Joints
advertisement

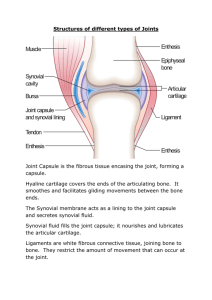
Joints Joints (Articulations) o Articulation—________________________________________________________ o Functions of joints: ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Classification of Joints o Joints are classified and sub classified in many ways o The first is by structure: ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ o The first 2 reflect the type of connective tissues binding them together o Synovial allows many ranges of movement and is the one we think of when we think of joints Three functional classifications: Synarthroses—__________________________ Amphiarthroses—__________________________ Diarthroses—_________________________ Fibrous Joints o ___________________________________________________________________ o _____________________________ o Most are synarthrotic (___________________) o Three types: ______________________ Rigid, interlocking joints containing short connective tissue fibers Allow for growth during youth In middle age, sutures ossify and are called synostoses ______________________ Bones connected by ligaments (bands of fibrous tissue) Movement varies from immovable to slightly movable ______________________ Peg-in-socket joints of teeth in alveolar sockets Fibrous connection is the periodontal ligament Cartilaginous Joints o Bones united by cartilage o ______________________________ o Two types: __________________________ _________________________________________________________ All are synarthrotic __________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Strong, flexible amphiarthroses Synovial Joints o Include all limb joints; most joints of the body o Distinguishing features: __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Outer fibrous capsule of dense irregular connective tissue Inner synovial membrane of loose connective tissue __________________________________________________________ Lubricates and nourishes articular cartilage __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Join bone to bone and can be inside or outside of the joint capsule __________________________________________________________ Small packets of connective tissue containing synovial fluid Movements at Synovial Joints o _____________________________ o _____________________________ Flexion, extension, hyperextension Abduction and adduction Circumduction o _____________________________ Pronation (_______________) and supination (_________________) o _____________________________ Dorsiflexion, plantar flexion of the foot Inversion, eversion Protraction, retraction Opposition Gliding Movements o _____________________________________________________________________ o Examples: Intercarpal joints Intertarsal joints Between articular processes of vertebrae Angular Movements o _____________________________________________________________________ __________________—decreases the angle of the joint __________________— increases the angle of the joint __________________—excessive extension beyond normal range of motion Angular Movements o _____________________________________________________________________ __________________—movement away from the midline __________________—movement toward the midline __________________—flexion + abduction + extension + adduction of a limb so as to describe a cone in space Rotation o _______________________________________________________________________ o Examples: Between C1 and C2 vertebrae Rotation of humerus and femur Special Movements o Movements of the foot: ___________________ (upward movement) (digging your heal) ___________________ (downward movement) (standing on your tiptoe) ___________________ (turn sole medially) ___________________ (turn sole laterally) o Movements in a transverse plane: ___________________ (anterior movement) ___________________ (posterior movement) o ___________________ (lifting a body part superiorly) o ___________________ (moving a body part inferiorly) o ____________________________________ Movement in the saddle joint so that the thumb touches the tips of the other fingers Structural Classification of Synovial Joints o Six types, based on shape of articular surfaces: _____________________ Flat or slightly curved surfaces Short gliding movements _____________________ Motion along a single plane _________________ and __________________ only _____________________ Rounded end of one bone conforms to a “sleeve,” or ring of the other Permits rotation only _____________________ (____________________) Both articular surfaces are oval One bone nestled in a depression on the other Permit all _________________ movements _____________________ Allow greater freedom of movement than condyloid joints Each articular surface has both concave and convex areas _____________________ _____________________________________________________ Shoulder (______________________) Joint o _________________________________________________________________ o Easily and most frequently dislocated joint Stability is sacrificed for greater freedom of movement o Ball-and-socket joint: ________________________________________________ o Bursae of this joint are especially large and numerous to reduce the great amount of friction that happens here Inflammation of these bursae can cause restriction of motion and pain _________________________________________________________ Elbow Joint o __________________________________________________________________ o Hinge joint formed mainly by the _____________________________________ o Extremely stable for 3 reasons: The bony surfaces of the humerus and ulna interlock The _____________________ is very thick The capsule is reinforced by ____________________ Hip (__________________) Joint o __________________________________________________________________ o Head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the coxal bone o The combination of an almost complete bony socket, a strong joint capsule, supporting ligaments, and muscular padding makes this an extremely stable joint o __________________________________________________________________ Knee Joint o __________________________________________________________________ o Three joints surrounded by a single joint cavity: ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ o At least 12 associated bursae o Joint capsule is reinforced by muscle tendons and ligaments ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________