Ch 18 Review - Stephanie Dietterle Webpage
advertisement

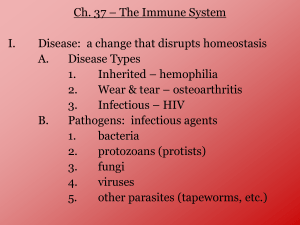
Ch 18 Review A toxin is not a kind of pathogen One reason the skin acts as a barrier against pathogens is because pathogens are killed by oil & sweat A kind of white blood cell that destroys pathogens is a(n) phagocyte One function of T cells is to recognize antigens HIV can be spread by drug users sharing needles, from a pregnant mother to her baby during childbirth, and by sexual contact When a person has an allergy, his or her immune system is overly sensitive to a foreign substance called a(n) allergen You could catch a cold by sharing a glass of water with another person People with diabetes may not produce enough insulin Cancer is a disease in which cells multiply uncontrollably A fever, the production of toxins, and the destruction of pathogens by phagocytes are part of the body’s inflammatory response system Organisms that cause disease are called pathogens Some bacteria cause disease by producing a poisonous chemical called a(n) toxin A person who is injected with antibodies acquires passive immunity The symptoms of an allergy appear when the body releases a chemical called histamine A carcinogen is a substance in the environment that causes cancer T cells and B cells are involved in the body’s defense against pathogens, which is called the immune response Colds and flu can be spread across a room by coughing Asthma is a disorder in which the respiratory passages narrow significantly In the inflammatory response, certain type of white blood cells fight the pathogens A person with diabetes has high levels of glucose in the blood Cancer cells may form tissue masses called tumors HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. It attacks the body’s immune system and causes acquired immune deficiency syndrome, or AIDS. The immune system of a person with AIDS cannot protect the body against illness Four sources of pathogens o An infected person: example kissing a person with a cold or flu o Contaminated object: drinking from a glass that a person with the flu has used o Infected animal: malaria is transmitted to humans by tropical mosquitoes o Soil, food, or water: botulism can be spread through foods that have been improperly canned Three barriers that keep pathogens from getting into the body o The skin is a physical barrier and its oils and sweat can kill pathogens o Mucus and cilia in the respiratory system trap pathogens and help the body to get rid of them o Saliva in the mouth helps to kill pathogens, and acid in the stomach kills pathogens that you swallow Why do doctors not give you an antibiotic to treat a bad cold? It’s because to treat a cold antibiotics kill only bacteria, and a cold is caused by a virus. To treat your cold you could get over the counter medicines The inflammatory response is the body’s second line of defense. It is a general response that is the same for any pathogens. Fluids and phagocytes leak out of the circulatory system into surrounding tissue. Phagocytes surround and consume pathogens Active immunity is when the body produces its own antibodies, either by getting vaccinated or by being sick with the disease. Example: a baby getting antibodies from its mother when still inside her body or from the mother’s milk Passive immunity is when the body acquires antibodies from an outside source. Example: a person who is injected with antibodies to prevent rabies