userfiles/1786/my files/safety & sanitation principles?
advertisement

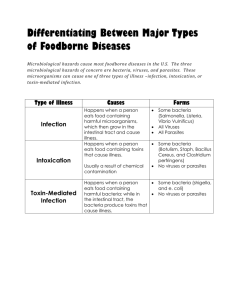
WORKING SAFELY Accidents can easily happen in a busy kitchen. However it ‘s the personal responsibility of each worker to practice safety at all times Workplace accidents cost the foodservice industry over 48billion per year. OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration plays a large role in keeping the workplace safe. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also play a role in workplace safety. Requires foodservice operations to track how they handle and dispose of hazardous materials such as cleaning products and pesticides. PERSONAL PROTECTIVE CLOTHING Foodservice operations often provide protective clothing to help to control contamination. Make sure that uniforms are clean. Dirty uniforms are an ideal place for bacteria to grow. Change when they get dirty. GLOVES Latex Uniseal Powder-free gloves Nitrile Plastic Vinyl The type of gloves worn depends on the task you are doing. Change gloves When they become soiled or torn At least every four hours of single use After handling any raw food PROTECTIVE CLOTHING Shoes Shoes should be sturdy and slip resistant for safety Closed-toe shoes Back braces Lifting heavy items PERSONAL INJURIES Responsible for helping to prevent slips and falls, Cuts, Burns and scalds, and Other personal injuries in the kitchen LOCKOUT/TAGOUT To protect workers from faulty equipment, OSHA implemented a lockout/tagout procedure. Lockout/tagout requires all necessary switches on electrical equipment to be locked out and tagged when they are malfunctioning. This prevents the equipment from being used while it is being repaired. FIRE SAFETY Fire Prevention Fire Protection Equipment Fire extinguishers Class A Wood, paper, cloth, plastic Class B Grease, oil, chemicals Class C Electrical cords, switches, wiring Class D Combustible switches, wiring, metals, iron Class K Fires in cooking appliances involving combustible vegetable or animal oils and fats. FIRE SAFETY Hood and sprinkler systems Every foodservice establishment has fire emergency procedures. It’s the employees responsibility to be familiar with them . Keep customers during emergencies If discover a fire: call the fire department regardless of the size of the fire. Help customers and coworkers leave the building as quickly and calmly as possible. PREPARING FOR EMERGENCIES Emergency numbers First aid assisting an injured person until professional medical help can be provided. American Red Cross training courses General emergency tips: Check the scene and stay calm. Check the victim. Keep him or her comfortable and calm Call the local emergency number for professional medical help. Care for the victim by administering first aid according to the first aid manual. Keep people who are not needed away from the victim Complete an accident report. FIRST AID FOR BURNS Call emergency number for medical assistance. Remove the person from the source of the heat. Cool the burned skin to stop the burning. Cold water from faucet not ice or ice water. Never apply ointments, sprays, antiseptics, or remedies unless instructed to do so by a medical professional. Bandage the burn as directed in your first aid manual Minimize the risk of shock. Keep the victim from getting chilled or overheated. FIRST AID FOR WOUNDS Four types of wounds: Abrasions-scrape and is considered a minor cut. Lacerations-are cuts or tears in the skin that can be quite deep. Avulsions-occurs when a portion of the skin is partially or completely torn off. Punctures-wounds occur when the skin is pierced with a pointed object. Require immediate attention, if severe, call emergency help immediately. Minor cuts: Put on disposable gloves to protect against infection Clean the cut place a bandage over the cut Apply direct pressure over the sterile gauze or bandage to stop any bleeding from the cut. FIRST AID FOR CHOKING Food blocking a person’s airway Heimlich maneuver CPR-cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care that is performed on people who are unresponsive. SECTION 7-2 SANITATION CHALLENGES Foodborne illnesses kill approximately 8,000 people each year and make many more people sick Foodservice professionals need to know how to create a clean, disease-free environment for food preparation. Prevention WHAT IS CONTAMINATION? Sanitary-clean environment Contaminated is harmful microorganism or substances are present in food. Contamination can happen in two ways. Direct contamination occurs when raw foods, or the plants or animals from which they come are exposed to toxins, or harmful organisms or substances. Cross-contamination is the movement of chemicals or microorganisms from one place to another. Sanitation means healthy or clean and whole. Sanitation also refers to healthy and sanitary conditions and effective sanitary practices. Hazards are sources of dangers can result in contaminated food. BIOLOGICAL HAZARDS Biological hazards come from microorganisms such as bacteria . Other types include viruses, parasites, and fungi Plants and fish can also carry harmful toxins Disease causing microorganisms cause the majority of foodborne illnesses. FOODBORNE ILLNESS Microorganisms such as bacteria, and virus are the root cause of foodborne illness. These microorganisms can grow in and on food when it isn’t handled properly. Other conditions that lead to foodborne illness: Poor personal hygiene Food handler illness INDIVIDUALS MOST AT RISK Infants The elderly Pregnant women People who are chronically ill or have weakened immune systems RESPONDING TO AN OUTBREAK Inform the manager or supervisor of you suspicions immediately Avoid panic Save any food you suspect may be contaminated Report any information you may have about the situation to your supervisor. Any outbreak of foodborne illness must be reported to the Department of Health. An outbreak could cost the establishment thousands of dollars in legal fees, insurance cost, and loss of customers. BACTERIA Bacteria are tiny single-celled microorganism, can make people very sick Symptoms: Nausea Abdominal pain Vomiting May also include: headache, dizziness, chills Multiply very rapidly Some do not need oxygen to grow Prefer foods that are high in protein and moisture VIRUSES Viruses are responsible for many food related illnesses In order to grow viruses need a host, or another living cell Once inside the host the virus can multiply Viruses can survive freezing and cooking Transmitted easily from person to person Poor hygiene PARASITE Parasites are larger than bacteria and viruses. They must live in or on a host to survive Parasites are often found in poultry, fish, and meats Common parasite: Protozoa Roundworms Flatworms Parasites can be eliminated from food by following proper cooking methods HAZARDS Fungi are found in soil, plants, animals, water, and in the air. Mushrooms Molds are a form of fungus that you may have seen growing on bread or cheese. Mold can grow at nearly any temperature so they are often associated with food spoilage. Yeast is most often associated with bread and the baking process. Beneficial. However if yeast is present in other foods such as sauerkraut, honey, and jelly it can cause spoilage. PERSONAL HYGIENE Using proper hand-washing techniques Practicing good grooming and cleanliness techniques Wearing gloves and other protective clothing when required Maintaining good health Immediately reporting any illnesses or injuries to the supervisor. CHEMICAL HAZARDS Chemical hazards are caused by chemical substances such as cleaning supplies, pesticides, food additives, and toxic metals. Detergents Hygiene detergents Degreasers Abrasive cleaners Acid cleaners Pesticides PHYSICAL HAZARDS Physical hazards are caused by particles, such as glass chips, metal shavings, hair, bits of wood, or other foreign matter, that could get into food. Found in food itself, bone shards or chips Most contamination occurs when food-handlers do not follow proper safety and sanitation practices. Pest management Always a possibility of insects and rodents wherever there is food. Carry harmful bacteria and spread disease A clean and sanitary environment is not attractive to most pests