Unit 4C Urinary - Iowa State University
advertisement

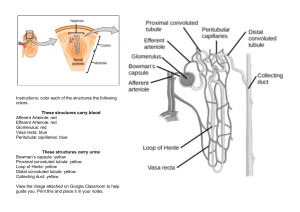
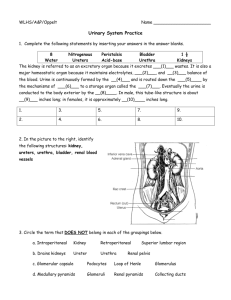
Human Physiology Unit 4C: Urinary: Renal Structures Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Paige Stieneke BIOL 256 Dr. Karri Haen April 8, 2013 Matching. Select the correct name for each anatomical structure: 1. ___ Peritubular capillaries 2. ___ Efferent arteriole 3. ___ Afferent arteriole 4. ___ Cortex 5. ___ Medulla 6. ___ Interlobar vein 7. ___ Interlobar artery 8. ___ Arcuate vein 9. ___ Arcuate artery 10. ___ Glomerulus 11. ___ Vasa recta Kidneys 1. What is the major function of kidneys? 2. What is the structural and functional unit of the kidney? a. Where does filtration occur in the nephron? b. What does the proximal convoluted tubule reabsorb? c. What structure is found between the proximal and distal convoluted tubule? i. Descending Limb: (Thick, thin) segment that reabsorbs (water, ions) ii. Ascending Limb: (Thick, thin) segment that reabsorbs (water, ions) Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu d. True or False: The distal convoluted tubule functions more in reabsorption rather than secretion i. What process aids in the movement of ions? e. Which two cell types are found in the collecting tubules? i. How can these two cell types be distinguished? 3. True or False: Filtrate contains all plasma except for protein and other cells! 4. What is found in urine? 5. (Afferent, Efferent) arterioles go toward the glomerulus, and (afferent, efferent) arterioles go away from the glomerulus 6. List the 3 processes of urine formation: a. ______________: Cells, proteins, large molecules are filtered out, leaving plasma (except for proteins) i. Where do cells, proteins and large molecules go? ii. Where does plasma (excluding proteins) go? b. ______________: Ions removed from tubular fluid and put back into bloodstream c. ______________: From peritubular capillaries into tubule’s lumen (ex: drugs for excretion) Two Types of Nephrons: 1. a. Most nephrons that produce (dilute, concentrated) urine 2. a. Loops of Henle dip deeply into medulla, produce (dilute, concentrated) urine Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu