2-3 Carbon Compounds: Organic Biomolecules
advertisement

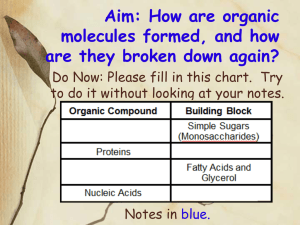
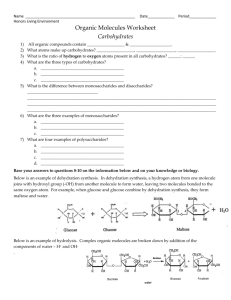
2-3 Carbon Compounds: Organic Biomolecules What is a compound? What do you think a carbon compound is? Carbon’s properties Carbon is very versatile It can bond with other carbon atoms It can form strong covalent bonds with many different elements 95% of the body is only made of 6 elements C H O N P S It can make four bonds at a time 4 single bonds 2 double bonds 1 double bond & 2 singles 1 triple bond & 1 single bond It can make bonds in many different shapes Sheets, Rings, Branches, Long chains, Buckieballs Carbon Bonds Carbon: Functions of organic biomolecules found in living things Carbohydrates energy & structure Lipids storage, protection & sending chemical messages as hormones & steroids Nucleic acids DNA & RNA, store & transmit hereditary Proteins metabolism, structure, fight disease, enzymes control the rate of reactions Macromolecules What does “mer” mean? – Part or piece What does “mono” mean? – one What does “poly” mean? – many So What is a monomer? – One piece is a monomer…. like a lego block What is a polymer? – Add many of those pieces together and you get a polymer!…like a finished lego project. Polymerization Adding monomers together to make a polymer! – This is achieved by dehydration synthesis. Dehydration Synthesis • What does dehydrate mean? • Take out water • What does synthesis mean? • To make • So dehydration synthesis is….. • Making something by taking water out • Making a polymer by removing water and making room for a bond between monomers Start with monomers End with a polymer & water Dehydration Synthesis beginning to end Hydrolysis What does hydro mean? water What does lysis mean? Lysis sounds like slices! So, hydrolysis means….. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Breaking bonds in a polymer to get monomers by adding water Dehydration synthesis is the reverse of hydrolysis! Carbohydrates What do you think “carbo” means? What does “hydrate” mean? three What does “poly” mean? one What does “tri” mean? water What does “mono” mean? carbon many What does “saccharide” mean? sugar Carbohydrates Carbon-water -CH2O Main source of energy for living things Used for structure in some Supplies energy for all cell activities are also known as saccharides (sugars) Monosaccharides are the smallest unit (monomers) Disaccharides found as simple sugars Glucose, Galactose, Fructose Sucrose , Lactose Polysaccharides used as storage and structure (polymers) Glycogen, Starch, Cellulose Monosaccharides -the monomers Disaccharide Monosaccharide + monosacharide = Disaccharide Is that dehydration synthesis or hydrolysis? Dehydration Synthesis What do you think this is? How many rings do you see? Tri= 3 Polysaccharide -starches What Contains Carbohydrates? What contains Carbohydrates? Which are better for you? Lipids • Fats, oils, and waxes • Look like the letter “E” • Mostly carbon and hydrogen • Very little oxygen • Many are formed by combining glycerol (green) with 3 fatty acid chains (red) – o Stores energy – o Helps form membranes – o Waterproof coverings – o Chemical messengers – o Steroids (hormones) What contains lipids? Saturated Lipids Solid at room temperature! • Full of Hydrogens • Only single bonds between C & H Unsaturated Lipids Liquid at room temperature • Has at least one double or triple bond between C & H Polyunsaturated Lipids • More than one double or triple bond between C & H This is still an “E” just flipped around! Nucleic Acids Biomolecules that transmit and store genetic information Formed from: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, & phosphorous Monomers are nucleotides A Nucleotide Three parts 5-carbon sugar ring A phosphate group A nitrogen base: Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine or Uracil Two types of polymers RNA – ribonucleic acid DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid What contains Nucleic Acids Can you see the monomers? Formed from carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Monomers are amino acids Three parts An amine group on one side.(NH2) A carboxyl on the other (COOH) changeable group called R 20 different type Proteins are necessary for life Control the rate of reactions Regulate cell processes Form body parts such as bones, skin, hair, nails, muscles Transport substances in and out of cells Help fight disease Pizza? Which bimolecules are found in pizza. Explain. What do you think would happen if someone followed the Atkins diet? How do vegetarians get protein? What if they didn’t eat those foods? What if you cut out all fat in your diet?