body systems test review key
advertisement

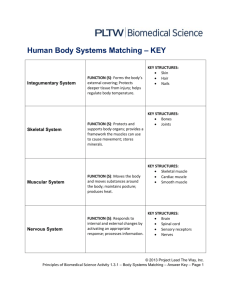
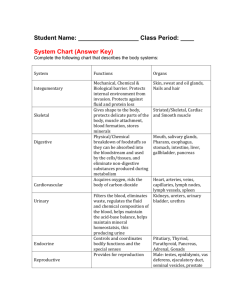
BIOLOGY 1 PAP BODY SYSTEMS TEST REVIEW KEY 1. 2. 3. WHAT IS A SYNAPSE? The synapse is the small gap between adjacent neurons, it consists of an ending that contains neurotransmitters, chemicals, used to send the nerve impulse across the gap so the nerve impulse can contain on its journey. WHAT ARE ALVOLI? Tiny arir sacs in the lungs that increase the surface of the lungs to increase the rate the gases are exchanged between the air and the lungs. NAME AND DESCRIBE THE TWO PARTS OF THE SKELETON. The 2 main parts of the human skeleton are the: 1) There is the axil skeleton (consists of the 80 bones in the head and trunk of the human body) 4. 5. 6. 7. 2) The Appendicular Skeleton (consists of 126 bones in the human body which make motion possible and protects the organs of digestion, excretion, and reproduction) HOW MANY BONES ARE IN THE JHUMAN BODY? 206 WHERE DOES DIGESTION BEGIN? The mouth with the chewing and adding of saliva, a digestive enzyme. WHAT IS THE PHARYNX? The throat NAME AND DESCRIBE THE THREE TYPES OF CIRCULATION? systemic circulation-network of vessels that carry blood from the heart to the body and from the body back to the heart coronary circulation-network of arteries and veins that supplies blood to all the cells of the heart pulmonary circulation-network of vessels that carries blood to and from the lungs 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. NAME THE 4 CHAMBERS OF THE HUMAN HEART. Left atrium, right atrium, right ventricle & left ventricle. WHICH STORES BLOOD? Both Atria WHICH ONE PUMPS BLOOD? Both ventricles What do ovaries produce? Eggs and the femal hormones estrogen and progesterone WHAT DO TESTES PRODUCE? Sperm and the male hormone testosterone NAME AND DESCRIBE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLE TISSUUE. WHICH ONE ARE VOLUNTARY AND WHICH ONES ARE INVOLUNTARY? The 3 types of muscle tissue are cardiac, smooth, and skeletal. Cardiac muscle cells are located in the walls of the heart, appear striated, and are under involuntary control. Smooth muscle fibers are located in walls of hollow visceral organs, except the heart, appear spindle-shaped, and are also under involuntary control. Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. They are striated in appearance and are under voluntary control. DEFINE DIGESTION. The process of breaking down food by mechanical and enzymatic action in the alimentary canal, DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, into substances that can be used by the body. WHAT AE VILLI? WHY ARE THEY IMPORTANT? Small, finger-like projections that protrude from the epithelial lining of the intestinal wall and increase the surface area of the intestinal wall to increase the rate of absorption of nutrients into the blood stream. WHAT ARE IMPULSES? A nerve impulse is an electro-chemical signal that travels along an axon (neuron). TRACE THE PATH A SPERM CELL TRAVELS AS IT EXITS THE BODY. The key male reproductive organs that sperm travels thru include the testes, epididymis, urethra, vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal vesicle, and penis. The testes are composed of coiled structures called seminiferous tubules, which are the sites of sperm production. The structure on top of the seminiferous tubules in the testes is the epididymis. The sperm migrate from of the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis. Within the epididymis, the sperm mature while they are stored in this structure, mature sperm travel from the epididymis through the vas deferens, a muscular tube, which propels sperm forward through smooth muscle contractions. The sperm arrive first at the ampulla, where secretions from the seminal vesicle are added, from the ampulla, seminal fluid is propelled forward through the ejaculatory ducts toward the urethra, passing first by the prostate gland, where a milky fluid is added to form semen. Finally, the semen is ejaculated through the far end of the urethra. DEFINE OVULATION. Ovulation is one part of the female menstrual cycle whereby a mature ovarian follicle (part of the ovary) discharges an egg (also known as an ovum, oocyte, or female gamete). It is during this process that the egg travels down the fallopian tube where it may be met by a sperm and become fertilized. TRACE THE PATH OF DIGESTION THROUGH THE HUMAN BODY. First, the food goes in the mouth. It is broken down by the teeth and the salivary enzymes which catalyze only carbohydrates. after that, the tongue will be responsible for pushing the food into the pharynx. Next, the food goes to the esophagus. The esophagus contains smooth muscles responsible for the peristaltic movement of food. Due to this movement, the food enters the cardiac sphincter of the 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. stomach. Inside the stomach, the gastric juice and HCl is being secreted. the gastric juice contains enzymes which act in digesting the food. Then, the digested food exits the stomach through the pyloric sphincter. It now reaches the first part of the small intestine which is the duodenum. It is where the head of the pancreas lie. pancreatic juice and bile salts FROM the gallbladder are secreted to the duodenum. These also contain other enzymes responsible for breaking down larger molecules into simpler ones. The small intestine contains villi and micro villi which are used for the absorption of water and nutrients from the digested food. After passing the small intestine, it passes to the large intestine, no digestion occurs in the large intestine. The large intestine is responsible for shaping of the feces while the bile gives its yellow color. The waste or feces then passes to the anal canal and then to the rectum and to the anus. Finally the waste can be excreted by the body. WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? The skeletal system's primary function is to form a solid framework that supports and protects the body's organs and anchors the skeletal muscles WHAT OTHER NAMES ARE USED FOR THE DIGESTIVE TRACT? The digestive system is also known by a number of other names, including the gut, the digestive tube, the alimentary canal, the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, the intestinal tract, and the intestinal tube. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE IN LENGTH AND IN DIAMETER OF THE SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE? The small is longer, but the large is thicker, WHAT IS THE LARGEST VEIN IN YOUR BODY? The largest vein in the human body is the inferior vena cava. This vein has a main function of taking back deoxygenated blood from the bottom half of the body. WHICH BONE COVERS AND PROTECTS THE HEART? The ribs and the sternum. DEFINE MENSTRUATION. The process in a woman of discharging blood and other materials from the lining of the uterus at intervals of about one lunar month from puberty until menopause, except during pregnancy. TRACE THE PATH AN IMPIULSE TRAVELS. STIMULI > SENSORY RECEPTORS > SENSORY NEURONS > CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (SPINAL CORD) > RELAY NEURONS > BRAIN > MOTOR NEURONS > EFFECTOR MUSCLE OR GLAND WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONAL UNITS OF THE KIDNEYS CALLED? Nephrons are the individual collecting ducts. WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM? Produces and release more than 20 major hormones directly into the bloodstream where they can be transported to cells in other parts of the body that regulate the body to maintain homeostasis. The major glands that make up the human endocrine system include the: hypothalamus. pituitary gland. WHAT ARE NEUROTRANSMITTERS? A chemical substance, LIKE ACETYLCHOLINE, that is released at the end of a neuron by the arrival of a nerve impulse and, by diffusing across the synapse or junction, causes the transfer of the impulse to another nerve fiber, a muscle fiber, or some other structure. WHICH ENDOCRINE GLAND IS THE MASTER GLAND? Although it is no bigger than a pea, the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain just beneath the hypothalamus, is considered the most important part of the endocrine system. It's often called the "master gland" because it makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE PANCREAS? Produces and secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to regulate blood glucose concentration TRACE THJE PATH OF BLOOD STARTING WITH THE RIGHT ATRIUM. right atrium > tricuspid valve > right ventricle > pulmonary valve > pulmonary artery > lungs > pulmonary veins > left atrium > mitral valve > left ventricle > aortic valve > aorta > Circulated to rest of body > inferior and superior vena cava > and back to right atrium WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM? The major functions of the muscular system are: 1. Body movement due to the contraction of skeletal muscles 2. Maintenance of posture also due to skeletal muscles 3. Respiration due to movements of the muscles of the thorax 4. Production of body heat, which is necessary for the maintenance of body temperature, as a byproduct of muscle contraction 5. Communication, such as speaking and writing, which involve skeletal muscles 6. Constriction of organs and vessels, especially smoother muscles that can move solids and liquids in the digestive tract and other secretions, including urine, from organs 7. Heart beat caused by the contraction of cardiac muscle that propels blood to all parts of the body 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. WHATIS THE SCAPULA? Shoulder blade. WHAT IS THE CLAVICLE? Collarbone WHAT IS THE KNEECAP? Patella WHAT IS THE THIGH BONE? Femur WHAT IS THE NAME OF THE CALF MUSCLE? Gastrocnemius WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM? Fight infections and protect against disease. WHAT IS THE FUNCTIONOF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM? To get rid of nitrogen waste and toxic compounds from the body. 39. WHAT DOES THE KIDNEY DO? The kidneys do many things that keep you healthy, including: cleaning and filtering your blood to remove wastes. 40. WHAT LARGE MUSCLE COVERS THE THIGH BONE? Quadriceps. 41. WHAT DOES THE LARGE INTESTINE DO? Forms the solid feces by reabsorbing water into the body. 42. WHAT DOES THE THYROID DO? Produce thyroid hormones to regulate our metabolic rate and affect weight and energy level. 43. WHICH SIDE OF THE BODY IS CONTROLLED BY THE LEFT SIDE OF THE BRAIN? Muscles on the right side of the body.