Chapter 26 - Urinary System
advertisement

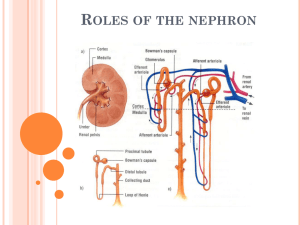
Chapter 26 - Urinary System Urine Production 1-2 L a day for normal healthy adult Filtration: The movement of fluid across the filtration membrane as a result of pressure difference. The fluid that is pulled from the blood becomes the filtrate. 21% of the total blood is the Renal fraction from the total cardiac output which is the blood that leaves the heart. The filtration barrier is composed of the __________________ epithelium of the capillaries that compose the glomerulus, the basement membrane of that epithelium, and the podocytes (specialized cells). The capillaries of the glomerulus are 100-1000 times more permeable than normal capillaries. It works to prevent all blood cells and vital proteins from leaving the capillaries, but lets all the waste out. Smooth muscle in the efferent and afferent arterioles allow the pressure to be changed when needed by enlarging or constricting the diameter of the blood vessels. Reabsorption: Defined: The movement of substances from the filtrate back into the blood. The filtrate leaves the Bowman's capsule and flows through the PCT, DCT, to the Collecting duct - tubular reabsorption takes place here. Inorganic salts, organic molecules, and about 99% of the filtrate volume leave into the interstitial fluid from the lumen of the nephron. Which epithelium do you think would be most effective at this role of tubular reabsorption? _________________________ Amino acids, glucose, potassium, and chloride ions are actively transported via K/Na Pumps and carrier molecules in the PCT. By the end of the PCT 65% of the filtrate is reabsorbed. Other things like fructose, sodium, calcium and bicarbonate ions are moved into the interstitial space via cotransport or secondary active transport. Passive movement of some organics occurs in the loop of Henle via the ______________________ epithelium (hint: think diffusion). The permeability of H2O is greatly reduced in the DCT and collecting duct and is under hormonal control -(ADH) Antidiuretic hormone. It makes the walls more permeable to H20. Secretion: Defined: The active transport of substances into the nephron. Some substances (by-products of metabolism) become toxic in high concentrations, and some drugs and other molecules not produced by the body are removed by the nephron. Tubular secretion can be active or passive. Ammonia is synthesized in the epithelium of the nephron and diffuses into the lumen. Other substances that are actively secreted by the cuboidal cells include: Hydrogen ions, potassium ions, penicillin, and paraaminohippuric acid.