File
advertisement

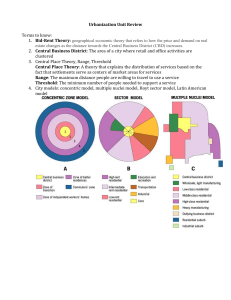
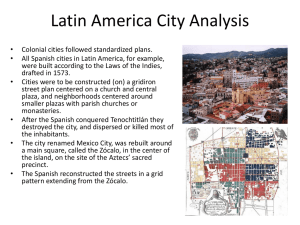
Vocab and Concepts Central Place Theory Site vs. Situation CBD Suburbs Shantytowns / favelas Suburban sprawl Edge cities Primate Cities Rank-size rule Gentrification New Urbanism New Vocab White Flight – Middle class (not always white) residents leaving the urban center for the suburbs WASPs –White Anglo-Saxon (British) Protestants Federal Home Loan Programs – Laws like the G.I. Bill made affordable loans available to millions of Americans after WWII Levittowns – Quickly made homes / towns that were made to keep pace with demand after WWII New Vocab Colonial cities – Cities with origins as centers of colonial trade or administration. Many of these cities retain their European-style buildings and street design (Mumbai, India) Gateway Cities - Places where immigrants enter a new country (New York, Miami) Megacities – City with population over 10 million people Megalopolis – Two or more cities and their urbanized areas merge together (N.E. US) World cities – global center for finance, trade, commerce (New York, London, Tokyo) Resource vs. Transportation Nodes Resource Transportation Towns or cities founded City founded because two because of their proximity to a natural resource Example: Sacramento (gold) or more lines of transportation intersect Example: San Francisco Forms of Settlements Dispersed Settlements Common in Western US Linear Settlements Common in Europe but found everywhere. Follows road or river (transportation) Nucleated Settlements Found mostly in England and Central Europe. Defined by settlements around central market or church Concentric Zone Model First observed by Ernest Burgess during his studies of Chicago. Can apply to many North American cities. Sector Model The Hoyt Sector Model developed by Homer Hoyt in 1939. The model can also be applied to North American cities and accounts for ethnic and affluent neighborhoods. Multiple Nuclei Model Pioneered by Chauncey Harris and Edward Ullman in their observations of North American cities as the suburbs developed. Note the development of outlying business districts Galactic City or Peripheral Model The Galactic City model is also observed in North America and represents the rising importance of suburban CBDs. Latin American City Model Obviously found in Latin America. This model reflects the regions European Colonial past. Specifically, cities in Latin America reflect the Spanish influence and the Laws of the Indies which governed the way cities were built. For instance, many cities will feature a plaza or central square and a main road leading out from the plaza. Fall Line Cities Cities that are as far up a coastal river that a boat can travel before waterfall or narrowing river. This forces goods to be offloaded to another form of transportation Example: Albany, New York