Chapter 12 PowerPoint Slides

Introduction to
Geography
Arthur Getis, Judith Getis, &
Jerome D. Fellmann
Urban Geography
Chapter 11
Overview
The Functions of Urban Areas
The Location of Urban Settlements
Systems of Urban Settlements
Inside the City
Suburbanization in the U.S.
Central City Change
World Urban Diversity
The Functions of Urban Areas
Retailing
Wholesaling
Manufacturing
Business Services
Entertainment
Political & Official
Administration
Military Defense Needs
Social & Religious
Service
Public Services
Education
Transportation &
Communications
Meeting Places
Recreation
Visitor Services
Residential Areas
The Location of Urban
Settlements
Site
Break-in-bulk locations
River crossings, head-of-navigation locations, railheads
Situation
The Economic Base
Basic sector
Workers engaged in “export” activities
Nonbasic sector
Support the urban area, but do not bring in outside money
Basic/nonbasic ratio
Multiplier effect
Systems of Urban Settlements
The Urban Hierarchy
Rank-Size Rule
Primate cities
World cities
Urban influence zones
Towns in Agricultural Areas
Central Place Theory
Network cities
Central Place Theory
Walter Christaller
A model for helping to explain town interdependence
Threshold & range
A hierarchy exists of numerous small towns offering basic goods and services and fewer large towns offering a wider range of goods
Inside the City
Competitive bidding for land determines much of the land use within the city
In general, population density & land values decrease as distance from the CBD increases
Peak-value intersections
Population densities tend to show a hollow center
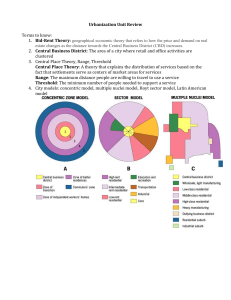
Models of Urban Land
Structure
Concentric Zone Model
Sector Model
Multiple-Nuclei Model
Social Areas of Cities
City residents, especially in larger, more complex cities, will often segregate themselves based on:
Social status
Family status
Ethnicity
Institutional Controls
Local & national governments pass laws to control urban life
Zoning and other nonmarket controls
Suburbanization in the U.S.
Metropolitanization & suburbanization after
WWII
Housing developments served as a pull factor to the suburbs
Industries followed the trend
Suburbs began to rival the power of the central city
Edge Cities
Central City Change
Constricted central cities
Suburbanization reduced the economic base of the central city and isolated its residents
Immigration & gentrification have revived many urban areas
Expanding central cities
Cities have expanded automobile linkages to keep the suburbs within the sphere of the central city
World Urban Diversity
U.S. & Canadian cities
West European cities
East European cities
Cities in the Developing World
Latin America
Asia
Africa