2.4 review
advertisement

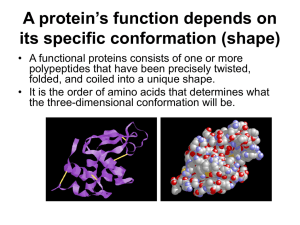
Topic 2.4 Protein Review **Review all the “understanding” statements at the beginning of each section. Key facts 2.4 29. Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. 30. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. 31. The sequence of amino acids in polypeptides is coded for by genes. 32. A protein may consist of one or more than one polypeptide linked together. 33. Some proteins contain amino acids that are not included in the “20.” They are the result of modifications after the synthesis of the polypeptide. 34. Examples of modified amino acids are found in collagen. Complete the following. 2.4 Proteins 1) What are the building blocks of proteins called? 2) Draw a condensation reaction between two amino acids. What is the name of the bond that is formed as a result? 3) Discuss why the same 20 amino organisms are used by most organisms to make proteins. 4) Distinguish between a polypeptide and a protein. 5) What is an “R” group? How many different ones are there? 6) Give an example of the largest and smallest proteins in the human body and their relative size. 7) What is the formula for figuring out the # of possible sequences of given X number of amino acids? 8) What is the role of genes in polypeptide synthesis? 9) Be able to describe the difference between the primary, secondary and tertiary & quarternary structure of a protein. 10) When a protein loses its shape and no longer works, it has become__________. 11) Be able to give at least 6 examples of protein functions in our body. 12) What is a proteome? 13) Provide a named example of proteins form from 1, 2, 3 & 4 polypeptides and discuss where they are found and their function. 14) Discuss the following 6 proteins: Rubisco, Insulin, Immunoglobulin, Rhodopsin, Collagen, & Spider Silk 15) Tell whether the following represents hydrolysis or condensation. a. amino acid + amino acid --------- dipeptide + water ______________ 16) Name the process that results in protein synthesis.____________________ 17) What general macromolecule are most enzymes?___________________ 18) Why are proteins globular and not fibrous proteins? 19) What factors help to determine the shape of an enzyme (protein), and therefore control their extreme specificity toward substrates? 20) What happens in denaturation? What are causes?