Month 3 Cost of Production 3
advertisement

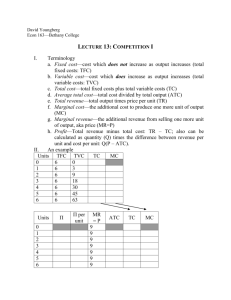
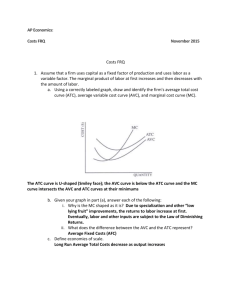
Warm-Up, 10/24 Marginal cost always intersects average variable cost at A. The profit-maximizing quantity B. The minimum of marginal cost C. The maximum of average variable cost D. The minimum of average variable cost E. The maximum of marginal cost The Costs of Production (21) Day 3 Go over homework Alas, tomorrow I must draw out the lesson… Like an ol’OT Extra Credit—up to a 2.32% increase in your average Have a story to present tomorrow which includes the following: 1. 15 terms spread among all the chapters we have covered 2. A minimum of 600 words 3. An Aristotelian or Magical Realist Plot 4. At least three standing ovations from the class following uproarious laughter Alas, tomorrow I must draw out the lesson… Like an ol’OT Questions to answer today?! 1. What are all the measures of cost relevant to a firm? 2. What are the differences between short run and long run? 3. Economies of scale—what IS that? Relationship Between Marginal Cost and Average Total Cost Whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost, average total cost is falling. Whenever marginal cost is greater than average total cost, average total cost is rising. Relationship Between Marginal Cost and Average Total Cost The marginal-cost curve crosses the average-total-cost curve at the efficient scale. Efficient scale is the quantity that minimizes average total cost. Relationship Between Marginal Cost and Average Total Cost $3.50 $3.00 $2.50 MC Costs $2.00 ATC $1.50 $1.00 $0.50 $0.00 0 2 4 6 Quantity of Output (glasses of lemonade per hour) 8 10 12 The Various Measures of Cost It is now time to examine the relationships that exist between the different measures of cost. The Various Measures of Cost Big Bob’s Bagel Bin Quantity of Bagels 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Total Cost $2.00 $3.00 $3.80 $4.40 $4.80 $5.20 $5.80 $6.60 $7.60 $8.80 $10.20 $11.80 $13.60 $15.60 $17.80 Fixed Cost $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 $2.00 Average Average Average Variable Fixed Variable Total Marginal Cost Cost Cost Cost Cost $0.00 $1.00 $2.00 $1.00 $3.00 $1.00 $1.80 $1.00 $0.90 $1.90 $0.80 $2.40 $0.67 $0.80 $1.47 $0.60 $2.80 $0.50 $0.70 $1.20 $0.40 $3.20 $0.40 $0.64 $1.04 $0.40 $3.80 $0.33 $0.63 $0.97 $0.60 $4.60 $0.29 $0.66 $0.94 $0.80 $5.60 $0.25 $0.70 $0.95 $1.00 $6.80 $0.22 $0.76 $0.98 $1.20 $8.20 $0.20 $0.82 $1.02 $1.40 $9.80 $0.18 $0.89 $1.07 $1.60 $11.60 $0.17 $0.97 $1.13 $1.80 $13.60 $0.15 $1.05 $1.20 $2.00 $15.80 $0.14 $1.13 $1.27 $2.20 Big Bob’s Cost Curves... $20.00 $18.00 Total Cost Curve $16.00 Total Cost $14.00 $12.00 $10.00 $8.00 $6.00 $4.00 $2.00 $0.00 0 2 4 6 8 Quantity of Output (bagels per hour) 10 12 14 16 Big Bob’s Cost Curves... 3.5 3 2.5 MC Costs 2 1.5 ATC AVC 1 0.5 AFC 0 0 2 4 6 8 Quantity of Output 10 12 14 16 Three Important Properties of Cost Curves Marginal cost eventually rises with the quantity of output. The average-total-cost curve is Ushaped. The marginal-cost curve crosses the average-total-cost curve at the minimum of average total cost. Costs in the Long Run For many firms, the division of total costs between fixed and variable costs depends on the time horizon being considered. In the short run some costs are fixed. In the long run fixed costs become variable costs. Consequences of the Long Run In the long run, firms can go out of business or change their scale… They will choose the scale that maximizes their profits Costs in the Long Run Because many costs are fixed in the short run but variable in the long run, a firm’s long-run cost curves differ from its short-run cost curves. Average Total Cost in the Short and Long Runs... Average Total Cost ATC in short run with small factory ATC in short run with medium factory ATC in short run with large factory ATC in long run 0 Quantity of Cars per Day Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Economies of scale occur when long-run average total cost declines as output increases. Diseconomies of scale occur when longrun average total cost rises as output increases. Constant returns to scale occur when long-run average total cost does not vary as output increases. Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Average Total Cost ATC in long run Economies of scale 0 Constant Returns to scale Diseconomies of scale Quantity of Cars per Day