2011
advertisement

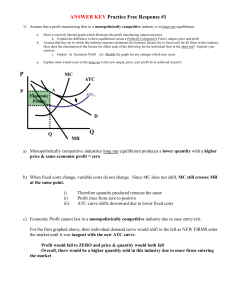
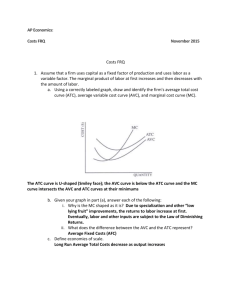
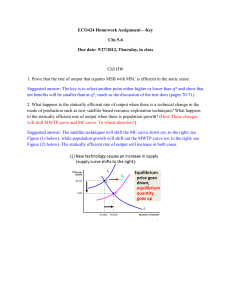
NAME: ________________________________________________ FNR 407 Examination No. 1, 2010 (6) 1. For a specified production process of a given firm, explain why the portion of the marginal cost (MC) curve that lies below the average variable cost (ATC) is not part of its short-run supply curve. Be certain to explain the relevance of ATC, including the meaning of ATC and how it’s calculated. (6) 2. Assuming that a for-profit firm has been operating for a number of years and its overall operations are fairly stable, what is the advantage to the firm of making management decisions using marginal analysis? (Don’t say to maximize profit, that’s a given.) (6) 3. A firm conducts a discounted cash flow analysis for the purchase of a new machine. They calculate an NPV using a discount rate of 6%, the average rate of return for the firm’s capital investments. The NPV is $1.0 million on a $150 million investment. The boss then calls and says that the firm’s average rate of return was recalculated to be 5%. The boss wants to know immediately whether or not this investment would cover a 5% rate of return. What do you the boss? What’s you basis for this answer? 1 NAME: ________________________________________________ (6) 4. Assume a firm is evaluating an investment opportunity that will have a 10 year payback. They have the cash to make the investment so they don’t have an interest cost for borrowed funds. Is there an opportunity cost for this investment? How would they include this cost in their analysis of whether or not the investment should be made? (6) 5. How is the price of money (capital) measured? Explain what would make this price go up and what would make it go down. (6) (6) 6. 7. Within the context of a single tree, what are the economic/financial implications of the tree being both the thing producing the product (machine) and the product produced (output)? A monopoly exists when there is only one firm providing a good or service to more than one consumer (purchaser). Why can’t the monopolist charge whatever they want for the good or service they produce? If not how do they determine the price to sell their goods or service at once they’ve equated MC and MR to determine the profit maximizing level of production? 2 NAME: ________________________________________________ (5) 8 .In the figure below if the current price is P1 would you expect this price to continue for very long? What adjustments would occur by producers and by consumers? Show on the graph what you think the long-run market equilibrium price would be. P P1 Supply curve Demand curve Q Why don’t sunk costs matter when a firm is making decisions about how to improve their financial performance by changing how they do something? (6) 9. (5) 10. If a firm sells into a very competitive market and the market price is in the $10 to $12 range, what should the firm use as their MR. 3 NAME: ________________________________________________ (6) 11. If a firm raises its price and its total revenue goes down, is it selling in an elastic or inelastic market? If a firm knows that its price elasticity of demand is -1 and it wants to maximize total revenue should it decrease, increase, or not change it price? There are only two firms producing widgets in a given market area. Their MC’s are given in the table along with the associated level of output. What is the supply curve for this market area? (Fill in the empty columns) (6) 12. Firm A’s Q 500 600 700 800 900 1,000 1,100 1,200 (6) Firm A’s MC $200 $400 $600 $900 $1,300 $2,000 $5,000 $7,000 Firm B’s Q Firm B’s MC 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 $400 $600 $900 $1,300 $2,000 $5,000 $9,000 12,000 Market Q Range in Market price $200 $400 $600 $900 $1300 $2000 $5000 $9000 13. An investor can purchase a warehouse room full of 5 year old wine in oak casks for $500,000. The seller estimates that after bottling the wine in the casks will be worth $1,500,000 in 4 years. What rate of return would the investor earn if he made this investment and the value estimated by the seller came true? 4 NAME: ________________________________________________ (6) 14. For the situation shown in the graph below describe this firm’s net revenue (profit) level for each of the three price levels shown. $ Marginal cost Total average cost P1 P2 P3 Q P1 – P2 – P3 - (6) 15. A timberland owner expects to earn an 8 percent rate of return on her investments. She owns a 25 year old stand of pine that could be sold today for $600 per acre as pulpwood. If she waits 5 years the stand could be sold for $900 per acre as sawtimber. Should she sell the stand now or wait 5 years? 5 NAME: ________________________________________________ (6) 16. The Acme Lumber Company produces pallet lumber that it sells into a highly competitive market. Its average sales price is $120 per MBF cash-and-carry on the dock at their mill. Its fixed costs total approximately $15,000 per month. Its marginal cost is currently running at $135 per MBF, shown on the graph. Given the marginal cost curve below should Acme increase or decrease its output? $’s MC $135 Q1 (6) Q 17. Why is the typical production function [output = f(inputs)] sinusoidally shaped? 6