region - Fort Bend ISD
advertisement

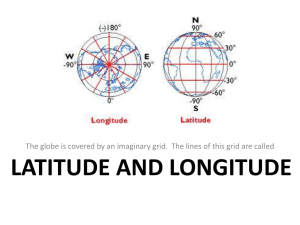
The Five Themes of Geography MR. HELP MR. HELP • • • • • M—Movement R—Region H/E—Human Environment Interaction L—Location P—Place MOVEMENT It helps explain how people, goods, and ideas get from one place to another. REGION Geographic area displaying some type of unity. –Landforms –Language –Industry –Climate - Government - Religion - Vegetation Types of Regions 1. Formal Regions Defined by governmental or administrative boundaries. United States, Houston, The Rockies 2. Functional Regions Regions defined by a function Airline, Newspaper, Public Transport 3. Perceptual Regions Regions loosely defined by people’s perceptions. The Middle East, The South Human Environment Interaction Describes how people adapt to and change their environment. LOCATION Where is it in the World? ABSOLUTE latitude and longitude. an address RELATIVE Where is it in terms of other locations? The Marshall Islands are 10' North latitude and 165' East longitude. Chad is located south of Libya, west of Sudan, East of Niger and North of the Central African Republic Latitude and Longitude Challenge 30N, 95W Houston, Texas 32S, 116E Perth, Australia 30N, 31E Cairo, Egypt 41N, 29E Istanbul, Turkey PLACE Physical – landforms, bodies of water, climate, soil, animals, plant life Human – Architecture, Religion, Language, Government, Clothing, Food San Francisco