bacteria
advertisement

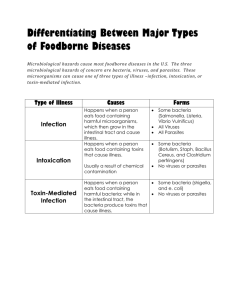
The nature of microorganisms and parasites FS0102 1 2000 Microorganisms classified by their significance pathogenic organisms spoilage organisms useful organisms FS0102 2 2000 Dangerous microorganisms and parasites Foodborne diseases FS0102 3 2000 ‹ bacteria ‹ moulds ‹ viruses ‹ parasites Major bacteria causing foodborne disease Aeromonas spp. Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus cereus Salmonella spp. Brucella spp. Shigella spp. Campylobacter jejuni Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium botulinum Vibrio cholerae Clostridium perfringens Vibrio parahaemolyticus Escherichia coli Vibrio vulnificus Listeria monocytogenes Yersinia enterocolitica FS0102 4 2000 Spoilage microorganisms bacteria Yeasts moulds FS0102 5 2000 Food products made with useful microorganisms fermented meats yoghurt Cheese beer leavened bread soy sauce fermented soybean (tofu) FS0102 6 2000 Useful microorganisms Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) These ferment carbohydrates into organic acids which inhibit ‹ ‹ ‹ ‹ ‹ Salmonella Staphylococcus Listeria Clostridium E. coli LAB are found in ‹ ‹ ‹ ‹ FS0102 7 2000 Plants Soil Animals Human Gut Microorganisms are very small YOGHURT 1 cup of yoghurt contains 20 X this number! World population is 5.9 BILLION i.e. 5 900 000 000 FS0102 8 2000 i.e. 120 000 000 000 separate living organisms. Microorganisms are very small Cell wall Ribosomes FS0102 9 2000 Cytoplasmic membrane Nuclear body Cytoplasm Bacterial division 1 2 3 4 5 FS0102 10 2000 Bacterial growth curve Toxic - - - - - - - - - - - -+++++++++++ Spoils _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 + + + Time to spoilage 2 1 0 Time Lag phase FS0102 11 2000 Log phase Stationary phase Phases of bacterial growth lag phase (short) period of adjustment to environment logarithmic growth phase growth begins and accelerates to a phase of rapid, constant exponential growth stationary phase depletion of nutrients and accumulation of toxic metabolic products growth is slowed to a point where cell division and cell death are in balance death phase population decreases due to death of cells FS0102 12 2000 Some toxigenic moulds causing foodborne disease Aspergillus spp. Fusarium spp. Penicillium spp. ( Main sources - fruits, nuts and grains ) FS0102 13 2000 Major viruses causing foodborne disease Hepatitis A and E viruses Small Round Structured Viruses (e.g. Norwalk agent) Rotavirus Polio virus FS0102 14 2000 Virus structure Protein Capsule Poliovirus Hepatitis-A virus Rotavirus Norwalk-like or SRSV Nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) FS0102 15 2000 Virus levels required for infection and detection infection 10 -100 particles / ml detection 105 - 106 particles / g (by electron microscopy) 104 - 105 particles / g (by radioimmunoassay) FS0102 16 2000 Examples of peak excretion period of some faecal viruses FS0102 17 2000 SRSV 1 - 3 days Astrovirus 1 - 4 days Rotavirus 1 - 7 days Adenovirus prolonged Coronavirus prolonged Hepatitis A virus pre-jaundice The human intestines - the source and target of foodborne viruses cause diarrhoea ‹ ‹ ‹ ‹ ‹ Small round structured viruses (SRSV) Astrovirus Adenovirus Coronavirus Rotavirus do not cause diarrhoea ‹ ‹ ‹ ‹ FS0102 18 2000 Hepatitis A virus Poliovirus Echovirus Coxsackievirus Major parasites causing foodborne disease Protozoa • Cryptosporidium • Entamoeba histolytica • Giardia • Toxoplasma Helmints • Angiostrongylus • Fasciola • Anisakis • Fasciolopsis • Ascaris • Haplorchis • Opisthorchis • Paragonimus • Capillaria • Gnathostoma • Trichinella FS0102 19 2000 • Cysticercus cellulosae Transmission of trichinellosis Infected person Adults in intestine encysted larvae in muscle Adults in intestine RAT PIG encysted larvae in muscle FS0102 20 2000 Adults in intestine encysted larvae in muscle Transmission of cysticercosis Infected person Cysticercus cellulosae in the body Taenia saginata Regurgitating Taenia solium Contaminated vegetable, water Adult in intestine Eggs in soil FS0102 21 2000 Transmission of toxoplasmosis Cat Infected person Bradyzoite in meat Oocyst ingestion Transplacenta transmission Baby FS0102 22 2000 Mammals Birds (Cattle, pig goat etc.) handling meat Transmission of anisakiasis Infected person Adult in Marine mammals Fish encysted larvae 3rd stage larvae in krill Acute abdominal pain FS0102 23 2000 2nd stage larvae Transmission of ascariasis Infected person Adult worms in intestine Contaminated hand Contaminated vegetables with night soil Unsegmented eggs excreted FS0102 24 2000 Infective eggs Transmission of fascioliasis Infected person Adults in bile duct Sheep Aquatic plants encysted metacercaria Juvenile migrate to other organs ie. brain, eye, muscle FS0102 25 2000 Snail cercaria Transmission of giardiasis Giardia cysts in intestine Infected person Water used to wash fruit and vegetables Drinking water Transfer to mouth Giardia lamblia excreted Cyst in water Cysts on hands Cyst FS0102 26 2000 Transmission of cryptosporidium The Environment Effluents, slurry & sludge dumped on land Liquid discharges and effluents dumped in water Recreational use of land and water Food chain Water treatment system Farm Animals Indigenous wildlife FS0102 27 2000 Human Imported exotic livestock Pets Nature of bacteria, moulds, viruses and parasites - Key messages (1) foodborne diseases are caused by bacteria, moulds, viruses, and parasites certain microorganisms are of greater significance than others for humans bacteria and moulds multiply on foods and may produce toxins understanding the factors controlling growth of microorganisms allows us to control them in food FS0102 28 2000 Nature of bacteria, moulds, viruses and parasites - Key messages (2) bacteria may be harmful or useful bacteria, yeasts and moulds can be used to preserve foods lactic acid bacteria secrete lactic and other organic acids organic acids inhibit pathogens in food and in the gut viruses and parasites do not grow in food FS0102 29 2000