchange Rate - Exchange rate for a
forward transaction.
28- 5
Foreign Exchange Markets
Forward Premiums and Forward Discounts
Example - The Peso spot price is 10.9892 peso per
dollar and the 3 month forward rate is 11.0408 Peso
per dollar, what is the premium and discount
relationship?
28- 6
Foreign Exchange Markets
Forward Premiums and Forward Discounts
Example - The Peso spot price is 10.9892 peso per
dollar and the 3 month forward rate is 11.0408 Peso
per dollar, what is the premium and discount
relationship?
Spot Price
T
- 1 = Premium or (-Discount )
Forward Price
4
10.9892
- 1 = -1.90%
11.0408
28- 7
Foreign Exchange Markets
Forward Premiums and Forward Discounts
Example - The Peso spot price is 10.9892 peso per dollar and
the 3 month forward rate is 11.0408 Peso per dollar, what
is the premium and discount relationship?
Answer - The dollar is selling at a 1.90% premium, relative
to the peso. The peso is selling at a 1.90% discount,
relative to the dollar.
28- 8
Exchange Rates
Example
Swiss franc spot price is SF 1.4457 per $1
Swiss franc 6 mt forward price is SF1.4282 per $1
The franc is selling at a Forward Premium
The Dollar is selling at a Forward Discount
This means that the market expects the dollar to get weaker,
relative to the franc
Example (premium? discount?)
The Japanese Yen spot price is 101.18 per $1
The Japanese 6mt fwd price is 103.52 per $1
28- 9
Exchange Rates
Example
What is the franc premium (annualized)?
franc Premium = 2 x ( 1.4457 - 1.4282) = 2.45%
1.4282
Dollar Discount = 2.45%
Example
What is the Yen discount (annualized)?
Yen Discount = 2 x ( 103.52 - 101.18) = 4.26%
103.52
Dollar Premium = 4.26%
28- 10
Exchange Rate Relationships
Basic Relationships
1 + rforeign
1 + r$
1 + i foreign
equals
equals
equals
E(sforeign / $)
f foreign / $
S foreign / $
1 + i$
equals
S foreign / $
28- 11
Exchange Rate Relationships
1) Interest Rate Parity Theory
1 + rforeign
1 + r$
=
f foreign / $
S foreign / $
The ratio between the risk free interest rates in two
different countries is equal to the ratio between the
forward and spot exchange rates.
28- 12
Exchange Rate Relationships
Example - You have the opportunity to invest
$1,000,000 for one year. All other things being
equal, you have the opportunity to obtain a 1 year
Mexican bond (in peso) @ 7.35 % or a 1 year US
bond (in dollars) @ 5.05%. The spot rate is
10.9892 peso:$1 The 1 year forward rate is 11.2274
peso:$1
Which bond will you prefer and why?
Ignore transaction costs
28- 13
Exchange Rate Relationships
Example - You have the opportunity to invest $1,000,000 for one year. All
other things being equal, you have the opportunity to obtain a 1 year Mexican
bond (in peso) @ 7.35 % or a 1 year US bond (in dollars) @ 5.05%. The
spot rate is 10.9892 peso:$1 The 1 year forward rate is 11.2274 peso:$1
Which bond will you prefer and why? Ignore transaction costs
Value of US bond = $1,000,000 x 1.0122 = $1,050,500
Value of Mexican bond = $1,000,000 x 10.9892 = 10,989,200 peso exchange
10,989,200 peso x 1.0735 = 11,796,906 peso
bond pmt
11,796,906 peso / 11.2274= $1,050,725
exchange
28- 14
Exchange Rate Relationships
2) Expectations Theory of Exchange Rates
f foreign / $
S foreign / $
=
E(sforeign / $)
S foreign / $
Theory that the expected spot exchange rate
equals the forward rate.
28- 15
Exchange Rate Relationships
3) Purchasing Power Parity
1 + i foreign
1 + i$
=
E(sforeign / $)
S foreign / $
The expected change in the spot rate equals
the expected difference in inflation between
the two countries.
28- 16
Exchange Rate Relationships
Example - If inflation in the US is forecasted at
2.5% this year and Mexico is forecasted at 4.5%,
what do we know about the expected spot rate?
Given a spot rate of 10.9892 peso:$1
1 + i foreign
1 + i$
=
E(sforeign/$)
S foreign/$
1 .045 E(sforeign/$ )
=
1 + .025 10.9892
solve for Es
Es = 11.204
28- 17
Exchange Rate Relationships
4) International Fisher effect
1 + rforeign
1 + r$
=
1 + i foreign
1 + i$
The expected difference in inflation rates
equals the difference in current interest rates.
Also called common real interest rates
28- 18
Exchange Rate Relationships
Example - The real interest rate in each country is
about the same
r (real )
1 + rforeign
1 + i foreign
1.0735
=
- 1 = .027
1.045
1 + r$ 1.0505
r (real )
=
- 1 = .025
1 + i $ 1.025
28- 19
Exchange Rates
Another Example
You are doing a project in Switzerland which has an initial cost of $100,000. All
other things being equal, you have the opportunity to obtain a 1 year Swiss loan (in
francs) @ 8.0% or a 1 year US loan (in dollars) @ 10%. The spot rate is 1.4457sf:$1
The 1 year forward rate is 1.4194sf:$1
Which loan will you prefer and why? Ignore transaction costs
Cost of US loan = $100,000 x 1.10 = $110,000
Cost of Swiss Loan = $100,000 x 1.4457 = 144,570 sf
144,570 sf x 1.08 = 156,135 sf
156,135 sf / 1.4194 = $110,000
If the two loans created a different result, arbitrage exists!
exchange
loan pmt
exchange
28- 20
Exchange Rates
Swiss Example
Given a spot rate of sf:$
Given a 1yr fwd rate of
1.4457:$1
1.4194:$1
If inflation in the US is forecasted at 4.5% this year, what
do we know about the forecasted inflation rate in
Switzerland?
E (Sf/$) = E ( 1 + if )
Sf/$
E ( 1 + i$ )
1.4194 = E( 1 + i)
1.4457
1 + .045
solve for i
i = .026 or 2.6%
28- 21
Exchange Rates
Swiss Example
In the previous examples, show the equilibrium of
interest rates and inflation rates
1 + rf = 1.08 = .9818
1 + r$
1.10
E ( 1 + if ) = 1.026 = .9818
E ( 1 + i$ )
1.045
1/30/2006
1/30/2004
1/30/2002
1/30/2000
1/30/1998
1/30/1996
1/30/1994
1/30/1992
1/30/1990
1/30/1988
1/30/1986
1/30/1984
1/30/1982
1/30/1980
1/30/1978
1/30/1976
1/30/1974
1/30/1972
1/30/1970
Percent error
28- 22
Forward Rate vs. Actual Spot Rate
Percent error in the one month forward rate for Swiss Franc per US $
compared to actual spot rate
25.0
20.0
15.0
10.0
5.0
0.0
-5.0
-10.0
-15.0
-20.0
28- 23
International Prices
The Big Mac Index – The price of a Big Mac in
different countries (Feb 1, 2007)
Country
Canada
China
Denmark
Euro area
Japan
Mexico
Local Price Converted
to U.S. Dollars
Country
Local Price Converted
to U.S. Dollars
3.08
1.41
4.84
3.82
2.31
2.66
Philippines
Russia
South Africa
Switzerland
United Kingdom
United States
1.74
1.85
2.14
5.05
3.9
3.22
28- 24
Purchasing Power & Exchange Rates
28- 25
Exchange Rates
Nominal versus Real Exchange Rates
U.S. Dollar /
UK (in log
scale)
28- 26
Exchange Rates
Nominal versus Real Exchange Rates
U.S. Dollar /
France (in
log scale)
28- 27
Exchange Rates
Nominal versus Real Exchange Rates
U.S. Dollar /
Italy (in log
scale)
28- 28
Interest Rates and Inflation
Countries with the highest interest rates generally have the highest
inflation rates. In this diagram each of the 55 points represents a
different country.
28- 29
Auto Industry Data 2003
28- 30
Exchange Rate Risk
Example - Honda builds a new car in Japan for a cost +
profit of 1,715,000 yen. At an exchange rate of 120.700Y:$1
the car sells for $14,209 in Indianapolis. If the dollar rises
in value, against the yen, to an exchange rate of 134Y:$1,
what will be the price of the car?
1,715,000 = $12,799
134
Conversely, if the yen is trading at a
forward discount, Japan will
experience a decrease in
purchasing power.
28- 31
Exchange Rate Risk
Example - Harley Davidson builds a motorcycle for a
cost plus profit of $12,000. At an exchange rate of
120.700Y:$1, the motorcycle sells for 1,448,400 yen in
Japan. If the dollar rises in value and the exchange rate is
134Y:$1, what will the motorcycle cost in Japan?
$12,000 x 134 = 1,608,000 yen
28- 32
Exchange Rate Risk
Currency Risk can be reduced by using
various financial instruments
Currency forward contracts, futures
contracts, and even options on these
contracts are available to control the risk
28- 33
Capital Budgeting
Techniques
1) Exchange to $ and analyze
2) Discount using foreign cash flows and
interest rates, then exchange to $.
3) Choose a currency standard ($) and
hedge all non dollar CF.
28- 34
Example
Outland Corporation is building a plant in Holland to produce reindeer
repellant to sell in that country. The plant is expected to produce a cash
flow (in guilders ,000s) as follows. The US risk free rate is 8%, the
Dutch rate is 9%. US inflation is forecasted at 5% per year and the
current spot rate is 2.0g:$1.
year
1
2
3
4
5
400
450
510
575
650
Q: What are the 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 year forward rates?
A:
E (Sf/$) = E ( 1 + if )t solve for E(S)
Sf/$
E(S) 2.02
E ( 1 + i$ )t
2.04
2.06
2.08
2.10
28- 35
Example
Outland Corporation is building a plant in Holland to produce reindeer
repellant to sell in that country. The plant is expected to produce a cash
flow (in guilders ,000s) as follows. The US risk free rate is 8%, the
Dutch rate is 9%. US inflation is forecasted at 5% per year and the
current spot rate is 2.0g:$1.
year
1
2
3
4
5
400
450
510
575
650
Q: Convert the CF to $ using the forward rates.
1
2
3
4
5
400
450
510
575
650
E(S) 2.02
2.04
2.06
2.08
2.10
CF$
221
248
276
310
CFg
198
28- 36
Example
Outland Corporation is building a plant in Holland to produce reindeer
repellant to sell in that country. The plant is expected to produce a cash
flow (in guilders ,000s) as follows. The US risk free rate is 8%, the
Dutch rate is 9%. US inflation is forecasted at 5% per year and the
current spot rate is 2.0g:$1.
year
1
2
3
4
5
400
450
510
575
650
What is the PV of the project in dollars at a risk
premium of 7.4%?
$ discount rate = 1.08 x 1.074 = 1.16
PV = $794,000
28- 37
Example
Outland Corporation is building a plant in Holland to produce reindeer
repellant to sell in that country. The plant is expected to produce a cash
flow (in guilders ,000s) as follows. The US risk free rate is 8%, the
Dutch rate is 9%. US inflation is forecasted at 5% per year and the
current spot rate is 2.0g:$1.
year
1
2
3
4
5
400
450
510
575
650
What is the PV of the project in guilders at a risk
premium of 7.4%? Convert to dollars.
$ discount rate = 1.09 x 1.074 = 1.171
PV = 1,588,000 guilders
exchanged at 2.0:$1 = $794,000
28- 38
Political Risk
Political Risk Scores
Maximum Score
Luxembourg
Netherlands
Singapore
UK
Japan
Germany
United States
Italy
China
Brazil
Russia
India
Indonesia
Somalia
A = Govt stability
B = Socioeonmic conditions
C = Investment profile
D = Internal conflict
E = External conflict
F = Corruption
A
12
B
12
C
12
D
12
E
12
F
6
G
6
H
6
I
6
J
6
K
6
L
4
Total
100
11
9
11
9
11
9
11
9
11
9
12
9
9
5
11
11
9
10
8
8
8
9
7
6
7
4
4
1
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
8
8
9
9
6
3
12
11
11
10
12
11
11
11
12
11
9
8
8
5
12
12
12
9
10
10
8
11
11
11
10
9
11
4
5
5
5
5
4
5
4
3
2
4
2
2
1
1
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
4
5
6
6
1
1
3
6
6
5
6
5
5
5
3
5
2
4
4
2
2
6
6
5
6
5
5
5
3
5
2
4
4
2
2
5
5
6
4
6
4
5
5
5
3
2
2
2
2
5
6
2
6
5
5
6
4
1
5
4
6
4
1
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
2
2
1
3
2
0
95
91
87
86
86
83
81
78
71
69
68
59
52
27
G = Military in politics
H = Religious tensions
I = Law and order
J = Ethnic tensions
K = Democratic accountability
L = Bureaucracy quality
28- 39
Web Resources
Click to access web sites
Internet connection required
www.oecd.org
www.bankofengland.co.uk
www.ecb.int
www.oanda.com
www.x-rates.com
www.emgmkts.com
www.securities.com
www.prsgroup.com