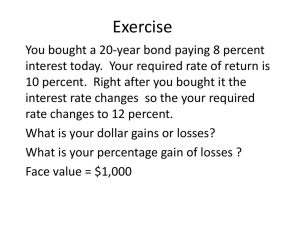EXAM
advertisement

EXAM Management of Financial Institutions Question No: 1 (marks: 2) Pension funds are the example of: a. b. c. d. Financial intermediaries Financial markets Borrowers Lenders Question No: 2 (marks: 2) In Pakistan regulation and supervision of the banking industry is settled by: a. b. c. d. National bank SECP State bank Ministry of finance Question No: 3 (marks: 2) Through which one of the following central bank influences the money supply in an economy: a. b. c. d. Monetary policy Prudential regulations Open market operation Banking ordinance Question No: 4 (marks: 2) Buying of securities results in printing of new money and lowering the supply of specific security this process is known as: a. b. c. d. Purchase of securities Repurchase of securities Discounting of securities Rediscounting of securities Question No: 5 (marks: 2) Financial regulators, such as the______________ supervises the capital markets in their respective countries to ensure that investors are protected against frauds. a. b. c. d. State bank International chamber of commerce Security & exchange commission Banking inspection department Question No: 6 (marks: 2) Which one of the following is NOT the division of exchange policy department? a. b. c. d. Policy division Exchange companies division Investment division Recruitment division Question No: 7 (marks: 2) Banks seek to maximize____________ for a given amount of risk on their balance sheet. a. Profitability b. Loans c. Deposits d. Securities Lecture # 28 Banks seek to maximize profitability for a given amount of risk on their balance sheet. Question No: 8 (marks: 2) The amount of capital a bank is required to hold is the function of which one of the following? The amount of required reserve b. The credit rating requirement c. The amount and quality of assets d. Leverage requirement Lecture # 16 The amount of capital a bank is required to hold is a function of the amount and quality of its assets. a. Question No: 9 (marks: 2) Mutual funds belong to a group of financial intermediaries known as: a. b. c. d. Investment companies Banks Pension funds Insurance companies Question No: 10 (marks: 2) Which one of the following is responsible for overall governance of the mutual funds? Directors Government c. Government’s agent d. Shareholders Lecture # 22 The directors of the fund are responsible for overall governance of the fund. a. b. Question No: 11 (marks: 2) ACAC is the acronym of which of the following? a. b. c. d. Access customer advocate center Agricultural credit advisory committee Agricultural credit accounting committee Agricultural credit accounting commission Question No: 12 (marks: 1) Which of the following functions is NOT performed by the audit department? a. b. c. d. Financial audit Operational audit Information technology audit Research & development Question No: 13 (marks: 1) Which of the following stands for GFS? a. b. c. d. Government Finance Statistics Global Field Services Global Financial System Global Forecast System Question No: 14 (marks: 1) Which of the following countries got the first loan from World Bank? a. b. c. d. Germany Norway France United States of America Question No: 15 (marks: 1) Which of the following channels of commercial banks is known as computerized telecommunications device? a. b. c. d. Branch Automated teller machine Telephone banking Online banking Question No: 16 (marks: 1) Which of the following role is played by the board of directors of a bank? a. b. c. d. Make deposits Make loans Oversee bank activities Handle withdrawals Question No: 17 (marks: 1) Which one of the following is responsible for the supervision of non banking financial institutions? Securities & exchange commission b. State Bank c. Chamber of commerce d. Ministry of finance Lecture # 19 a. The responsibility for supervision of nonbank finance companies has been separated and transferred to Securities Exchange Commission. Question No: 18 (marks: 1) In which of the following forms the National Investment Trust units are traded? Share b. Debenture c. Bond d. Certificate Lecture # 23 Mutual Funds were introduced in Pakistan in 1962, with the public offering of National Investment (Unit) Trust (NIT) which is an open-end mutual fund in the public sector. a. Question No: 19 ( M a r k s: 3 ) For investment purpose customers always judge the profitability of the bank. To attract more customers how a bank can enhance its profitability? Answer: Banks can increase their customer base and their profitability by providing all services under one roof namely traditional banking services and the more modern financaial services like investment banking, credit card services, mutual fund services, life insurance products. Also by charging customers based on their credit profie i.e higher charges for low credit worthy clients they can increase their charges and fees. Also by developing new products which will be used by people in their everyday life and than charging a small fee for the same the banks can increase their profits. Question No: 20 ( M a r k s: 3 ) Define merchant banks. Answer: Merchant banks are those banks which are involved in any type of trading. These kind of banks also provide shares to customers. They also buy and sellcompanies. They raise capital for the companies in various ways like IPO, Debt instruments and convertible instruments. Question No: 21 ( M a r k s: 5 ) Pakistan is not able to sustain growth over the long term. Do you agree with this statement? Give reasons to support your answer. Answer: Pakistan has been trying like all its neighbours to achieve a growth in excess of 7%however there have been multiple of factors that has pegged it back namely, the US led war in Afghanistan, the earthquakes, which have happened, the riots that have taken place in Karachi, global slowdown, the ever present threat of a war with India. Inspite of all these factors Pakistan economy has shown great strength and determination in achieving growth of 7% in few years. Question No: 22 ( M a r k s: 5 ) Banks provide investment facilities to its customers. How customers can judge the management soundness and profitability of the banks? Answer: The financial statements of the banks are not easy for everyone to interpret. As a result in order to judge the management soundness what one can do is check the various operational and profitability ratios of the concerned banks against the ones shown by the good banks and against the averages for the banking industry. One of the ratio is the amount of income generated against the expenses incurred to earn the same. This will enable us to know the margin of safety. Another way can be to compare the interest income against interest expense. Also one can compare how much fixed expenses are being incurred, how much are the overheads etc and compare with other banks to see the soundness of management. Question No: 23 ( M a r k s: 5 ) If State Bank has capital shortage and wants to borrow, what are the possible sources through which it can get loan? Answer: In order to raise liquidity the SBP can do the following: 1) Sell securities in the open market and raise cash. 2) Change the reserve requirements of the bank. 3) Borrow from domestic lenders and financial institutions. 4) Issue new domestic bonds. 5) Borrow from external agencies like the IMF or ADB. 6) Issue foreign bonds to Pakistanis residing abroad. 7) Issue foreign bonds to the world markets. The following questions are worth 3 points each. Provide the single best response. 1.The primary goal of a publicly-owned firm interested in serving its stockholders should be to a. Maximize expected total corporate profit. b. Maximize expected EPS. c. Minimize the chances of losses. d. Maximize the stock price per share. e. Maximize expected net income. 2. Which of the following actions are likely to reduce agency conflicts between stockholders and managers? a. Paying managers a large fixed salary. b. Increasing the threat of corporate takeover. c. Placing restrictive covenants in debt agreements. d. All of the statements above are correct. e. Statements b and c are correct. 3. In recent years, both expected inflation and the market risk premium (kM - kRF) have declined. Assume that all stocks have positive betas. Which of the following is likely to have occurred as a result of these changes? a. The average required return on the market, kM, has remained constant, but the required returns have fallen for stocks that have betas greater than 1.0. b. The required returns on all stocks have fallen by the same amount. c. The required returns on all stocks have fallen, but the decline has been greater for stocks with higher betas. d. The required returns on all stocks have fallen, but the decline has been greater for stocks with lower betas. e. The required returns have increased for stocks with betas greater than 1.0 but have declined for stocks with betas less than 1.0. 4. The risk-free rate is 5 percent. Stock A has a beta = 1.0 and Stock B has a beta = 1.4. Stock A has a required return of 11 percent. What is Stock B's required return? a. 12.4% b. 13.4% c. 14.4% d. 15.4% e. 16.4% 5. Assume that the risk-free rate is 5 percent and that the market risk premium is 7 percent. If a stock has a required rate of return of 13.75 percent, what is its beta? a. 1.25 b. 1.35 c. 1.37 d. 1.60 e. 1.96 6.You have determined the profitability of a planned project by finding the present value of all the cash flows from that project. Which of the following would cause the project to look more appealing in terms of the present value of those cash flows? a. The discount rate decreases. b. The cash flows are extended over a longer period of time, but the total amount of the cash flows remains the same. c. The discount rate increases. d. Statements b and c are correct. e. Statements a and b are correct. 7. Your family recently obtained a 30-year (360-month) $100,000 fixed-rate mortgage. Which of the following statements is most correct? (Ignore all taxes and transactions costs.) a. The remaining balance after three years will be $100,000 less the total amount of interest paid during the first 36 months. b. The proportion of the monthly payment that goes towards repayment of principal will be higher 10 years from now than it will be this year. c. The monthly payment on the mortgage will steadily decline over time. d. All of the statements above are correct. e. None of the statements above is correct. 8. What is the present value of a 5-year ordinary annuity with annual payments of $200, evaluated at a 15 percent interest rate? a. $ 670.43 b. $ 842.91 c. $1,169.56 d. $1,348.48 e. $1,522.64 9. You are considering buying a new car. The sticker price is $15,000 and you have $2,000 to put toward a down payment. If you can negotiate a nominal annual interest rate of 10 percent and you wish to pay for the car over a 5-year period, what are your monthly car payments? a. $216.67 b. $252.34 c. $276.21 d. $285.78 e. $318.71 10. You just bought a house and have a $150,000 mortgage. The mortgage is for 30 years and has a nominal rate of 8 percent (compounded monthly). After 36 payments (3 years) what will be the remaining balance on your mortgage? a. $110,376.71 b. $124,565.82 c. $144,953.86 d. $145,920.12 e. $148,746.95 The following questions are worth 3 points each. Provide the single best response. 1.If markets are in equilibrium, which of the following will occur: a. Each investment's expected return should equal its realized return. b. Each investment's expected return should equal its required return. c. Each investment should have the same expected return. d. Each investment should have the same realized return. e. All of the statements above are correct. 2. Johnston Corporation is growing at a constant rate of 6 percent per year. It has both common stock and non-participating preferred stock outstanding. The cost of preferred stock (kp) is 8 percent. The par value of the preferred stock is $120, and the stock has a stated dividend of 10 percent of par. What is the market value of the preferred stock? a. $125 b. $120 c. $175 d. $150 e. $200 3. A share of common stock has just paid a dividend of $2.00. If the expected long-run growth rate for this stock is 15 percent, and if investors require a 19 percent rate of return, what is the price of the stock? a. $57.50 b. $62.25 c. $71.86 d. $64.00 e. $44.92 4. Cartwright Brothers' stock is currently selling for $40 a share. The stock is expected to pay a $2 dividend at the end of the year. The stock's dividend is expected to grow at a constant rate of 7 percent a year forever. The risk-free rate (kRF) is 6 percent and the market risk premium (kM - kRF) is also 6 percent. What is the stock's beta? a. 1.06 b. 1.00 c. 2.00 d. 0.83 e. 1.08 5.A project has an up-front cost of $100,000. The project's WACC is 12 percent and its net present value is $10,000. Which of the following statements is most correct? a. The project should be rejected since its return is less than the WACC. b. The project's internal rate of return is greater than 12 percent. c. The project's modified internal rate of return is less than 12 percent. d. All of the statements above are correct. e. None of the statements above is correct. 6. The Seattle Corporation has been presented with an investment opportunity that will yield cash flows of $30,000 per year in Years 1 through 4, $35,000 per year in Years 5 through 9, and $40,000 in Year 10. This investment will cost the firm $150,000 today, and the firm's cost of capital is 10 percent. Assume cash flows occur evenly during the year, 1/365th each day. What is the payback period for this investment? a. 5.23 years b. 4.86 years c. 4.00 years d. 6.12 years e. 4.35 years 7. Braun Industries is considering an investment project that has the following cash flows: Year Cash Flow 0 1 2 3 4 -$1,000 400 300 500 400 The company's WACC is 10 percent. What is the project's payback, internal rate of return (IRR), and net present value (NPV)? a. Payback = 2.4, IRR = 10.00%, NPV = $600. b. Payback = 2.4, IRR = 21.22%, NPV = $260. c. Payback = 2.6, IRR = 21.22%, NPV = $300. d. Payback = 2.6, IRR = 21.22%, NPV = $260. e. Payback = 2.6, IRR = 24.12%, NPV = $300. 8. A project has the following net cash flows: Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 Project Cash Flow -$ X 150 200 250 400 100 At the project's WACC of 10 percent, the project has an NPV of $124.78. What is the project's internal rate of return? a. 10.00% b. 12.62% c. 13.49% d. 15.62% e. 16.38% 9. A decrease in the debt ratio will generally have no effect on __________. a. Financial risk. b. Total risk. c. Business risk. d. Market risk. e. None of the above is correct. (It will affect each type of risk above.) 10. From the information below, select the optimal capital structure for Minnow Entertainment Company. a. Debt = 40%; Equity = 60%; EPS = $2.95; Stock price = $26.50. b. Debt = 50%; Equity = 50%; EPS = $3.05; Stock price = $28.90. c. Debt = 60%; Equity = 40%; EPS = $3.18; Stock price = $31.20. d. Debt = 80%; Equity = 20%; EPS = $3.42; Stock price = $30.40. e. Debt = 70%; Equity = 30%; EPS = $3.31; Stock price = $30.00. A. Multiple choice questions (15 points in total) Choose the best answer. 1. Which of the following represents an investment activity? a. The firm buys a new piece of equipment b. The firm buys back shares of stock c. The firm pays dividends on common stock d. The firm retires some bonds before they were due to mature e. The firm issues bonds The best answer is A. 2. Which of the following statements is most correct? a. An advantage of the sole proprietorship is unlimited liability. b. A disadvantage of a partnership is separation of decision-making and control. c. A disadvantage of a sole proprietorship is double taxation. d. A disadvantage of a sole proprietorship is limited life. e. An advantage of the partnership is easy access to capital. The best answer is D. The sole proprietorship’s life is limited to that of its owner. 3. A cost incurred by the principal in an agency relationship to limit the actions of the agent is referred to as: a. Bonding cost b. Monitoring cost c. Residual loss d. Fiduciary cost e. Cost of working capital The best answer is B. Monitoring costs are borne by the principal to “watch” the agent. 4. Which of the following is an internal source of financing for the firm? a. Current assets b. Retained earnings c. Depreciation d. Long-term debt The best answer is B. The only sources of financing listed below are B and D, but D is an external source of financing. 5. Which of the following items is deductible by corporations in computing their taxable income? a. Interest paid b. Dividends paid to common shareholders c. Dividends paid to preferred shareholders d. b and c only e. a, b, and c are all deductible for corporations The best answer is A. Dividends paid are not deductible. 6. Comparing the financial performance of Google, Inc. to a major group of competitors in the same industry is one example of a(n): a. Benchmarking analysis Trend analysis Peer group analysis Agency analysis The best answer is C. b. c. d. 7. Beta is a measure of: a. Firm-specific risk b. Total risk c. Systematic risk d. Unsystematic risk e. Diversifiable risk The best answer C. Beta measures systematic risk (which is the same as nondiversifiable or market risk). 8. Which of the following statements is false? a. The CAPM has one factor while the APT allows many factors b. The CAPM assumes a positive relationship between expected return and risk. c. The APT assumes a negative relationship between expected return and risk. d. All of the above statements are true. The best answer is C. The APT also assumes a positive relationship between expected return and risk. It just uses different factors to account for this than those used in the traditional CAPM 9. If an investor holds only stock in IBM Corporation the relevant measure of risk will be a. Beta b. Expected return c. Standard deviation d. Covariance e. Correlation The best answer is C. The appropriate measure of risk when only one stock is holed is standard deviation. Beta is appropriate risk measure when holding more than one security. The others are not risk measures. 10. The CAPM implicitly assumes that investors will not be compensated for ________ since it is diversifiable. a. Systematic risk b. Total risk c. Market risk d. Unsystematic risk The best answer D. The CAPM uses beta to indicate that investors will be compensated for market risk (same as systematic risk). They will not be compensated for total risk, but total risk does not fit the second half of the sentence. Some of total risk is diversifiable, but some is not. Therefore, the correct answer that suits the entire sentence is unsystematic risk (same as firmspecific or diversifiable risk). B. Short answers (50 points in total) 1. (5 points) A prestigious investment bank designed a new security that pays a quarterly interest of $10 permanently. What is the price of the security if the state annual interest rate is 12 percent, compounded quarterly? Payment = $10 quarterly, r = 12%, quarterly. In this case, the “r” we have is not the periodic rate and that is what we need to use. Use r = 12%/4 = 3%; PV = payment r = $10/0.03 = $333.33 2. (5 points) What is the present value of end-of-year cash flows of $2,000 per year, with the first cash flow received two years from today and the last one 22 years from today? Use a discount rate of 8 percent. This is an ordinary annuity. The total number of periods is 20. PMT = $2,000; N = 20; I/Y = 8%; CPT PV PV = $19,636.2948 To find PV of this cash flow now I discount it two periods back: FV = $19,636,29; N= 2; I/Y = 8%; CPT PV 3. PV = $16,834.9578 (5 points) Your employer has agreed to make 80 quarterly payments of $400 each into a trust account to fund your early retirement. The first payment will be made 3 months from now. At the end of 20 years (80 payments), you will be paid 10 equal annual payments, with the first payment to be made at the end of Year 20. The funds will be invested at 8%, quarterly compounding. This rate is not expected to change over time. How large will each of your 10 receipts be? This is a two-step problem. The first step is to solve for the future value of the payments that your employer is making. Since payments are quarterly and interest is quarterly, use the periodic rate. PMT = $400; I/Y = 2%; N = 80; CPT FV FV = $77,508.78 The second step is to use this FV as the PV of the payments you will be receiving annually. Since you are receiving annual payments, convert the period rate in this step to annual rate (EAR). EAR = (1 + 0.02)4 – 1 = 0.082432 = 8.2432% Also, since the first receipt will be at the end of Year 20 and the last payment by the employer was also at the end of Year 20, this is an annuity due. Change calculator to BEG: PV = $77,508.78; N = 10; I/Y = 8.2432; CPT PMT PMT = $10,788.78 [Note: If you do not change calculator to BEG: You must discount the FV back one period.] PV = $77,508.78/1.082432 = $71,606.1425 PV = $71,606.1425; N = 10; I/Y = 8.2432; CPT PMT PMT = $10,788.78 4. (5 points)A bond is sold at $923.14 (below its par value of $1000). The bond has 15 years to maturity and investors require a 10-percent yield on the bond. What is the coupon rate for the bond if the coupon is paid semiannually? PV = -923.14; N = 30 periods; I/Y = 5%; FV = 1,000 CPT PMT PMT = $45 or 4.5% of par value paid semiannually Annual coupon payment = $45 x 2 = $90 5. (5 points)The current price of a 10-year, $1,000 par value bond is $1,158.91. Interest on this bond is paid every six months, and the nominal annual yield is 14 percent. Given these facts, what is the annual coupon payment on this bond? N = 20; PV = 1,158.91; FV = 1000; I/Y = 7%; CPT PMT PMT = $85 Since the payments are semi-annual, multiply by two to get the annual payment. So, PMT = 85 x 2 = 170 which is 17% of par value. 6. (5 points)You have just purchased a newly issued $1,000 five-year Vanguard Company bond at par. This five-year bond pays $60 in interest semiannually. You are also considering the purchase of another Vanguard Company bond that returns $30 in semiannual interest payments and has six years remaining before it matures. This bond has a face value of $1000. (a) What is the effective annual return on the five-year bond? Assume that the annual (coupon) rate you used in part (a) is the correct interest rate (YTM) for the bond with six years remaining before it matures. (b) What should you be willing to pay for that bond? a) For the 5-year bond, since PV = FV, then coupon rate = yield. Coupon rate = (60 x 2) 1000 = 12% (annualized). Therefore, the annualized yield is 12%, but the question is about the effective yield. So, we use the EAR formula. EAR = (1 + r)t - 1 = (1 + 0.06)2 - 1 = 0.1236 = 12.36% Remember the “r” in the formula above stands for periodic rate and the “t” stands for the number of compounding periods in a year. The rate is 6% per semiannual period and there are 2 semiannual periods in a year. b) The price you will be willing to pay is: PMT = 30; N = 6 x 2 = 12; FV = 1000; I/Y = 6; CPT PV 7. PV = $748.48 (5 points) What will be the nominal rate of return on a preferred stock with a $100 par value, a stated dividend of 8 percent of par, and a current market price of $140? P=Dk D = 8% x 100 = $8 k = D P = 8 140 = 0.0571 = 5.71% 8. (5 points) A stock is trading at $80 per share. The stock is expected to have a yearend dividend of $4 per share which is expected to grow at some constant rate g throughout time. The stock’s required rate of return is 14 percent. If you are an analyst who believes in efficient markets, what would be your forecast of g? P0 = $80; D1 = $4; k = 14% k = (D1 P0) + g g = k - (d1 P0) = 0.14 - (4 80) = 0.14 - 0.05 = 0.09 = 9% 9. (10 points)A common stock pays a current dividend of $2. The dividend is expected to grow at an 8 percent annual rate for the next three years; then it will grow at 4 percent in perpetuity. The appropriate discount rate is 12 percent. What is the price to this stock? D1 = 2.00 x (1.08) = 2.16; D2 = 2.16 x (1.08) = 2.3328; D3 = 2.3328 x (1.08) = 2.5194; D4 = 2.5194 x (1.04) = 2.6202; This is the new growth period, so we use 4% instead of 8%. P3 = D4 (k - g) = 2.6202 (0.12 - 0.04) = $32.7525 To value the cash flows using the worksheet: CF0 = 0 CF1 = 2.16 this indicates dividend 1 is to be valued CF2 = 2.3328 this indicates dividend 2 is to be valued CF3 = 2.5194 + 32.7525 this indicates dividend 3 and the price that represents dividends 4 to infinity are to be valued I = 12% use “k”, not “g” – growth rate! CPT NPV NPV = $28.89 C. Problem solving (35 points in total) 10. (10 points) Based on the following information calculate the expected return and the standard deviation for the two stocks. State of Economy Probability of State of Economy Rate of Return Rate of Return on stock A on stock B Recession 0.10 6% -20% Normal 0.60 7% 13% Boom 0.30 11% 33% a. What is the expected return on stock A and stock B? b. What is the variance and standard deviation for stock A and stock B? c. What isof the standard deviation of an equally weighted portfolio of these two stocks if the correlation is 0.2? Solution: a) The expected return of an asset is the sum of the probability of each return occurring times the probability of that return occurring. So, the expected return of each stock asset is: E(RA) = .10(.06) + .60(.07) + .30(.11) = .0810 or 8.10% E(RB) = .10(-.2) + .60(.13) + .30(.33) = .1570 or 15.70% b) To calculate the standard deviation, we first need to calculate the variance. To find the variance, we find the squared deviations from the expected return. We then multiply each possible squared deviation by its probability, and then add all of these up. The result is the variance. So, the variance and standard deviation of each stock are: 2A= .10(.06 - .0810)^2 + .60(.07 - .0810)^2 + .30(.11 - .0810)^2 = .000369 A= (.00037)^(1/2)= .01921 or 1.921% 2B= .10(.-2 - .1570)^2 + .60(.13 - .1570)^2 + .30(.33 - .1570)^2 = .022161 B= (.02216)1/2 = .14886 or 14.89% c) To calculate the portfolio standard deviation, we first need to calculate the variance. To find the variance we use the formula based on the individual stocks’ variances and the covariance between the two stocks. So, the portfolio variance is: p2 = wA2A2 + wB2B2 + 2wAwB ABAB p2 = (0.5^2)(0.01923^2) + (0.5^2)(0.1489^2) + 2(0.5)(0.5)(0.2)( 0.0192)( 0.1489) 2 p = 0.0059183 11. (8 points) Security A has an expected return of 8 percent with a standard deviation of 1.5 percent. Security B has an expected return of 12 percent with a standard deviation of 2.4 percent. The two securities have a correlation coefficient of 0.20. If you invest 40 percent of your funds in Security A and 60 percent in Security B, the standard deviation of the portfolio will be (Note: change calculator to 6 decimals). Covariance ab = a b = 0.2(0.015)(0.024) = 0.000072 Portfolio p2 = (0.4^2)(0.015^2) + (0.6^2)(0.024^2) + 2(0.4)(0.6)(0.000072) = p2 = 0.000036+ 0.000207 + 0.000035 = 0.000278 Portfolio standard deviation is = 0.016673 = 1.67%. 12. (10 points) The market value of the shares of Microsoft Corporation is currently $24 million, and their beta is 1.4. Microsoft has a nominal (face value) $6 million of 8 percent coupon debt outstanding, which matures in 7 years (the par is $1000). These bonds have a beta of 0.1, and they currently yield 10 percent market interest. The expected market return is 14% and the risk-free rate of return is 5% a. What is the total market value of the firm? (Note: MV is the sum of the equity and debt market values). b. What is the weighted average beta of Microsoft’s assets? What is the required rate of return on Microsoft’s assets? (Hint: use CAPM equation with the computed average beta) Solution: a) Total Market value of firm = Market value of debt + Market value of Total MV = $5,415,780 + $24,000,000 = $29,415,780 Where: Value of equity = $24,000,000 Value of debt = $902.63 × 6,000 = $5,415,780 Number of bond outstanding = 6,000,000/1000 = 6,000 I have used the financial calculator to find the market price per bond: PMT = 80; N = 7; I/Y = 10%; FV = 1000 CPT PV = -$902.63 b) Beta of assets = Beta of equity (Equity/Value) + Beta of debt (Debt/Value) Beta = 1.4 × (24/29.415) + 0.1 × (5.415/29.415) = 1.161 Required rate of return on firm’s assets = 5% + 1.161(14% - 5%) = 15.444% 13. (7 points) Baxter Video Product’s sales are expected to increase by 20% from $5 million in 2010 to $6 million in 2011. Its assets totaled $3 million at the end of 2010. Baxter is already at full capacity, so its assets must grow at the same rate as projected sales. At the end of 2010, current liabilities were $1 million, consisting of $250,000 of accounts payable, $500,000 of notes payable, and $250,000 of accruals. The after-tax profit margin is forecasted to be 5%, and the forecasted dividend payout ratio is 70%.Use the AFN equation to forecast Baxter's additional funds needed for the coming year. Solution: AFN = (A0*/S0)∆S – (L0*/S0)∆S – (PM)(S1)(1 – Payout rate) $3,000,000 $500,000 AFN = $1,000,000 – $1,000,000 – 0.05($6,000,000)(1 $5,000,000 $5,000,000 – 0.7) AFN = (0.6)($1,000,000) – (0.1)($1,000,000) – ($300,000)(1 - 0.7) AFN = $600,000 – $100,000 – $90,000 AFN = $410,000. 1.Which of the following statements best describes the optimal capital structure? a. The optimal capital structure is the mix of debt, equity, and preferred stock that maximizes the company's earnings per share (EPS). b. The optimal capital structure is the mix of debt, equity, and preferred stock that maximizes the company's stock price. c. The optimal capital structure is the mix of debt, equity, and preferred stock that minimizes the company's weighted average cost of capital (WACC). d. Statements a and b are correct. e. Statements b and c are correct. 2. Which of the following factors is likely to encourage a corporation to increase the proportion of debt in its capital structure? a. An increase in the corporate tax rate. b. An increase in the personal tax rate. c. An increase in the company's degree of operating leverage. d. The company's assets become less liquid. e. An increase in expected bankruptcy costs. 3. The Price Company will produce 55,000 widgets next year. Variable costs will equal 40 percent of sales, while fixed costs will total $110,000. At what price must each widget be sold for the company to achieve an EBIT of $95,000? a. b. c. d. e. $2.00 $4.45 $5.00 $5.37 $6.21 4. Texas Products Inc. has a division that makes burlap bags for the citrus industry. The division has fixed costs of $10,000 per month, and it expects to sell 42,000 bags per month. If the variable cost per bag is $2.00, what price must the division charge in order to break even? a. $2.24 b. $2.47 c. $2.82 d. $3.15 e. $2.00 5. Which of the following statements best describes the theories of investors' preferences for dividends? a. Modigliani and Miller argue that investors prefer dividends to capital gains. b. The bird-in-hand theory suggests that a company can reduce its cost of equity capital by reducing its dividend payout ratio. c. The tax preference theory suggests that a company can increase its stock price by increasing its dividend payout ratio. d. One key advantage of a residual dividend policy is that it enables a company to follow a stable dividend policy. e. The clientele effect suggests that companies should follow a stable dividend policy. 6.Trenton Publishing follows a strict residual dividend policy. All else being equal, which of the following factors are likely to cause an increase in the firm's per-share dividend? a. An increase in its net income. b. The company increases the proportion of equity financing in its target capital structure. c. An increase in the number of profitable projects that it wants to fund this year. d. Statements a and b are correct. e. All of the statements above are correct. 7. Albany Motors recently completed a 3-for-1 stock split. Prior to the split, the company had 10 million shares outstanding and its stock price was $150 per share. After the split, the total market value of the company's stock equaled $1.5 billion. What was the price of the company's stock following the stock split? a. $ 15 b. $ 45 c. $ 50 d. $150 e. $450 8. Tarheel Computing's stock was trading at $150 per share before its recent 3-for-1 stock split. The 3-for-1 split led to a 5 percent increase in Tarheel's market capitalization. (Market capitalization equals the stock price times the number of shares.) What was Tarheel's price after the stock split? a. $472.50 b. $ 50.00 c. $ 47.62 d. $428.57 e. $ 52.50 9. Brock Brothers wants to maintain its capital structure that consists of 30 percent debt and 70 percent equity. The company forecasts that its net income this year will be $1,000,000. The company follows a residual dividend policy and anticipates a dividend payout ratio of 40 percent. What is the size of the company's capital budget? a. $ 600,000 b. $ 857,143 c. $1,000,000 d. $1,428,571 e. $2,000,000 10. Makeover Inc. believes that at its current stock price of $16.00 the firm is undervalued in the market. Makeover plans to repurchase 2.4 million of its 20 million shares outstanding. The firm's managers expect that they can repurchase the entire 2.4 million shares at the expected equilibrium price after repurchase. The firm's current earnings are $44 million. If management's assumptions hold, what is the expected per-share market price after repurchase? a. $16.00 b. $17.26 c. $18.18 d. $20.00 e. $24.40 1.Which of the following are reasons why companies move into international operations? a. To take advantage of lower production costs in regions of inexpensive labor. b. To develop new markets for their finished products. c. To better serve their primary customers. d. Because important raw materials are located abroad. e. All of the statements above are correct. 2. Multinational financial management requires that a. The effects of changing currency values be included in financial analyses. b. Legal and economic differences be considered in financial decisions. c. Political risk be excluded from multinational corporate financial analyses. d. Statements a and b are correct. e. All of the statements above are correct. 3. If one Swiss franc can purchase $0.71 U.S. dollar, how many Swiss francs can one U.S. dollar buy? a. 0.71 b. 1.41 c. 1.00 d. 2.81 e. 0.50 4. Currently, in the spot market $1 = 106.45 Japanese yen, 1 Japanese yen = 0.00966 euro, and 1 euro = 9.0606 Mexican pesos. What is the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Mexican peso? a. $1.00 = 2,222 Mexican pesos b. $1.00 = 9.3171 Mexican pesos c. $1.00 = 0.0556 Mexican peso d. $1.00 = 0.1073 Mexican peso e. $1.00 = 152.6 Mexican pesos 5. A textbook sells for $75 in the U.S. market. Exchange rates are such that 1 British pound (£) equals $1.58 U.S. dollars. Assume that purchasing power parity holds, what should the textbook sell for in Britain? a. £ 47.47 b. £ 75.00 c. £118.50 d. $ 47.47 U.S. e. £ 61.24 6. In the spot market, 1 U.S. dollar equals 1.035 euros. 6-month German securities have an annualized return of 6 percent (and therefore have a 6-month periodic return equal to 3 percent). 6-month U.S. securities have an annualized return of 6.5 percent and a periodic return of 3.25 percent. If interest rate parity holds, what is the dollar to euro exchange rate in the 180-day forward market? a. $1 U.S. = 0.9685 euro b. $1 U.S. = 0.9593 euro c. $1 U.S. = 1.0000 euro d. $1 U.S. = 1.0325 euros e. $1 U.S. = 1.0475 euros 1. On the recommendations of the Finance Manager, the board of directors will accept the project if----- a) Benefit Cost Ratio is less than one b) Net Present Value is greater than zero c) Internal Rate of Return is less than cost of capital d) Pay Back Period is greater than target period 2. Identify from the following statements , one statement which is not concerning to market analysis----- a) Production possibilities and constraints b) Consumer behaviour, intentions, motivations, attitudes, preferences and requirements 3. c) Extent of competition and market share d) Suitability of production process From the following sources of finance , find out the free source of finance----- 4 a) Equity Capital b) Preference Capital c) Retained Earnings d) None of the above From the following information, compute the operating cycle of LMP Ltd.-No of days the raw material remain in stock is 60 days, suppliers credit available for 15 days, production time 15 days, finished goods inventory period 15 days, realization from customers takes 25 days. The operating cycle therefore would be---- a) 115 days b) 100 days c) 75 days d) 85 days 5 If the fixed and variable cost at 50% production capacity are Rs.20000 and Rs.30000, respectively, the a) Rs.50000 b) Rs.62000 c) Rs.70000 d) Rs.58000 total cost at 70% capacity will be----- 6. Commercial paper , is an short term usance promissory note with fixed maturity period , issued by----a) Corporates & primary dealers b) All India financial Institutions c) (a) and (b) above d) None of the above 7. Surabhi Enterprises has given you the following information. The Re-order level 4000 units, minimum usage 300 units per week, minimum lead time 2 weeks and reordering quantity 2000 units. The maximum stock level of Surabhi Enterprises should be----- a) 1900 units b) 5400 units c) 2900 units d) 4000 units 7. SusheelHightech Ltd. are selling designer furniture to top customers. There is no direct competition for their product. They are negotiating a big order from one wealthy business magnate. While giving the quotation they should follow ------ a. conversions cost pricing method b. market based pricing c. marginal cost pricing d. full cost pricing 8. Under cash budget system method, working capital is determined by ----a) ascertaining level of current assets b) ascertaining level of current liabilities c) finding cash gap after taking in to account projected cash inflows and outflows d) all of the above 9. IRR is calculated for one of the following purposes----- a) Working capital finance b) Pre-shipment finance c) Project finance d) Post shipment finance 10 Actual Sales minus Break Even Sales means----- a) Profit on sales b) Margin of safety sales c) Loss on sales d) Sales at which no profit or no loss is resulted 11 Conversion cost is calculated on the basis of following formula----- a) Direct Material plus Direct Labour b) Direct Material plus total overheads c) Direct Labour plus direct overheads d) Direct Material plus Administrative Cost 12 Under which method, the cost s are classified under fixed and variable cost and only variable costs are charged to products while fixed cost are written off to Profit and Loss Account. a. standard costing b. Marginal Costing c. Absorption costing d. Job costing 13 The following statements are pertaining to Letter of Credit (LC). One of the statements is wrong. Choose the wrong statement a. All letters of credit in India relating to the foreign trade are subject to provisions of "Uniform Customer and Practice for Documentary Credit" (UCPDC). b. The provisions of UCPDC have the status of law c. The parties to a LC bind themselves to UCPDC provisions by specifically agreeing to do. d. The UCPDC provisions help to arrive at unambiguous interpretation of terms used in LC 15) Which of the following is not part of working capital management? (a) credit period to buyers (b) proportion of current assets to be financed by long term debt (c) dividend payout (d) cash credit limit 16) In an operating cycle which of the following is not there (a) acquisition of raw material (b) acquisition of power (c) acquisition of consumables (d) conversion of raw material into work-in-progress 17) A low current assets ratio implies one of the following (a) greater liquidity & lower risk (b) poor liquidity & higher risk (c) greater liquidity & greater risk (d) poor liquidity & lower risk (a) 19. Financing temporary current assets with short term finance and permanent current assets with long term finance refers to (a) matching approach (b) conservative approach (c) casual approach (d) conservative approach 23) The formula for Economic Order Quantity(EOQ) is------ ( A= stock usage, C = cost of ordering, H= cost for holding stock per unit) a) √2AC/H b) √2ACH c) √2CH/A d) √AH/2C 24) If a buyer of goods gets a discount of 1.5% on a supply of Rs. 100 , if the amount is paid within 10 days where the normal credit period is 50 days. What is the annualized benefit to the buyer if he pays within 10 days. a) 12.75% b) 13.69% c) 14.21% d) 13.65% 25)which of the following is not a risk involved in carrying inventory a) obsolescence of the product b) physical deterioration in the goods c) price fluctuation in the product d) increase in the price of raw material 26) Factoring means e) another entity buys your debts f) another entity buys your credits g) another entity loans an amount to you h) none of the above Question 1: GHI Ltd. manufacturers two products :Product G and Product H. The Variable cost of the manufacture is as follows: Product G Product H Direct Material 3 10 Direct Labour (Rs.6 per 18 12 4 4 hour) Variable Overhead Product G sells for Rs.40 and Product H at Rs.30. During the month of January, the Company is having only 21000 of direct labour. The maximum production capacity of Product G is 5000 units and Product H is 10000 units. From the above facts, answer the following: I. The contribution from Product G and H together is----- a) Rs.32 b) Rs.19 c) Rs.27 d) Rs.40 II. The contribution per labour hour from Product H is----- e) Rs. 4 f) Rs. 2 g) Rs. 3 h) Rs. 5 III. The contribution per labour hour from Product G is----- a) Rs.2 b) Rs.5 c) Rs.15 d) Rs.3 IV. The company can maximize profit if it can choose one of the following combination e) Product G- 3500 units and Product H -5250 units f) Product G- 5000 units and Product H -3000 units g) Product G- 4500 units and Product H -6000 units h) Product G- 4000 units and Product H -4500 units Question 2: A Company producing a single product sells it at Rs. 100 each. The marginal cost of production is Rs.60 each and fixed cost is Rs.40000. Answer the following questions from this information: I. The amount of sales to earn a profit of Rs.50000 a) Rs.225000 b) Rs.125000 c) Rs.500000 d) Rs.90000 II The new break even sales if sales price is reduced by 10% a) Rs.100000 b) Rs.120000 c) Rs.90000 d) Rs.110000 Question 3: Three Investment projects have the following net cash flows. Decide which of them should be accepted using the payback period method. YEA PROJECT PROJECT PROJECT Project D R A B C 0 (10000) (15000) (20000) (30000) 1 5000 5000 10000 0 2 5004 5000 10000 0 3 20000 5000 4000 100000 4 1000 10000 2000 120000 5 - 5000 - 60000 a) Project D b) Project A c) Project C d) Project B Question 4: The cash flow in respect of two projects is given below. The cost of capital is 12% , the discount factor of 12% is also given. Year Project A Project B Discount Factor Discount Factor @ 12% @ 16% 0 (200) (300) 1 1 1 60 100 0.8929 0.8620 2 60 100 0.7972 0.7431 3 60 90 0.7118 0.6406 4 60 70 0.6355 0.5522 5 60 70 0.5674 0.4761 Answer the following question using the above information. I II What is the NPV of Project A (in Rs.) a) 216.29 b) 16.29 c) 200 d) 182.24 What is the NPV of Project B (in Rs.) III IV V a) 260.28 b) 300 c) 17.27 d) 71 What is the Profitability Index of Project A a) 1.30 b) 1.08 c) 1 d) 0.91 What is the Profitability Index of Project B a) 0.86 b) 1 c) 1.06 d) 1.23 What is IRR of Project A a) 15.24% b) 14.24% c) 16.24% d) 14.50% Question 5: The following is the information of XYZ Ltd for last 2 years (Rs. in Lakh). 2005 2004 Difference Profit before 68 83 Tax 34 41 Profit after Tax 34 42 Dividends 28 27 1 Retained 6 15 (9) Tax Earnings How the above information is shown in the cash flow statement----- a) At the sources column Rs.34 Lakh will be shown on account of Profit from operations and on uses column dividend payment of Rs. 28 Lakh will be shown b) At the sources column Rs.6 Lakh will be shown on account of Profit from operations and on uses column nothing is shown c) At the sources column nothing is shown on account of Profit from operations and on uses column Rs.9 Lakh is shown d) At the sources column nothing is shown on account of Profit from operations and on uses column Rs.8 Lakh is shown CASELET Read the following and answer Cost / unit Raw material 50 Direct labour 20 Overheads 40 Total cost 110 No. of units 10,000 No. of units Sold on credit 8000 Average raw material in stock : 1 month Average work in progress : Average finished goods in stock : ½ month ½ month Credit by supplier : 1 month Credit to debtor : 2 months Take 1 year = 12 months 20) Investment of working capital in raw material inventory is (a) 41666 (b) 50000 (c) 33333 (d) 10000 21) Investment in working capital for finished goods is a) 45833 b) 49090 c) 56453 d) 50000 22)current assets in respect of debtors a) 174541 b) 146666 c) 152500 d) 154326