biology midterm review
advertisement

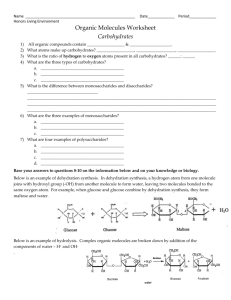
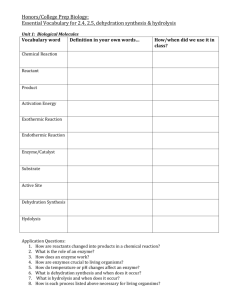
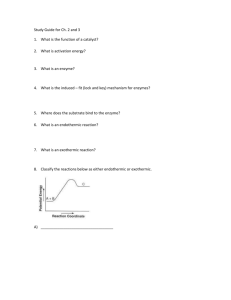
HONORS BIOLOGY MIDTERM REVIEW Characteristics of Life Be able to state the characteristics of life and provide an example of each. The Cell Be able to compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Be able to compare and contrast plant and animal cells. Also, what is a virus? Be able to identify the various types of structures (ex. phospholipids, cell membrane proteins) that compose the cell membrane and be able to explain how these structures function individually and in concert with other molecules. Also review what the cell membrane looks like. Be able to identify the statements of the Cell Theory. Be able to identify the functions of certain organelles (ex. Mitochondria, ribosome, etc.) Inorganic Chemistry Review different types of bonds—covalent (nonpolar and polar) and ionic. Be able to describe what a valence electron is and how it determines the chemical properties of an element. Be sure to know how to distinguish if an element is an isotope. Review the structure of water molecules and arrangement of water molecules during bonding. Bacteria Be able to identify the 3 main shapes and general groupings of bacteria. Describe the difference between gram + and gram – bacteria. Be able to discuss the effects of antibiotics on bacteria. Carbohydrates/ Structure of DNA Identify the monomers and polymers of carbohydrates. Be able to explain how carbohydrates form through dehydration synthesis and become broken down through hydrolysis. Be able to identify the structure of carbohydrates and how to count the number of atoms to find the chemical formula. Be able to recognize structural and functional differences between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides Review what an isomer looks like. Be ready to distinguish what iodine, benedict’s, & biuret test for (macromolecule lab) Be able to label a diagram of the DNA molecule. Review the base-pairing rules and the various types of bonds within the double helix. Protein Structure Identify the monomers and polymers of proteins. Be able to explain how proteins form through dehydration synthesis and become broken down through hydrolysis. Be able to identify the four levels of protein structure including the specific bonds present in secondary and tertiary levels. Explain what can denature a protein. Explain the function that enzymes have in the cell and how they interact with substrates. Lipids Identify the monomers and polymers of lipids. Be able to explain how lipids form through dehydration synthesis and become broken down through hydrolysis. Be able to recognize the difference between a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid. Cell Transport Be able to use a graph to determine solute concentration in an unknown solution. Predict how the size of potato cores will change when put in hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions. (Remember the potato lab) Be able to distinguish between diffusion, osmosis, endocytosis, exocytosis, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis. Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis Review the limits on cell size (i.e. surface area-to-volume ratio) Be familiar with all of the components of the cell cycle with an emphasis on the stages of mitosis. Be able to identify and distinguish between chromosomes, chromatids, and chromatin. Be able to identify what organic molecules make up a chromosome. Be able to follow a pair of homologous chromosomes through the process of meiosis I and II. Be able to distinguish between haploid and diploid chromosome numbers. Protein Synthesis Be able to discuss the roles of DNA, mRNA, and tRNA during transcription and translation. Be able to transcribe & translate a segment of DNA Review base-pairing rules for RNA