Business Information Systems
advertisement

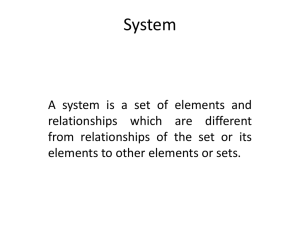
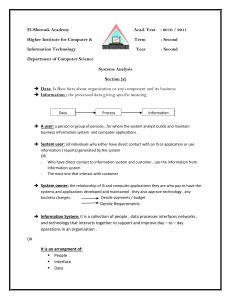
Transaction Processing Systems A transaction is a record of an event that signifies a business exchange A transaction processing system is a basic business system that support the functions of •Recording •Monitoring •Evaluating the basic activities of the business Fig. 13.1 Transaction Processing Systems Examples of basic manufacturing/production systems are: materials purchasing receiving shipping process control numerical control equipment quality control labor costing robotic systems Examples of basic sales/marketing systems are: sales telemarketing order processing point-of-sales systems credit authorization Figure 13.4 Amazon.com Order Processing System Examples of basic finance/accounting systems are: accounts receivable accounts payable general ledger payroll cash management loan processing check processing securities trading Examples of basic human resource systems are: personnel record keeping applicants tracking positions listing training and skills benefits Questions to ask • • • • Where does the system obtain its data? What does the system do with the data? What problems does the system solve? What differences does the system make? Office Automation Systems • Data work: use, manipulate, or disseminate information • Knowledge work: create new information using judgment & creativity – Discipline/Principle/Profession/Certification • Office work: coordinate & integrate workers from different functional areas An office automation system is any application of information technology that increases the productivity of office workers document management word processing desktop publishing electronic communications electronic scheduling data management project management Figure 16.2 Four Functions of Management Figure 16.4 Manager’s Time 3 roles of a manager 1. Interpersonal – figurehead, leader, liaison 2. Informational – monitor, spokesperson, disseminator 3. Decisional – entrepreneur, mediator, resource allocator, negotiator Management Support Systems • MIS: summarize & report on the basic operations of a company • DSS: provide data & models interactively to support semi-structured problem solving • EIS: provide data from both internal & external sources to support unstructured problem solving Figure 16.5 An MIS Figure 16.7 An DSS Figure 16.9 An ESS Artificial Intelligence: the study of how to make computers to do things that require some level of intelligence: •Learn/understand from experience •Acquire & retain knowledge •Respond quickly & successfully to new situations •Solve problems Expert Systems • Solve problems that require expertise • Use facts and reasoning (rules of thumb) • Explain what it knows and its reasoning process 3 components: • Knowledge base • Inference engine • User interface